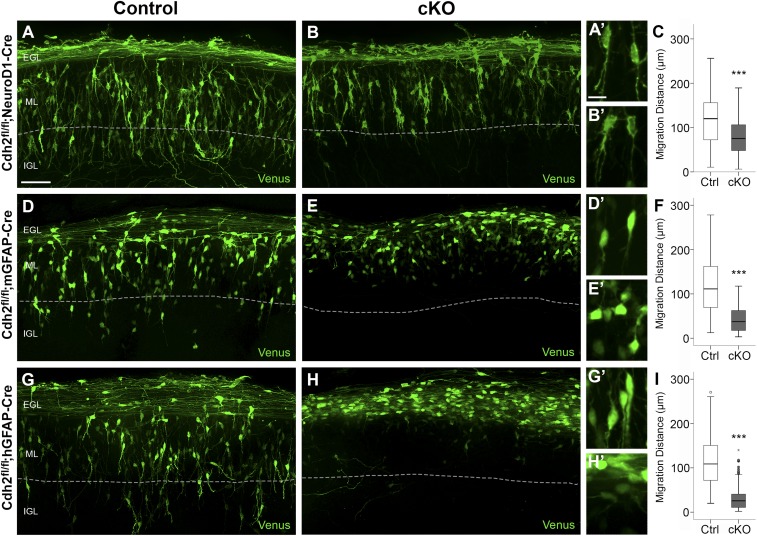
Fig. 4.
Glial CDH2 is essential for glial-guided neuronal migration. Organotypic ex vivo slice cultures prepared from the cerebellum of P8 Cdh2fl/fl control and Cdh2-cKO mice, electroporated with Venus, and fixed after 60 h. In slice cultures from control mice (A, D, and G) Venus-expressing GCPs migrated radially across the ML and extended a leading process in the direction of migration. Although most Venus-positive GCPs lacking Cdh2 extended a leading process (B), their median migration distance was reduced by 37% (C). In ex vivo slices where BG lacked Cdh2 (E), or where both GCPs and BG lacked Cdh2 (H), Venus-positive GCPs had a rounded or multipolar morphology, failed to extend a leading process, and migrated a shorter distance away from the field of labeled parallel fibers into the ML, indicating a stalled migration. Dotted lines indicate the ML/IGL boundary. (A′, B′, D′, E′, G′, and H′) Representative cell morphologies are shown at higher magnification. (F and I) The median migration distance was reduced by 66% (BG cKO) (F) and 76% (GCP + BG cKO) (I). ***P < 0.001. (Scale bars: 50 µm in A, B, D, E, G, and H and 10 µm in A′, B′, D′, E′, G′, and H′.)