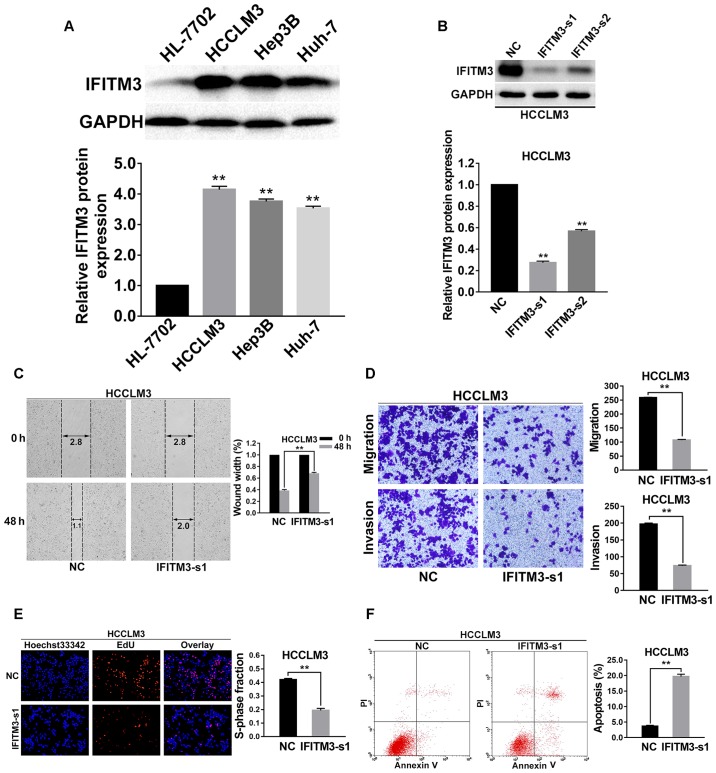
Figure 2.
Knockdown of IFITM3 inhibits invasion, migration, proliferation and promotes apoptosis of HCC cells. (A) Western blot analysis of IFITM3 expression in human normal hepatocyte cells (HL-7702) and 3 HCC cell lines (Hep3B, HCCLM3 and Huh-7) which indicated that IFITM3 protein expression in HCC cells was significantly higher than that in normal liver cells. **P<0.01 compared with the HL-7702 cells. (B) Two different IFITM3 siRNA sequences were transiently transfected into HCCLM3 cells to knockdown expression of IFITM3. After 48 h of transfection, western blot analysis revealed that the expression of IFITM3 was markedly downregulated with the IFITM3-siRNA groups. (C) Wound healing assay results revealed that wound closure was delayed with IFITM3 knockdown in HCCLM3 cells compared with NC groups at 48-h time-points after transfection. (D) Migration and invasion assays indicated that the migration and invasion abilities of IFITM3-s1 transfection HCCLM3 cells were decreased compared with the NC groups. (E) EdU proliferation assays revealed that the proliferation abilities were significantly reduced in IFITM3-s1-transfected HCCLM3 cells than in the NC groups. Blue, Hoechst 33342 staining of nuclei with all cells. Red, Apollo staining of EdU with proliferating cells. Overlay, the percentage of proliferating cells. (F) The apoptosis rate of HCCLM3 cells transfected with IFITM3-s1 was significantly higher than in the NC groups. **P<0.01 compared with the NC groups. NC, negative control; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; IFITM3, interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3.