Figure 1.
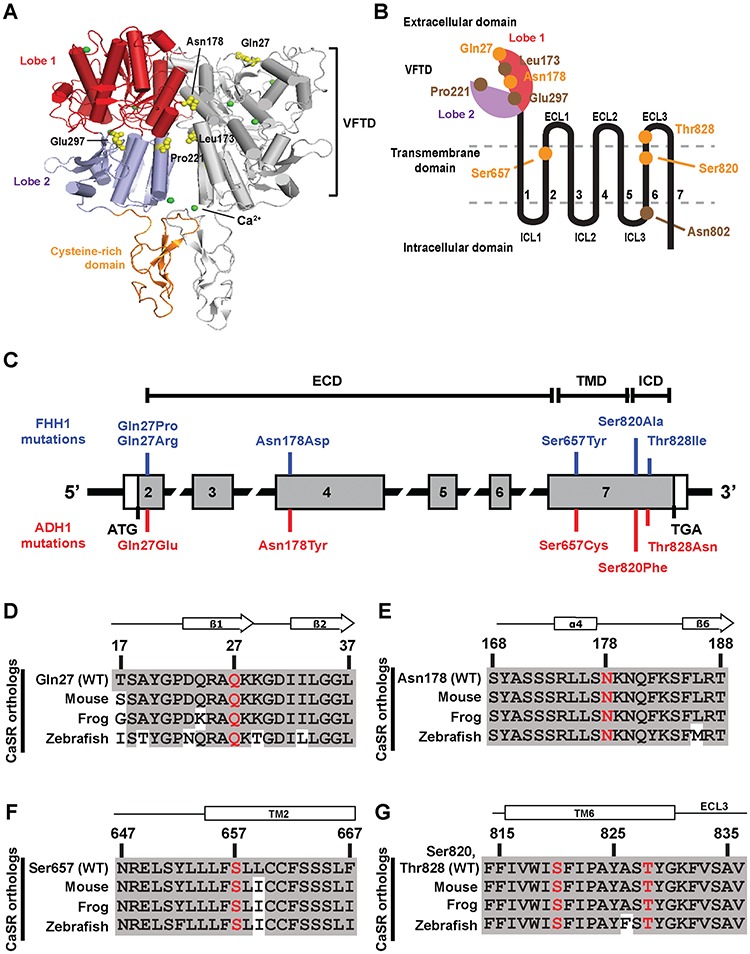
Location and evolutionary conservation of five CaSR disease-switch residues. (A) The crystal structure of the homodimeric human CaSR ECD (PDB ID 5K5S) (3). Each CaSR ECD monomer is comprised of a VFTD consisting of two lobes [lobe 1 (red) and lobe 2 (blue)] joined by a hinge region and a cysteine-rich domain (orange). Side chains of disease-switch residues Gln27 and Asn178 and previously reported disease-switch residues Leu173, Pro221 and Glu297 are shown as yellow spheres. Leu173 and Pro221 are located within the hinge region (Fig. S1). The calcium ions are shown as green spheres. (B) Schematic diagram of a CaSR monomer showing the extracellular bi-lobed VFTD, seven TMD helices (1–7) with ECL1–3 and ICL1–3 and the ICD. Lobe 1 of the ECD is shown in red and lobe 2 in purple. The locations of the five disease-switch residues (Gln27, Asn178, Ser657, Ser820 and Thr828) are indicated in orange, and reported disease-switch residues are indicated in brown. (C) Schematic representation of the genomic organization of the human CASR gene showing locations of the FHH1- and ADH1-associated disease-switch residue mutations identified in this study. The CASR gene consists of seven exons. Coding regions are shaded grey and untranslated regions are represented by open boxes. The ECD is encoded by exons 1–6 and the 5′ portion of exon 7, and the TMD and ICD by exon 7. The FHH1-associated (blue) and ADH1-associated (red) disease-switch residue mutations are shown above and below the exons, respectively. (D--G) Multiple protein sequence alignment of (D) residues 17–37 of the ECD β1-strand and β2-strand surrounding Gln27 (Q27); (E) residues 168–188 of the ECD α4-helix and β5-strand, surrounding Asn178 (N178) (3,4); (F) residues 647–667 of TM helix 2 surrounding Ser657 (S657); and (G) residues 815–836 of TM6 and ECL3 surrounding Ser820 (S820) and Thr828 (T828).
