Figure 7.
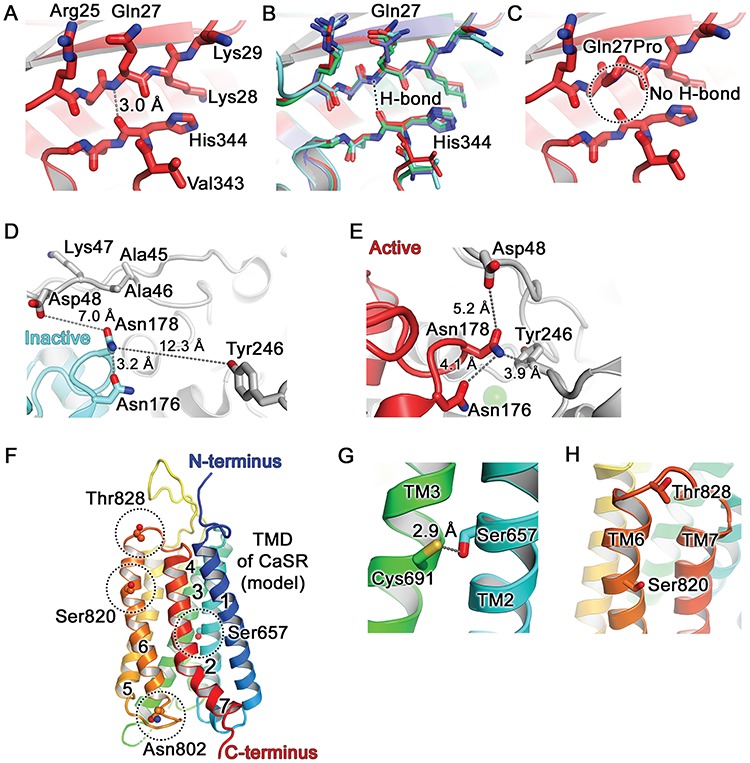
Structural analysis of CaSR disease-switch residues. (A) The Gln27 residue is located in the β1-strand of lobe 1 of the CaSR ECD, shown in the active conformation (PDB: 5K5S) (3) (Figs. 1 and S1). The peptide backbone amino group hydrogen on nitrogen (blue) of Gln27 forms a hydrogen bond (H-bond) with the peptide carbonyl group of His344 located in the α10 and α11 loop. (B) Superposition of all known crystal structures of CaSR: active conformation (carbons are in dark red as in panels A and C; PDB: 5K5S) (3), inactive conformation (cyan, PDB: 5K5T) (3), cyclomethyltryptophan/magnesium-bound form (green, PDB: 5FBK) (4), cyclomethyltryptophan/magnesium/gadolinium-bound form (blue, PDB: 5FBH,) (4). The Gln27-His344 interaction is not altered in the active and inactive conformations of the CaSR. (C) The FHH1-associated p.Gln27Pro mutation abolishes the Gln27-His344 hydrogen bond (circled). (D) The Asn178 is located at the lobe 1–lobe 1 dimer interface (Figs. 1 and S1). The side chain of Asn178 is exposed to solvent in the inactive conformation (cyan, PDB: 5K5T (3)) and is positioned at ≥7.0 Å from neighbouring residues (Asp48, Tyr246) on the opposing CaSR molecule. (E) The side chain of Asn178 is located within a tightly packed environment between two CaSR ECD protomers in the active conformation (PDB: 5K5S). Mutation to Asp178 or Tyr178 could alter the relative orientation between the two protomers. (F) Homology model of the CaSR TMD viewed parallel to the cell membrane and based on the structure of mGluR1 (PDB: 4OR2) (30). Side chains of Ser657, Asn802, Ser820 and Thr828 are shown as spheres (dashed circles). Seven TM helices are numbered. (G) The Ser657 residue is located within TM2 and its side chain projects towards Cys691 located on TM3. (H) The Ser820 residue is located within TM6 and its side chain points towards the transmembrane bilayer. The Thr828 residue is located within ECL3, which connects TM6 and TM7.
