Abstract
A procedure is developed for selective extraction of methylmercury (CH3Hg+) from heavily Hg-contaminated soils and sediments for determination by chemical vapor generation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (CVG-ICP-MS). Soils artificially contaminated with 40 µg g−1 inorganic mercury (Hg2+) or methylmercury chloride (CH3HgCl) were agitated by shaking or exposing to ultrasounds in dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) or nitric acid (HNO3) solutions at room temperature. Extractions in HCl (5 or 10% v/v) resulted in substantial leaching of Hg2+ from soils, whereas 5% (v/v) HNO3 provided selectivity for quantitative extraction of CH3Hg+ with minimum Hg2+ leaching. Agitation with ultrasounds in 5% (v/v) HNO3 for about 3 min was sufficient for extraction of all CH3Hg+ from soils. Coprecipitations with Fe(OH)3, Bi(OH)3 and HgS were investigated for removal of residual Hg2+ in soil extracts. Hydroxide precipitations were not effective. Thiourea or L-cysteine added to soil extracts prior to hydroxide precipitation improved precipitation of Hg2+, but also resulted in removal of CH3Hg+. HgS precipitation was made with dilute ammonium sulfide solution, (NH4)2S. Adding 30 µL of 0.35 mole L−1 to soil extracts in 5% (v/v) HNO3 resulted in removal of all residual Hg2+ without impacting CH3Hg+ levels. Vapor generation was carried out by reacting Hg2+-free soil extracts with 1% (m/v) NaBH4. No significant interferences were observed from (NH4)2S on the vapor generation from CH3Hg+. The slopes of the calibration curves for CH3HgCl standard solutions in 5% (v/v) HNO3 with and without (NH4)2S were similar. Limits of detection (LOD, 3s method) were around 0.08 µg L−1 for 5% (v/v) HNO3 blanks (n = 10) and 0.10 µg L−1 for 5% (v/v) HNO3 + 0.005 mol L−1 (NH4)2S blanks (n = 10). Percent relative standard deviation (%RSD) for five replicate measurements varied between 3.1% and 6.4% at 1.0 CH3HgCl level. The method is validated by analysis of two certified reference materials (CRM); purely Methylmercury sediment (SQC1238, 10.00 ± 0.291 ng g−1 CH3Hg+) and Hg-contaminated Estuarine sediment (ERM – CC580, 75 ± 4 ng g−1 CH3Hg+ and 132 ± 3 µg g−1 total Hg). CH3Hg+ values for SQC1238 were between 13.0 and 13.2 ng g−1, and 79 and 81 ng g−1 for ERM – CC580. Hg-contaminated soils (57 to 96 μg g−1 total Hg) collected from the floodplains of Oak Ridge, TN were analyzed for CH3Hg+ using the procedure by CVG-ICPMS. CH3Hg+ levels ranged from 30 to 51 ng g−1 and did not correlate with total Hg levels (R2 =0.01).
Keywords: Methylmercury, extraction, coprecipitation, soil/sediment, chemical vapor generation, ICP-MS
1. Introduction
Mercury is a ubiquitous element that is present in various forms in the environment, including elemental (Hg0), mercurous (Hg22+), mercuric (Hg2+), and alkylated mercury compounds (e.g., Methylmercury, CH3Hg+) [1,2]. The determination and speciation of Hg are important to understand the mobility, bioavailability in soils, sediments and biota, and potential toxicity on human and environmental health. Hg2+ is the predominant form in soil and waters. Hg0 are the major species in the atmosphere, while CH3Hg+ is present mostly in biota and foodchain. These mercury forms also exhibit different solubilities and toxicities. Elemental Hg and mercurous chloride (Hg2Cl2) have a water solubility of 5.6×10−5 g L−1 and 2.0×10−3 g L−1 at 25 °C, respectively [3,4]. Mercuric compounds, namely HgO and HgCl2, are more soluble in water for which solubilities are 0.051 g L−1 at 25 °C and 69 g L−1 at 20 °C, respectively [3,4]. In contrast, methylmercury chloride (CH3HgCl) is considered lipid soluble due to its lower solubility in water (0.10 g L−1 at 21 °C).
During the 1950s and early 1960s, elemental mercury (Hg) was used to produce enriched 6Li isotope at the Y-12 National Security Complex (Y-12 Plant) at the Oak Ridge Reservation of the Department of Energy (DOE) for manufacturing components of various nuclear weapons systems. It is estimated that 350,000 kg of Hg was released to the environment contaminating facilities, soil, sediment, surface water, and groundwater within the boundaries of the Y-12 Plant and the downstream environment along the East Fork Poplar Creek (EFPC) [5]. The EFPC floodplain soils were reported to contain predominantly cinnabar (HgS) form [5,6], but other inorganic and organic Hg species, including Hg0, HgCl2, Hg2Cl2, HgO and CH3Hg+ have been found within the Y-12 Facility boundaries and the 23-km long contaminated EFPC. Over the last 25 years, Hg fluxes from the Y-12 Plant have been reduced by various remediation efforts, yet, the Hg concentration in water continue to exceed both the regulatory limit (51 ng L−1) and the remediation goal (200 µg L−1) [5].
Methylmercury (CH3Hg+) is a known neurotoxin [3,7]. Not only is it more toxic than other Hg species, but also bio-accumulates in aquatic food chain posing reproductive and neurobehavioral health disparities to biota and humans [3,7]. Especially most Hg in fish and seafood is CH3Hg+. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) estimated a reference dose (RfD) of 0.1 µg kg−1 body weight based on daily oral exposure for methylmercury [8,9] while World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a maximum weekly intake of 1.6 µg kg−1 for the protection of public health [9,10]. In the environment, CH3Hg+ is produced by a series of biogeochemical transformations involving microorganisms (e.g., sulfate- and iron-reducing bacteria) [11–13]. These microbial-methylation processes are influenced by the organic matter, pH and redox potential of the environment [14–16]. Anaerobic conditions that occur in soils and wetlands also favor the transformation of Hg2+ to CH3Hg+ [17,18]. Nonetheless, most microorganisms responsible for methylation of Hg are also capable of degrading CH3Hg+, consequently its concentration rarely correlates with total Hg concentration [19,20]. Additionally, reductive and oxidative demethylation processes convert CH3Hg+ to Hg0 and Hg2+, respectively [21]. As a result, CH3Hg+ is often present in soils and sediments at much lower concentrations, typically 1.5% of total Hg [22,23], and thus its determination requires sensitive detection techniques and suitable separation methods, especially in the presence of elevated Hg2+ [15,24].
Various separation methods have been developed for speciation of Hg in environmental and biological samples, which include cloud-point extraction (CPE) [15,24–26], solid phase microextraction (SPME) [22,24,27–30], high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [24,31–36], and gas chromatography (GC) [15,22,24,31,37–40]. Chemical vapor generation (CVG) has been utilized as a popular approach to further improve the sensitivity and selectivity for CH3Hg+ determinations by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and atomic spectroscopy, namely fluorescence (AFS) and absorption (AAS) [15,25,31,32,41–43]. In recent applications, ICP-MS has been a dominant technique due to its high sensitivity, isotopic measurement capability and ease of coupling to CVG, HPLC and GC systems. A great deal of the studies to date, however, have undertaken the speciation of Hg in samples like seawater, wastewater seafood, blood, urine and hair that possess relatively low Hg levels and hence selectivity among Hg species could be achieved with chromatographic approaches or chemical vapor generation [22–43].
Unlike water and biological samples of low total Hg content, Hg-contaminated soil and sediments, such as that from Oak Ridge Reservation of the DOE, possess significantly high Hg levels (e.g., as high as 200 µg g−1) which is predominantly Hg2+ [5,6]. Chromatographic separation methods cannot tolerate such high levels of Hg as it could cause contamination and costly damages to analytical column and instrumentation nor highly sensitive CVG approaches employed for Hg speciation could provide desired selectivity for CH3Hg+ under heavy Hg2+ matrix. To alleviate the hurdles associated with Hg2+ matrix, separation of CH3Hg+ from soil matrix or removal of Hg2+ matrix is imperative besides the use of sensitive methods for accurate determinations [22,31,44–46]. Acid leaching followed by extraction into benzene or toluene (i.e., Westöö method) is perhaps by far the most popular approach for extraction of CH3Hg+ and other organomercury species from the solid samples [47,48]. Over the years, various extraction procedures, such as alkaline digestion with KOH-methanol mixture [49] and Universol® (an alkaline cocktail of reagents) [45], microwave- and/or ultrasound-assisted extraction in HCl-methanol [46] and HNO3 [50] have been developed as part of continued efforts to utilize robust, aqueous and less laborious methods. More recently, Carrasco and Vassileva [40] investigated various acidic and alkaline digestion/extraction methods for determination of CH3Hg+ from estuarine sediments, and reported that extraction with mixture of HNO3/CuSO4 provided the highest recoveries. Despite the improvements, nevertheless, acidic or alkaline digestion/extraction procedures reported so far require additional extractions with organic solvents followed by back-extraction into aqueous solution, neutralization and derivatization or alkylation steps prior to chromatographic separation [22,24,39,40,44]. CVG approaches in contrast offer less laborious sample preparation and sufficient selectivity due to the capability of differential chemical reduction of CH3Hg+ and Hg2+ to Hg0 vapor [24,43,46]. Hg2+ is more readily reduced to Hg0 than CH3Hg+, and thus removal of elevated Hg2+ matrix is desirable to achieve interference-free determination of CH3Hg+ from Hg-contaminated soil and sediments.
In this work, we have developed a method for selective and sensitive determination of CH3Hg+ from highly Hg-contaminated soils and sediments in an attempt to characterize CH3Hg+ distribution from the soils and sediments collected from the Oak Ridge, TN Reservation of DOE that were impacted by the legacy Hg-contamination of 1960’s. The objectives of the study were two-fold: (1) to determine the optimal conditions for selective extraction of CH3Hg+ from the soil matrix with minimal Hg2+, (2) to remove the residual Hg2+ from solutions to improve selectivity and accuracy for CH3Hg+ for determination by chemical vapor generation. Extractions in dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) and nitric acid (HNO3) were performed via shaking and ultrasonic agitation at room temperature to determine the extraction profiles of CH3Hg+ and Hg2+ from the soils artificially contaminated with Hg2+ or CH3Hg+. For optimal extraction conditions, hydroxide and sulfide coprecipitation schemes were investigated to eliminate the residual Hg2+ from soil extracts. Chemical vapor generation (CVG) conditions were optimized for the optimum extraction conditions. The method was validated with determination of CH3Hg+ in estuarine sediment certified reference material (ERM - CC580) and methylmercury sediment reference material (SQC1238) by CVG-ICP-MS and then applied to the determination of CH3Hg+ in Hg-contaminated soils from Oak Ridge, TN.
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and solutions
Ultra-pure deionized water was used throughout. Tap water fed through MaxCap® reverse-osmosis deionization (RO/DI) unit (SpectraPure Inc., Tempe, AZ) was gravity-fed into a 4-stage Barnstead™ E-Pure deionization system producing ultra-pure deionized water with minimum resistivity of 18.0 MΩ cm resistivity. A 10 µg mL−1 Hg2+ solution was prepared from 1000 µg L−1 Hg2+ stock standard solution (Spex CertiPrep, Metuchen NJ) in 5% HNO3. All working solutions of Hg2+ were prepared from a 10 µg L−1 Hg2+ stock. The stock solution of CH3HgCl (1000 µg L−1) was prepared by dissolving the CH3HgCl salt (Aldrich, 99.9% pure, Lot# SBLQ9540V) in 0.5% (v/v) HCl and stored in plastic bottle. A secondary stock solution of 10 µg L−1 CH3HgCl was prepared and used for preparing working solutions of CH3Hg+. The standard solutions of Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ were prepared freshly before each run and the acidity was matched with that of the sample solutions (HCl or HNO3) used for preparing the samples. Sodium borohydride solutions (NaBH4, 99.8%, Sigma Aldrich) were prepared in 0.1% (m/v) NaOH (99.9%, Sigma Aldrich). Stannous chloride solution (SnCl2, Sigma, 98% Lot# S73836–039) were prepared in 0.5% (v/v) HCl. Trace metal grade hydrochloric acid (HCl, BDH Chemicals) and nitric acid (HNO3, BDH Chemicals) were used in all extraction and preparations. Hydrofluoric acid (HF, 48% m/v, Sigma Aldrich, 99.99%, Lot# 16595ME) was used for digesting soils for total Hg determination. Other reagents used for preparing stock solutions for coprecipitation studies include iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate, Fe(NO3)3·9H2O (Sigma Aldrich, 99.99%, Lot# 09007BD), bismuth(III) nitrate pentahydrate, Bi(NO3)3·5H2O (Alfa Aesar, +98%, Lot# I24Y019), ammonium sulfide, (NH4)2S (Sigma Aldrich, 47.2% m/v, Lot#00819DH), thiourea (Sigma Aldrich), L-cysteine (97%, Sigma Aldrich), and triethylamine, TEA (trace metal grade, Acros Organics, Lot# A0374495).
2.2. Instrumentation
All measurements were performed with a Varian 820MS ICP-MS instrument (Varian, Australia). The instrument was equipped with a peltier-cooled double-pass glass spray chamber, all teflon Ari-mist nebulizer (SCP Science, Champlain NY), quartz torch, CRI-type Pt sampler and skimmer cones and all-digital detector (DDEM, Model AF250, ETP Australia). Samples were introduced manually. The instrument was optimized daily with 5 µg L−1 138Ba, 25Mg, 115In, 140Ce, 208Pb solution for optimal sensitivity, oxides (156CeO+/140Ce+ < 3%) and doubly charged ions (138Ba2+/138Ba+ < 2%). Data collection was achieved by ICP-MS Expert software package (version 2.2 b126). Measurements were made with solution nebulization mode for total Hg determinations, and determining the recoveries in extraction and coprecipitation studies. Washout was performed by pumping 5% (v/v) HCl for 30 s using fast-pump mode (6 mL min−1) to clean up residual Hg before next measurement. Chemical vapor generation (CVG) was used for method validation and determination of CH3Hg+ from soil samples. A solution of 0.5% (m/v) potassium ferricyanide in 5% (v/v) HCl was used for Hg-washout as it was found effective in reducing memory effects on CVG-ICP-MS determinations [43]. The operating parameters of the ICP-MS instrument are summarized in Table 1 for nebulization and CVG modes. An internal standard (IS) solution of 5 µg L−1 germanium (Ge), rhodium (Rh), rhenium (Re) was used to correct for possible instrumental drift and matrix-related signal fluctuations during measurements with solution nebulization. The internal standard solution was mixed on-line with the calibration standard or sample solution. 185Re was used as IS for Hg. Data were collected for 200Hg and 202Hg isotopes in both nebulization and CVG modes.
Table 1.
Operating conditions for Varian 820MS ICP-MS in nebulization and vapor generation modes.
| ICP-MS | Nebulization | Vapor generation |
|---|---|---|
| RF Power (kW) | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| Plasma argon flow (L min−1) | 17 | 17 |
| Auxiliary argon flow (L min−1) | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Nebulizer argon flow (L min−1) | 1.1 | 1.5 |
| Sheath argon flow (L min−1) | 0.15 | 0.2 |
| Sampling depth (mm) | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| Sample flow rate (mL min−1) | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| Stabilization time (s) | 15 | 50 |
| Spray chamber temperature (°C) | 4 | 4 |
| Scan mode | Peak hopping | Peak hopping |
| Dwell time (ms) | 20 | 50 |
| Points/peak | 1 | 1 |
| Scans/peak | 4 | 10 |
| Scans/replicate | 4 | 10 |
2.3. Soil samples
Method development studies were conducted with Hg-free soils that were ground and sieved through 0.25-mm apertures. Sub-samples were digested in HNO3 and HF as described below (see section 2.4.1) and were analyzed by ICP-MS for Hg content before utilizing in any experimental work. Then, sub-samples of the soil were intentionally contaminated with Hg2+ or CH3Hg+ for investigating the acid extraction conditions. Briefly, about 0.5 g sub-samples (n = 4) were wetted (e.g., spiked) with 0.2 mL of 100 µg mL−1 Hg2+ or CH3HgCl standard solution in 15-mL conical test tubes. This introduced 20 µg or 40 µg g−1 Hg2+ or CH3HgCl to the soil matrix. Care was given to ensure the spiked soil was uniformly wetted in the tube. Then, all soil samples were air-dried for 48 to 72 h at room temperature.
Hg-contaminated soils were collected from a site located in a floodplain field of Lower East Fork Poplar Creek (LEFPC) of Oak Ridge, TN, USA. A total of 10 surface soils (0–10 cm) were randomly sampled from both woodland and wetland/grassland areas. Fresh field samples were stored in a refrigerator for total Hg and speciation measurements. Sub-samples were air-dried, ground and passed through 0.25-mm sieves. The soil at the study site was Armuchee soil (clay, mixed, thermic Ochreptic Hapludults) that is formed in residuum of shale and river alluvia.
2.4. Procedures
2.4.1. Soil digestion for total Hg determination in floodplain soils
For total Hg determination, approximately 0.1 g (n = 3) of floodplain soil samples was weighed into teflon vessels (70 mL inner volume) (Savillex) and digested in 5 mL HNO3 and 1 mL HF for 2 h at 120 °C on a graphite block digestion unit (SCP Science, Champlain NY). Then, the digestion temperature was increased to 140 °C and samples were digested for additional 3 h. After digestion, contents were cooled to room temperature, then transferred to 15-mL tubes and diluted to 10 mL with deionized water. All samples were centrifuged for 15 min at 5000 rpm to remove undissolved components. After centrifugation, 0.2 mL aliquots were taken and diluted to 2 mL with 0.1% (v/v) HCl and 5% (v/v) HNO3 in 2-mL graduated micro-centrifuge tubes (Fisher Scientific) for ICP-MS analysis.
Effectiveness of the digestion procedure and accuracy of instrumental measurements were verified with analysis of Montana soil (SRM 2710) and Domestic sludge (SRM 2781) certified reference materials from National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST, Gaithersburg, MD). Sub-samples (0.1 g, n = 5) of SRM 2710 and SRM 2781 were digested along with the floodplain soils using the procedure above. Similarly, 0.2 mL SRM solution (10 mL) were taken and diluted to 2 mL with 0.1% (v/v) HCl and 5% (v/v) HNO3 and analyzed by ICP-MS for total Hg. Preliminary experiments indicated that Hg2+ was relatively unstable in 5% (v/v) HNO3 solution. Within 3 to 4 days of preparation, signals for Hg2+ standard solutions declined about 20% in comparison to freshly prepared solutions. Addition of trace amounts of HCl improved the stability of Hg2+ standards for up to two weeks, and thus calibration standards ranging from 0 to 50 µg L−1 Hg2+ were prepared in 0.1% (v/v) HCl and 5% (v/v) HNO3 for total Hg measurements. A solution of 5% (v/v) HCl was ran through for 30 s at fast pump-mode (6 mL min−1) to washout Hg before introducing sample or standard solutions during measurements with nebulization mode.
2.4.2. Extraction of Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ from artificially contaminated soils via shaking
Treatment of soil and sediments with HCl and HNO3 have been an effective means for extracting Hg species [40,46,50]. Here, we attempted to determine the suitability of HCl and HNO3 extractions for selective separation of CH3Hg+ and Hg2+ from soil matrix. For this purpose, air-dried soils (0.5 g) contaminated with 20 µg Hg2+ or CH3HgCl were suspended in 10 mL of water, dilute HCl or HNO3 solutions (5 and 10% (v/v) concentrations) and shaken on a rocker shaker for 0, 1, 2, 6 and 24 h. For control set, unspiked soils (0.5 g, n = 4) were suspended similarly in water, HCl and HNO3 solutions. There were 24 soil suspensions (12 treatments and 12 controls) for each acid medium. Overall, 48 soil suspensions were processed concurrently.
For sampling, shaking was stopped and suspensions were allowed to rest for about 2–3 min for settling of suspending soils particles. Then, 0.5 mL aliquots from the top of the suspension was pipetted into 2-mL micro-centrifuge tubes and spun 10 min at 12, 000 rpm on an Eppendorf Model 5415D centrifuge to settle the residual suspending particles. Of the 0.5 mL supernatant solution, 0.1 mL was taken and diluted to 2 mL with 5% (v/v) HCl for HCl treatments and with 5% (v/v) HNO3 for HNO3 treatments. Samples were then analyzed by ICP-MS using Hg2+ or CH3HgCl standards (0 to 20 µg L−1) in 5% (v/v) HCl or 5% (v/v) HNO3 for each set. Washings were made between samples with 5% (v/v) HCl as described in section 2.4.1.
2.4.3. Extraction of Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ from artificially contaminated soils via ultrasonic agitation
In another series of experiments, the effect of ultrasound-assisted agitation was examined for the extraction of Hg2+ or CH3HgCl from soil matrix. Here, soils (n = 4) contaminated with Hg2+ or CH3HgCl were suspended similarly in 10 mL water, dilute HCl or dilute HNO3 along with the uncontaminated controls. Each suspension was then agitated by ultrasounds using a Fisher Scientific Model 100 Sonic Dismembrator equipped with a 2-mm diameter titanium microprobe. Sonication was implemented for 0, 3 and 6 min at 50% power setting. After each sonication, suspensions were allowed for 2 to 3 min for settling of soil particles. Then, 0.5 mL aliquot from the top layer was taken and spun as described above, and finally 0.1 mL of the spun suspension was diluted to 2 mL with either 5% (v/v) HCl or 5% (v/v) HNO3 and analyzed by ICP-MS as above to determine the extraction efficiency (e.g., recovery) of Hg2+ or CH3Hg+.
2.5. Removal of residual Hg2+ via hydroxide coprecipitation
Extraction studies performed with artificially contaminated soils indicated that a great deal of Hg2+ leached into solution. Unless removed, Hg2+ would confound, if not, preclude the accurate determination of CH3Hg+ by CVG-ICP-MS besides contaminating the sample introduction system. To avoid these hurdles, attempts were made to remove Hg2+ from the soil extracts by coprecipitation approaches. Hg shows high affinity to sulfur containing groups, such as thiourea and L-cysteine. It is also reported that Hg2+ coprecipitates with hydroxides of iron(III) [51] and bismuth (III) [52]. In a series of experiments, the coprecipitation of Hg2+and CH3Hg+ was examined with Fe(III) and Bi(III). A volume of 20 µL of 10 µg mL−1 Hg2+ or CH3HgCl was added into 2-mL microcentrifuge tubes (n = 5). To simulate elemental composition of soil extracts, 20 µL of 10 µg mL−1 multi-element solution (Ag, Al, As, Ba, Be, Cd, Cr, Co, Cu, Li, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Sb, Se, Sr, Tl, V, Zn) and 100 µL of 100 µg mL−1 of major element solution (Ca, Mg, Fe, Na, K, P, and Ti) were also added. Then, 0.2 mL of 10 mg mL−1 of Fe(III) (as nitrate) or Bi(III) (as nitrate) were added to each tube. The volume was completed to 2 mL with 5% (v/v) HNO3. The solution contained 100 µg L−1 Hg2+ or CH3HgCl in a matrix of 0.1 µg mL−1 of trace metals, 5 µg mL−1 of the major elements and 1000 µg mL−1 of Fe(III) or Bi(III) prior to precipitation. Precipitation of Fe(OH)3 and Bi(OH)3 was made by adding 0.2 mL of TEA. Upon adding TEA, nucleation of hydroxides occurred rapidly. For effective coprecipitation, solutions were allowed for 10 min for complete precipitation and then centrifuged for 15 min at 12,000 rpm. The supernatant solution was discarded. Pellets were washed gently, dissolved in 1 mL of 10% (v/v) HNO3, and then completed to 2 mL with water. All solutions were then analyzed by ICP-MS in nebulization mode to determine the recoveries (e.g., coprecipitation efficiency) for Hg2+ or CH3Hg+.
In another experiment, the effects of thiourea and L-cysteine were examined in combination with Fe(III) and Bi(III). Test solutions of Hg2+ or CH3HgCl (n = 5) were prepared similarly as above. A volume of 0.2 mL of 1% (m/v) thiourea or 1% (m/v) L-cysteine were added to the microcentrifuge tubes before adding other solutions, including Fe(III) and Bi(III). Precipitation, centrifugation and dissolution were performed as described above. The pellet solutions were analyzed for Hg2+ or CH3Hg+ content.
2.6. Removal of Hg2+ via sulfide coprecipitation
Mercury also forms strong sulfide precipitates, such as HgS which is highly insoluble even in acidic media [53,54]. Thus, as an alternative approach for removal of Hg2+, the precipitation of HgS was examined in simulated soil solutions using ammonium sulfide as coprecipitation agent. The test solutions of 100 µg L−1 Hg2+ or CH3HgCl (n = 5) were prepared similarly as described above in a matrix of trace metals and major elements. The volume was completed to 2 mL with 5% (v/v) HNO3. Precipitation was made by adding 30 µL of 0.35 mole L−1 ammonium sulfide solution, (NH4)2S. Contents were allowed to precipitate for about 10 min, and then centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 15 min. The supernatant solutions were analyzed by ICP-MS to determine the concentration of Hg2+ or CH3Hg+ remained in solution.
2.7. Optimization of chemical vapor generation conditions
Chemical vapor generation (CVG) as a sensitive approach offers selective reduction of Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ species to gaseous Hg0 under optimal conditions [24,43,45]. When coupled to ICP-MS, CVG provides unsurpassed sensitivity for detection of trace levels of Hg species. CVG measurements were carried using the setup illustrated in Fig. 1. The quartz spray chamber ICP-MS instrument was used as gas liquid separator. A polypropylene T-piece (1/8” i.d., 1/4” o.d.) purchased from a local hardware store was inserted through the nebulizer housing on the Teflon end-cap of the spray chamber. A 12-cm long PTFE transfer line (1.6 mm. i.d. & 1.8 mm o.d.) was inserted through the T-piece extending into the spay chamber. Outer end of the T-piece was sealed tightly to prevent gas leak. Carrier gas was supplied from the nebulizer argon port of the instrument through the lower arm of T-piece. Color-coded tygon pump tubings were used with the following diameters; sample and NaBH4: red-red stop (1.14 mm i.d.), waste: purple-white stop (2.79 mm i.d.). The mixing coil or reaction coil was 15-cm long PTFE tubing (1.0 mm i.d.) designated to mix the sample and NaBH4 solutions.
Fig. 1.
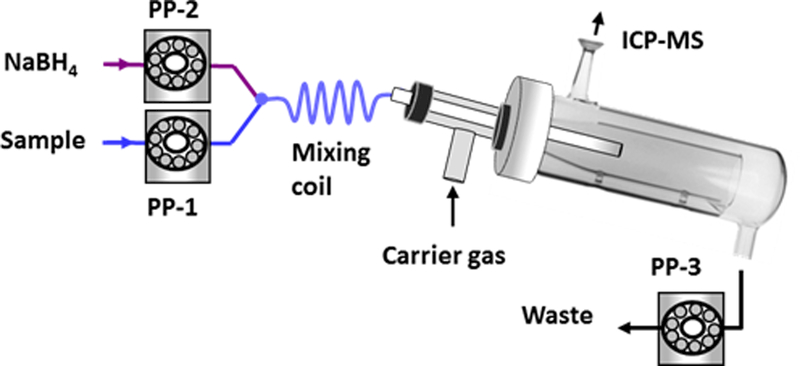
Schematic diagram of chemical vapor generation manifold for CH3Hg+ determination.
Experiments were performed with 10 µg L−1 Hg2+ or CH3HgCl solutions prepared in 5% (v/v) HNO3. Solutions were introduced via CVG manifold and reacted with 1% (m/v) NaBH4 or 1% (m/v) SnCl2 solution. At first, the acidity of medium was examined from 0 to 6% (v/v) HNO3. Then, the effects of reducing agents were examined on the generation of Hg vapor from Hg2+ or CH3HgCl. In the last step, interferences from (NH4)2S were investigated by measuring CVG signal profiles for 10 µg L−1 CH3Hg+ solutions that contained 30 µL of 0.35 M (NH4)2S against those in 5% (v/v) HNO3 (e.g., control). Calibration curves were constructed using 0, 0.5, 2, 5 and 10 µg L−1 CH3HgCl solutions prepared in 5% (v/v) HNO3 with and without (NH4)2S matrix. The slopes and limits of detection were compared to determine the most optimal setting for CVG-ICP-MS determinations. Washout was performed by running 0.5% (m/v) potassium ferricyanide solution in 5% (v/v) HCl before each test or sample solution to reduce memory effects.
2.8. Method validation and applications
The procedure was applied to the determination of CH3Hg+ in soils and sediments. Two soil and sediment certified reference materials (CRM) were used for method validation; methylmercury in sediment (SQC1238, Lot# LRAA7422)) and estuarine sediment (ERM CC580, Lot# 0650) that were obtained from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). The SQC1238 contained trace levels of CH3HgCl in soil, whereas ERM - CC580 was inorganic Hg sediment with trace levels of CH3Hg+. About 0.2 g sub-samples of these CRMs (n = 5) were suspended in 5 mL of 5% (v/v) HNO3 and subjected to ultrasounds using Fisher Scientific model 100 dismembrator for 2 to 3 min. After sonication, contents were centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 10 min. Then, 2 mL of extracts were taken into 2-mL centrifuge tubes. A volume of 30 µL of 0.35 M (NH4)2S was added to precipitate Hg2+ as HgS. Contents were centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 15 min to remove precipitated HgS. The supernatant solutions were transferred to new 2-mL tubes and analyzed by CVG-ICP-MS. To match the matrix, 30 µL of 0.35 M (NH4)2S solution were added to CH3HgCl calibration standards. Once the method was deemed accurate, floodplain soil samples were subjected to the optimized procedures as for the CRMs. About 0.2 sub-samples (n = 5) were placed in 15-mL tubes and suspended in 5% (v/v) HNO3 and exposed to ultrasounds. Coprecipitation in extracts was made as for the CRMs. The soil extracts were then analyzed by CVG-ICP-MS along with freshly prepared CRM samples and CH3HgCl calibration standards. Hg-washout was made with 0.5% (m/v) potassium ferricyanide solution in 5% (v/v) HCl as described above.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Total Hg levels of Hg-contaminated floodplain soil samples
Total Hg contents of Hg-contaminated floodplain soils varied between 57.4 ± 6.0 μg g−1 and 95.7 ± 3.4 μg g−1. Concentrations for individual soil samples are summarized in Table 6 (see section 3.7) along with CH3Hg+ levels. The results indicated persistence of Hg contamination from the catastrophic spill occurred more than a half century ago. Earlier reports have shown that these soils contain various inorganic and organic Hg species, but are mostly insoluble cinnabar, HgS [5,6]. Total Hg concentrations determined from SRM 2710 (Montana Soil Elevated Traces) and SRM 2781 (Domestic Sludge) digests were 34.1 ± 0.81 μg g−1 and 4.01 ± 0.65 μg g−1, respectively. The results were within the 95% confidence interval of the certified concentrations of SRM 2710 (32.6 ± 1.8 μg g−1) and SRM 2781 (3.68 ± 0.14 μg g−1). It should be noted that soil and sludge samples were not totally dissolved by the HNO3/HF digestion method; rather a partial dissolution was performed to extract Hg species from the alumino-silicate skeleton of the soil. Within this context, the results demonstrated that partial digestive dissolution with HNO3/HF mixture provide quantitative extraction of Hg from soil and sludge matrices. Various studies have also reported that Hg could also be extracted from soils even at mild acidic extractions with HCl or HNO3 [46,55].
Table 6.
Total mercury and methylmercury concentrations measured from the floodplain soils from Oak Ridge, TN. Total Hg levels measured via acid digestion of Hg-contaminated soils. Values are given as mean ± standard deviation of 3 replicates (n = 3) for total Hg and 5 separate replicates (n = 5) for methylmercury.
| Sample | CH3Hg+ (ng g−1) | Total Hg (µg g−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200Hg | 202Hg | 202Hg | |
| Soil 1 | 43 ± 6 | 45 ± 6 | 85.3 ± 1.6 |
| Soil 2 | 40 ± 8 | 41 ± 8 | 68.6 ± 5.3 |
| Soil 3 | 40 ± 12 | 40 ± 13 | 57.4 ± 6.0 |
| Soil 4 | 32 ± 3 | 33 ± 4 | 72.5 ± 4.5 |
| Soil 5 | 32 ± 9 | 33 ± 9 | 95.7 ± 3.4 |
| Soil 6 | 50 ± 10 | 51 ± 15 | 66.5 ± 1.4 |
| Soil 7 | 46 ± 5 | 47 ± 5 | 87.5 ± 6.6 |
| Soil 8 | 30 ± 2 | 31 ± 3 | 67.7 ± 3.3 |
| Soil 9 | 33 ± 9 | 33 ± 8 | 85.9 ± 6.5 |
| Soil 10 | 42 ± 11 | 42 ± 12 | 83.5 ± 6.7 |
3.2. Extraction of Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ from soils via shaking and ultrasonic agitation
The recoveries for the extraction of CH3HgCl or Hg2+ via shaking from the artificially contaminated soils in water, and dilute HCl and HNO3 are summarized in Table 2. Expected concentrations in 10-mL extracts were 200 μg L−1 for quantitative extraction of 20 μg CH3HgCl or Hg2+ from 0.5 g soil samples. Neither Hg2+ nor CH3Hg+ did show any significant leaching from soils in water in 24 h. Extractions with HCl resulted in leaching of more Hg2+ to solution in comparison to that with HNO3. Maximum extraction was about 71% in 10% (v/v) HCl after 24-h shaking, while that in 10 (v/v) HNO3 was about 18%. CH3Hg+ was extracted from the soils both in HCl and HNO3. The latter provided faster extraction. Within 1 h, more than 90% of CH3Hg+ extracted from the soil matrix in 5% (v/v) HNO3. In 10% (v/v) HNO3, CH3Hg+ extracted rapidly and quantitatively when soil suspension was inverted briefly for mixing (see Table 2 last row).
Table 2.
Recoveries for CH3Hg+ and Hg2+ for extraction from artificially contaminated soils with dilute HCl and HNO3 via shaking at room temperature. Values are mean ± standard deviation of five replicate extractions (n = 5).
| Analyte | Medium | Shaking time (h) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 24 | ||
| Recovery (%) | ||||||
| Hg2+ | Water | 0.95 ± 0.6 | 1.2 ± 1.0 | 2.0 ± 1.0 | 2.1 ± 1.0 | 4.2 ± 2.0 |
| 5% HCl | 24 ± 3 | 32 ± 6 | 34 ± 6 | 33 ± 5 | 38 ± 4 | |
| 10% HCl | 57 ± 5 | 65 ± 3 | 66 ± 4 | 66 ± 6 | 71 ± 6 | |
| 5% HNO3 | 3.5 ± 1.1 | 4.4 ± 2.1 | 3.9 ± 1.8 | 5.8 ± 1.0 | 15 ± 4 | |
| 10% HNO3 | 3.6 ± 1.2 | 5.2 ± 2.2 | 4.1 ± 2.1 | 7.4 ± 1.5 | 18 ± 3 | |
| CH3Hg+ | Water | 2.1 ± 1.3 | 2.4 ± 2.1 | 2.5 ± 1.5 | 3.2 ± 1.2 | 8.8 ± 3.0 |
| 5% HCl | 68 ± 7 | 79 ± 8 | 84 ± 7 | 82 ± 3 | 98 ± 7 | |
| 10% HCl | 78 ± 4 | 74 ± 4 | 74 ± 5 | 90 ± 5 | 91 ± 6 | |
| 5% HNO3 | 71 ± 7 | 91 ± 8 | 89 ± 7 | 92 ± 7 | 101 ± 7 | |
| 10% HNO3 | 95 ± 4 | 102 ± 6 | 102 ± 4 | 101 ± 4 | 103 ± 6 | |
The results for ultrasounds-assisted extraction are summarized in Table 3. Extraction patterns were similar to that with shaking, but occurred faster in minutes in contrast to hours. Leaching of Hg2+ to solution was also substantial in HCl. All Hg2+ leached into solution in 10% (v/v) HCl upon 6 min sonication. This result was consistent with that reported by Park et al. [46] who achieved extraction of Hg2+ and CH3Hg+ from an estuarine sediment reference material (BCR 580) in a (1:1 v/v) methanol and HCl mixture via sonication. Sonication in HNO3 also performed similarly for Hg2+ with that observed for shaking. Despite vigorous agitation, extraction of Hg2+ from the soils was very low; 4.7% and 8.6% for 6 min sonication in 5% and 10 (v/v) HNO3, respectively. Likewise, CH3Hg+ was extracted completely in 5% and 10 (v/v) HNO3 (Table 3). It was evident that 3 min agitation in 5% (v/v) HNO3 was optimal for fast and effective extraction of CH3Hg+ with minimal Hg2+ (e.g., 4.3% extraction). The Hg2+ concentration in soil extracts was about 8.6 µg L−1 (e.g, 4.3% of 200 µg L−1 Hg2+). HCl performed similarly to HNO3 on CH3Hg+, but a major limitation of HCl extraction was that a great deal of Hg2+, as high as 20% (ca. 40 µg L−1 Hg2+) leached into the solution under brief sonication (see Table 3). This was likely due to the solubilization of Hg2+ as soluble HgCl2 species. Though 10% (v/v) HNO3 afforded instantaneous extraction of CH3Hg+, it was not suitable for CVG measurements owing to vigorous reaction with NaBH4 that was essential for reduction of CH3Hg+ to Hg0.
Table 3.
Recoveries for CH3Hg+ and Hg2+ for extraction from artificially contaminated soils with dilute HCl and HNO3 via ultrasounds agitation at room temperature. Values are mean ± standard deviation of five replicate extractions (n = 5)
| Analyte | Medium | Sonication time (min) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 6 | ||
| Recovery (%) | ||||
| Hg2+ | Water | 0.95 ± 0.5 | 8.5 ± 3.2 | 12 ± 4 |
| 5% HCl | 24 ± 3 | 20 ± 5 | 29 ± 6 | |
| 10% HCl | 58 ± 5 | 84 ± 6 | 101 ± 6 | |
| 5% HNO3 | 3.5 ± 1.1 | 4.3 ± 1.8 | 4.7 ± 3.0 | |
| 10% HNO3 | 3.5 ± 1.2 | 5.5 ± 2.5 | 8.6 ± 2.0 | |
| CH3Hg+ | Water | 2.1 ± 1.3 | 33 ± 6 | 58 ± 5 |
| 5% HCl | 65 ± 3 | 86 ± 4 | 98 ± 2 | |
| 10% HCl | 82 ± 3 | 102 ± 5 | 101 ± 3 | |
| 5% HNO3 | 71 ± 6 | 100 ± 4 | 102 ± 5 | |
| 10% HNO3 | 94 ± 5 | 99 ± 4 | 104 ± 4 | |
3.3. Selective coprecipitation of Hg2+ from soil extracts
It should be noted that Hg-contaminated floodplain soils contained about 57.4 and 95.7 μg g−1 Hg, and accordingly 5% (v/v) HNO3 extracts of these soils are expected to contain at least 100 to 160 µg L−1 Hg2+ in 5 mL volume when 0.2 g samples are processed (e.g., 4.3% of total Hg). In the presence of high Hg2+ matrix, accurate determination of sub-µg L−1 levels of CH3Hg+ is hardly feasible by using traditional Hg2+ and total Hg CVG approaches. Besides, memory effects and contamination to CVG manifold and ICP-MS instrument are inevitable unless the residual Hg2+ is eliminated.
In order to remove the residual Hg2+ matrix in soil extracts, first attempt was made to coprecipitate Hg2+ with Bi(OH)3 and Fe(OH)3 in alkaline solutions as described in section 2.5. Nevertheless, neither Bi(OH)3 nor Fe(OH)3 coprecipitation was effective for removal of Hg2+ (Table 4). Though Fe(OH)3 coprecipitation removed as high as 23% of Hg2+, CH3Hg+ levels were also reduced (ca. 8.8%). The pH dependence of hydroxide precipitation could be a limitation for the lack of removal of Hg2+ since Fe(OH)3 and Bi(OH)3 precipitate within a narrow pH window of pH 8.5 to 9.3 [51,52]. The pH of the solutions after addition of TEA, on the other hand, was around pH 10 and 10.5. In the next attempt, combinations of thiourea and L-cysteine were examined in conjunction with Bi(III) and Fe(III) to improve coprecipitation of sulfuroly Hg2+ species onto Bi(OH)3 and Fe(OH)3. Both thiourea and L-cysteine increased removal of Hg2+ with Fe(OH)3 coprecipitation, but the results were far from being satisfactory; removal efficiency was 56% with L-cysteine + Fe(III) and 64% with thiourea + Fe(III). Obviously, any scenarios of the hydroxide coprecipitation were not suitable for coprecipitation of Hg2+ as they did impact CH3Hg+ in solution; especially thiourea significantly decreased CH3Hg+ levels with and without Fe(III) or Bi(III) (see Table 4). Thiourea and L-cysteine are known to form sulfomercurial complexes with organic mercury species [45]. It appears that these sulfomercurial complexes lead to coprecipitation of CH3Hg+ in alkaline conditions.
Table 4.
Recoveries for CH3Hg+ and Hg2+ from hydroxide and sulfide coprecipitation procedures implemented with Bi(III) and Fe(III) with and without thiourea and L-cysteine additives, and ammonium sulfide. Recoveries for ammonium sulfide precipitation are for the concentration of CH3Hg+ and Hg2+ remained in solution after precipitation of 100 μg L−1 CH3Hg+ or Hg2+. Results are given as mean ± standard deviation of 5 separate replicates (n = 5).
| Matrix/Precipitant | Recovery (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CH3Hg+ | Hg2+ | ||
| 1.0 mg mL−1 Bi(III) | 4.3 ± 1.9 | 8.8 ± 2.0 | |
| 1.0 mg mL−1 Fe(III) | 8.8 ± 1.0 | 23 ± 5 | |
| 0.1% L-cysteine | 2.5 ± 0.7 | 3.1 ± 0.6 | |
| 1.0 mg mL−1 Bi(III) + 0.1% L-cysteine | 2.8 ± 0.7 | 12.4 ± 0.8 | |
| 1.0 mg mL−1 Fe(III) + 0.1% L-cysteine | 7.6 ± 3.5 | 56 ± 7 | |
| 0.1% Thiourea | 13 ± 2 | 3.2 ± 2.2 | |
| 1.0 mg mL−1 Bi(III) + 0.1% Thiourea | 67 ± 2.0 | 26 ± 4.2 | |
| 1.0 mg mL−1 Fe(III) + 0.1% Thiourea | 25 ± 8 | 64 ± 4.2 | |
| 0.005 mol L−1 Ammonium sulfide | 102 ± 3 | 2.1 ± 1.1 | |
Third attempt was made to precipitate Hg2+ as insoluble HgS by adding 30 µL of 0.35 M aqueous (NH4)2S solution to 2-mL simulated soil solutions in 5% (v/v) HNO3. Precipitation occurred instantaneously after adding (NH4)2S. Solutions were briefly shaken, and then centrifuged. The acidic supernatant solutions were analyzed by ICP-MS. The results for CH3Hg+ and Hg2+ are shown in Table 4 (last row). The recoveries are for the CH3Hg+ and Hg2+ concentration remained in the solution after precipitation. It was clear that Hg2+ was effectively removed from the solution (from 100 µg L−1 to around 2 µg L−1). Unlike hydroxide coprecipitation, (NH4)2S did not interfere with stability or retention of CH3Hg+ in solution. Even increasing the volume up to 50 µL had no symptoms of precipitation, yet, the volume was kept at 30 µL to avoid any interferences from excessive sulfide (S2−) in vapor generation studies.
3.4. Optimization chemical vapor generation conditions
The concentrations of HNO3 and reducing agents (e.g., SnCl2 and NaBH4) were optimized for chemical vapor generation of 10 µg L−1 CH3Hg+ or Hg2+ solutions using the manifold shown in Fig. 1. The acidity was examined up to 6% (v/v) HNO3 for 1% (m/v) SnCl2 and 1% (m/v) NaBH4. The CVG profiles for CH3Hg+ and Hg2+ are shown in Fig. 2A. Signals for Hg2+ steadily increased up to 3% (v/v) HNO3 and leveled off afterwards, while that for CH3Hg+ reached a plateau at and above 4% (v/v) HNO3. The acidity of soils extracts - 5% (v/v) HNO3 - was within the operational acid range of the CVG. NaBH4 is essential for total Hg determination (Hg2+ + CH3Hg+) while SnCl2 is used for selective reduction of Hg2+ [31,45]. The signals for CVG of CH3Hg+ were at the baseline levels (ca. 3000–3500 cps) when reducing agent was SnCl2, which verified that SnCl2 did not affect CH3Hg+, but performed similarly to NaBH4 in reduction of Hg2+.
Fig. 2.
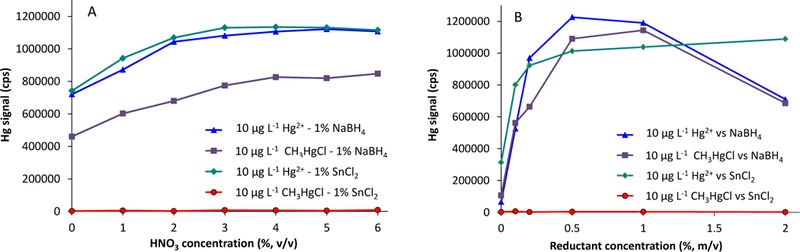
Vapor generation profiles from 10 µg L−1 CH3Hg+ and Hg2+. A = Effect of HNO3 concentration on Hg signals with 1% (m/v) NaBH4 and 1% (m/v) SnCl2. B = Effect of concentrations of NaBH4 and SnCl2 on vapor generation against 5% (v/v) HNO3.
The concentrations of NaBH4 and SnCl2 were examined from 0 to 2% (m/v) for both reagents and the results are illustrated in Fig. 2B. A concentration of 0.5% (m/v) SnCl2 was sufficient for complete reduction of Hg2+ to Hg0, while for CH3HgCl no significant signal was observed up to 2% (m/v) SnCl2. Higher concentrations of SnCl2 (e.g., 1 to 2%) caused white deposition along the mixing coil due to the oxidation of SnCl2 to SnO2 when mixed with HNO3. With NaBH4, CVG signals for Hg2+ and CH3HgCl showed maxima between 0.5 and 1% (m/v) NaBH4. However, reduction of CH3HgCl occurred consistently and more effectively with 1% (m/v) NaBH4. Signals declined at 2% (m/v) NaBH4 because of vigorous reaction between NaBH4 and HNO3 generating excessive H2 that consequently changed the optimal the carrier gas flow rate.
3.5. Interferences and analytical merits
Potential chemical interferences from excess sulfide were investigated on vapor generation for 10 µg L−1 CH3HgCl (n = 5, treatment) in 5% (v/v) HNO3 that contained 30 µL of 0.35 mole L−1 (NH4)2S in 2 mL volume (e.g., 0.005 mole L−1). A 10 µg L−1 CH3HgCl in 5% (v/v) HNO3 (n = 5, control) was used as control solution. No significant suppression or enhancement occurred in vapor generation in comparison to the control solutions. The ratio between treatment and control signals (cps) (e.g., treatment/control) was 0.94 ± 0.04 (e.g., 94 ± 4%). This result was further verified by constructing calibration curves for CH3HgCl (0 to 10 µg L−1) using 1% (m/v) NaBH4 as reducing agent. For 202Hg isotope, the slopes for 5% (v/v) HNO3 and 5% (v/v) HNO3 + 0.005 mole L−1 (NH4)2S were 84929 (R2 = 0.998) and 82450 (R2 = 0.999), respectively, demonstrating that (NH4)2S matrix had no effect on vapor generation of CH3HgCl in HNO3 solutions. Using the same calibration curves, limits of detection (LODs) were calculated for blank solutions (n = 10) of 5% (v/v) HNO3 and 5% (v/v) HNO3 + 0.005 mole L−1 (NH4)2S. The LODs (concentration equivalent to 3s of the blank standard deviation) were 0.12 and 0.10 µg L−1 for 200Hg and 202Hg, respectively in the presence of (NH4)2S. For 5% (v/v) HNO3 blanks, LODs were slightly lower but were not significantly different; 0.082and 0.085 µg L−1 for 200Hg and 202Hg, respectively. Eventually, the LODs were limited due to the persistent Hg background (ca. 4,000 cps) in the CVG system. Despite repetitive washings with 0.5% (m/v) potassium ferricyanide solution in 5% (v/v) HCl, background signals could not be fully eliminated. Still though, these LODs were sufficiently low to achieve determination of CH3Hg+ in the contaminated soils. Precision expressed as per cent relative standard deviation (%RSD) for 10 consecutive scans/readings (see Table 1) of 1.0 µg L−1 CH3HgCl solution was around 2.1%. For 5 separate replicate measurements, precision varied between 3.1% and 6.4% for 1.0 µg L−1 CH3HgCl standard solution.
3.6. Method validation and analysis of floodplain soils
For validation of the procedure, 0.2 g sub-samples (n = 5) of methylmercury sediment (SQC1238) and Estuarine sediment (ERM – CC580) were processed as described in section 2.8. CH3Hg+ determination was carried out using the optimized NaBH4 method (5% HNO3 vs 1% NaBH4) by CVG-ICP-MS. The remaining of the CRM solutions were reanalyzed using SnCl2 reduction method (e.g., 5% HNO3 vs 0.5% SnCl2) to determine the residual Hg2+, if any, remained after (NH4)2S precipitation. All calibration standards and blanks were prepared in 2-mL micro-centrifuge tubes and contained 30 µL of 0.35 mole L−1 of (NH4)2S solution to match with samples. The results for CRMs are summarized in Table 5 for 200Hg and 202Hg isotopes. The certified concentration for CH3Hg+ in SQC1238 was 10.00 ± 0.291 ng g−1. ERM – CC580 was heavily Hg-contaminated estuarine sediment with trace amounts of CH3Hg+; certified values were 132 ± 3 µg g−1 for total Hg and 75 ± 4 ng g−1 for CH3Hg+. The experimental values were between 13.0 ± 3 and 13.2 ± 3 ng g−1 for SQC1238 and 79 ± 8 and 81 ± 7 ng g−1 for ERM – CC580, where uncertainties are expressed as standard deviation for five replicate samples (Table 5). It should be noted that acceptance limits of CH3Hg+ for SQC1238 ranged from 5.13 to as high as 14.9 ng g−1, indicating inhomogeneity within sample. To improve precision, a sample size of 1.0 g is recommended for SCQ1238. In this work, measurements were made with 0.2 g samples. Despite higher mean CH3Hg+ levels, the experimental results agreed with the certified values; high uncertainty (e.g. variation) were likely related to small sample size and inhomogeneity. The analysis of the extracts with SnCl2 reduction method showed about 0.15 µg L−1 Hg2+ in solution though SQC1238 was fully methylmercury chloride, which was indicative of the fact that background Hg signals could have also contributed to uncertainty due to very low CH3Hg+ levels. For ERM-CC580, better accuracy was achieved with the certified values. Mean CH3Hg+ levels were slightly higher; 79 to 81 ng g−1 that were equivalent to about 3.2 µg L−1 CH3Hg+ in 5 mL extracts (0.2 g sample). This concentration was about 0.2 µg L−1 higher (ca. 6.5%) than that for the certificate value (3.0 µg L−1 CH3Hg+ at 75 ng g−1). Further, the concentration of residual Hg2+ in ERM-CC580 extracts varied from below LOD values (< LOD) to 0.180 µg L−1 when the remaining solutions were analyzed by CVG-ICP-MS using SnCl2 reduction. These results indicated that residual Hg2+ was effectively eliminated by HgS precipitation. Eventually, the concentrations for Hg2+ from both CRM extracts were within the vicinity of LODs and hence were likely affected from the persistent background signals.
Table 5.
Methylmercury concentrations measured from methlymercury sediment (SQC1238) and estuarine sediment (ERM – CC580) certified reference materials by the optimized CVG-ICP-MS. Values are given as mean ± standard deviation of 5 separate replicates (n = 5).
| Sample | CH3Hg+ concentration (ng g−1) |
Certified value (ng g−1) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 200Hg | 202Hg | ||
| SQC1238 | 13.0 ± 3 | 13.2 ± 3 | 10.00 ± 0.291 |
| ERM – CC580 | 81 ± 7 | 79 ± 8 | 75 ± 4 |
For analysis of floodplain soils, the same strategy was followed as for the method validation with CRMs. About 0.2 g sub-samples (n = 5) of the soils were subjected to the procedure. A set of SQC1238 and ERM – CC580 (n = 5) were also prepared freshly and analyzed concurrently by CVG-ICP-MS using NaBH4 reduction method. The results are summarized in Table 6 for 200Hg and 202Hg isotopes. CH3Hg+ levels ranged from 30 to 51 ng g−1 indicating that CH3Hg+ levels in the floodplain soils were much lower than the total Hg levels (ca. 0.05% of total Hg). Further, they did not correlate with total Hg levels (R2 = 0.01). Despite low levels, however, continuous leaching of CH3Hg+ to creek and riverine water could be a significant source for the persistent Hg levels in the waters of the EFPC at Oak Ridge, TN.
4. Conclusion
In this study, a new method is developed for selective extraction and determination of CH3Hg+ in soil and sediment samples, specifically in sediments contaminated with Hg. Between HCl and HNO3, the latter was most suitable for selective extraction of CH3Hg+ from soils. Ultrasonic agitation in 5% (v/v) HNO3 at room temperature afforded fast extraction of CH3Hg+ with minimal dissolution of inorganic Hg species. Residual Hg2+ leached into solution during extraction was effectively eliminated via HgS precipitation prior to vapor generation determinations. Both HNO3 extraction and HgS coprecipitation steps were vital components of the procedure to achieve inorganic Hg-free determinations of CH3Hg+, and to eliminate the deleterious effects and contamination that would otherwise occur inevitably in the presence of high Hg2+ matrix. Additionally, presence of small amounts of sulfide in analysis solutions had no adverse effects on chemical vapor generation of CH3Hg+. The procedure is simple and fast in contrast to chromatographic separation and speciation approaches, and more importantly it offers unique advantages for selective and accurate determination of trace amounts of highly toxic CH3Hg+ from heavily Hg-contaminated sediments and other environmental materials.
Acknowledgements
This work is by supported by the Department of Energy Office of Environmental Management (DOE-EM) Minority Serving Institution Partnership Program (MSIPP) managed by the Savannah River National Laboratory (SRNL) under Savannah River Nuclear Solutions (SRNS) contract 291435. Partial funding is provided the National Institutes of Health (NIH) through Research Centers in Minority Institutions (RCMI) Program (Grant No: G12RR013459) at Jackson State University (Grant No: 1461143). The views expressed herein are those of authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies, and any of their sub-agencies.
References
- [1].Grigal DF, Inputs and outputs of mercury from terrestrial watersheds: a review, Environ. Rev 10 (2002) 1–39. 10.1139/a01-013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [2].Hsu-Kim H, Kucharzyk KH, Zhang T, Deshusses MA, Mechanisms regulating mercury bioavailability for methylating microorganisms in the aquatic environment: A critical review, Environ. Sci. Technol 47 (2013) 2441–2456. 10.1021/es304370g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [3].Committee on the Toxicological Effects of Methylmercury, Toxicological Effects of Methylmercury, 2000. 10.17226/9899. [DOI]
- [4].He F, Gao J, Pierce E, Strong PJ, Wang H, Liang L, In situ remediation technologies for mercury-contaminated soil, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res 22 (2015) 8124–8147. 10.1007/s11356-015-4316-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [5].Brooks SC, Southworth GR, History of mercury use and environmental contamination at the Oak Ridge Y-12 Plant, Environ. Pollut 159 (2011) 219–228. 10.1016/j.envpol.2010.09.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Han FX, Su Y, Shi Z, Xia Y, Tian W, Philips V, Monts DL, Gu M, Liang Y, Mercury distribution and speciation in floodplain soils and uptake into native earthworms (Diplocardia spp.), Geoderma 170 (2012) 261–268. 10.1016/j.geoderma.2011.11.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Calabrese EJ, Iavicoli I, Calabrese V, Cory-Slechta DA, Giordano J, Elemental mercury neurotoxicity and clinical recovery of function: A review of findings, and implications for occupational health, Environ. Res 163 (2018) 134–148. 10.1016/j.envres.2018.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].EPA, Integrated Risk Information System (IRIS) Chemical Assessment Summary: Methylmercury (MeHg); CASRN 22967–92-6, (2001) 1–43.
- [9].Castro-González MI, Méndez-Armenta M, Heavy metals: Implications associated to fish consumption, Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol 26 (2008) 263–271. 10.1016/j.etap.2008.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [10].2003- Joint FAO-WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. In Sixty-first meeting.pdf, (n.d.).
- [11].Morel FMM, Milligan AJ, Saito MA, Marine Bioinorganic Chemistry: The Role of Trace Metals in the Oceanic Cycles of Major Nutrients, in: Treatise Geochemistry Second Ed., 2013. 10.1016/B978-0-08-095975-7.00605-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Parks JM, Johs A, Podar M, Bridou R, Hurt RA, Smith SD, Tomanicek SJ, Qian Y, Brown SD, Brandt CC, Palumbo AV, Smith JC, Wall JD, Elias DA, Liang L, The genetic basis for bacterial mercury methylation, Science 339 (2013) 1332–1335. 10.1126/science.1230667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [13].Hu H, Lin H, Zheng W, Tomanicek SJ, Johs A, Feng X, Elias DA, Liang L, Gu B, Oxidation and methylation of dissolved elemental mercury by anaerobic bacteria, Nat. Geosci 6 (2013) 751–754. 10.1038/ngeo1894. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Jiang T, Skyllberg U, Björn E, Green NW, Tang J, Wang D, Gao J, Li C, Characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) and relationship with dissolved mercury in Xiaoqing River-Laizhou Bay estuary, Bohai Sea, China, Environ. Pollut 223 (2017) 19–30. 10.1016/j.envpol.2016.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Gao Y, Shi Z, Long Z, Wu P, Zheng C, Hou X, Determination and speciation of mercury in environmental and biological samples by analytical atomic spectrometry, Microchem. J 103 (2012) 1–14. 10.1016/j.microc.2012.02.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Ravichandran M, Interactions between mercury and dissolved organic matter - A review, Chemosphere 55 (2004) 319–331. 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2003.11.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Tjerngren I, Karlsson T, Björn E, Skyllberg U, Potential Hg methylation and MeHg demethylation rates related to the nutrient status of different boreal wetlands, Biogeochemistry 108 (2012) 335–350. 10.1007/s10533-011-9603-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Åkerblom S, Bishop K, Björn E, Lambertsson L, Eriksson T, Nilsson MB, Significant interaction effects from sulfate deposition and climate on sulfur concentrations constitute major controls on methylmercury production in peatlands, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 102 (2013) 1–11. 10.1016/j.gca.2012.10.025. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Kelly C. a., Rudd JWM, St.Louis VL, Heyes A, Is total mercury concentration a good predictor of methyl mercury concentration in aquatic systems?, Water Air Soil Pollut 80 (1995) 715–724. 10.1007/BF01189723. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Bridou R, Monperrus M, Gonzalez PR, Guyoneaud R, Amouroux D, Simultaneous determination of mercury methylation and demethylation capacities of various sulfate-reducing bacteria using species-specific isotopic tracers, Environ. Toxicol. Chem 30 (2011) 337–344. 10.1002/etc.395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Xing Z, Zhao T, Bai W, Yang X, Liu S, Zhang L, Temporal and spatial variation in the mechanisms used by microorganisms to form methylmercury in the water column of Changshou Lake, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf 160 (2018) 32–41. 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.05.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Carrasco L, Díez S, Bayona JM, Methylmercury determination in biota by solid-phase microextraction. Matrix effect evaluation, J. Chromatogr. A 1174 (2007) 2–6. 10.1016/j.chroma.2007.09.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Mason RP, Lawrence AL, The concentration, distribution and bioavailability of mercury and methylmercury in sediments of Baltimore Harbor and the Chesapeake Bay, Environ. Toxicol. Chem 18 (1999) 2438–2447. [Google Scholar]
- [24].Amde M, Yin Y, Zhang D, Liu J, Methods and recent advances in speciation analysis of mercury chemical species in environmental samples: A review, Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab 28 (2016) 51–65. 10.1080/09542299.2016.1164019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [25].Chen J, Chen H, Jin X, Chen H, Determination of ultra-trace amount methyl-, phenyl- and inorganic mercury in environmental and biological samples by liquid chromatography with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after cloud point extraction preconcentration, Talanta 77 (2009) 1381–1387. 10.1016/j.talanta.2008.09.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Yuan CG, Lin K, Chang A, Determination of trace mercury in environmental samples by cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectrometry after cloud point extraction, Microchim. Acta 171 (2010) 313–319. 10.1007/s00604-010-0429-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [27].Díez S, Bayona JM, Determination of Hg and organomercury species following SPME: A review, Talanta 77 (2008) 21–27. 10.1016/j.talanta.2008.06.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [28].Shabani MB, Akagi T, Shimizu H, Masuda A, Determination of trace lanthanides and yttrium in seawater by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry after preconcentration with solvent extraction and back-extraction, Anal. Chem 62 (1990) 2709–2714. 10.1021/ac00223a012. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [29].Ma S, He M, Chen B, Deng W, Zheng Q, Hu B, Magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry for the speciation of mercury in environmental water and human hair samples, Talanta 146 (2016) 93–99. 10.1016/j.talanta.2015.08.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Krawczyk M, Stanisz E, Ultrasound-assisted dispersive micro solid-phase extraction with nano-TiO2 as adsorbent for the determination of mercury species, Talanta 161 (2016) 384–391. 10.1016/j.talanta.2016.08.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Leopold K, Foulkes M, Worsfold P, Methods for the determination and speciation of mercury in natural waters-A review, Anal. Chim. Acta 663 (2010) 127–138. 10.1016/j.aca.2010.01.048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [32].de Souza SS, Campiglia AD, Barbosa F, A simple method for methylmercury, inorganic mercury and ethylmercury determination in plasma samples by high performance liquid chromatography-cold-vapor-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, Anal. Chim. Acta 761 (2013) 11–17. 10.1016/j.aca.2012.11.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [33].Lemes M, Wang F, Methylmercury speciation in fish muscle by HPLC-ICP-MS following enzymatic hydrolysis, J. Anal. At. Spectrom 24 (2009) 663 10.1039/b819957b. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [34].Zhu S, Chen B, He M, Huang T, Hu B, Speciation of mercury in water and fish samples by HPLC-ICP-MS after magnetic solid phase extraction, Talanta 171 (2017) 213–219. 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.04.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Rodríguez-Reino MP, Rodríguez-Fernández R, Peña-Vázquez E, Domínguez-González R, Bermejo-Barrera P, Moreda-Piñeiro A, Mercury speciation in seawater by liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry following solid phase extraction pre-concentration by using an ionic imprinted polymer based on methyl-mercury-phenobarbital interaction, J. Chromatogr. A 1391 (2015) 9–17. 10.1016/j.chroma.2015.02.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [36].Rodrigues JL, de Souza SS, de Oliveira Souza VC, Barbosa F, Methylmercury and inorganic mercury determination in blood by using liquid chromatography with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and a fast sample preparation procedure, Talanta 80 (2010) 1158–1163. 10.1016/j.talanta.2009.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [37].Davis WC, Vander Pol SS, Schantz MM, Long SE, Day RD, Christopher SJ, An accurate and sensitive method for the determination of methylmercury in biological specimens using GC-ICP-MS with solid phase microextraction, J. Anal. At. Spectrom 19 (2004) 1546 10.1039/b412668h. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [38].Queipo Abad S, Rodríguez-González P, Davis WC, García Alonso JI, Development of a common procedure for the determination of methylmercury, ethylmercury, and inorganic mercury in human whole blood, hair, and urine by triple spike species-specific isotope dilution mass spectrometry, Anal. Chem 89 (2017) 6731–6739. 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Carrasco L, Vassileva E, Determination of methylmercury in marine biota samples: Method validation, Talanta 122 (2014) 106–114. 10.1016/j.talanta.2014.01.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [40].Carrasco L, Vassileva E, Determination of methylmercury in marine sediment samples: Method validation and occurrence data, Anal. Chim. Acta 853 (2015) 167–178. 10.1016/j.aca.2014.10.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [41].Wu L, Zheng C, Ma Q, Hu C, Hou X, Chemical vapor generation for determination of mercury by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, Appl. Spectrosc. Rev 42 (2007) 79–102. 10.1080/05704920601184234. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [42].Sánchez Trujillo I, Vereda Alonso E, García de Torres A, Cano Pavón JM, Development of a solid phase extraction method for the multielement determination of trace metals in natural waters including sea-water by FI-ICP-MS, Microchem. J 101 (2012) 87–94. 10.1016/j.microc.2011.11.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [43].Kenduzler E, Ates M, Arslan Z, McHenry M, Tchounwou PB, Determination of mercury in fish otoliths by cold vapor generation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (CVG-ICP-MS), Talanta 93 (2012) 404–410. 10.1016/j.talanta.2012.02.063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [44].Jagtap R, Maher W, Measurement of mercury species in sediments and soils by HPLC-ICPMS, Microchem. J 121 (2015) 65–98. 10.1016/j.microc.2015.01.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [45].Almeida ILS, Oliveira MDR, Silva JBB, Coelho NMM, Suitable extraction of soils and sediments for mercury species and determination combined with the cold vapor generation atomic absorption spectrometry technique, Microchem. J 124 (2016) 326–330. 10.1016/j.microc.2015.09.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [46].Park M, Yoon H, Yoon C, Yu J-Y, Estimation of mercury speciation in soil standard reference materials with different extraction methods by ion chromatography coupled with ICP-MS, Environ. Geochem. Health 33 (2011) 49–56. 10.1007/s10653-010-9363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [47].Westöö G, Determination of methylmercury compounds in foodstuffs II - determination of Methylmercury in fish, egg, meat and liver, Acta Chem. Scand 21 (1967) 1790–1800. 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.21-1790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [48].Hempel M, Hintelmann H, Wilken R-D, Determination of organic mercury species in soils by high-performance liquid chromatography with ultraviolet detection, Analyst 117 (1992) 669–672. 10.1039/AN9921700669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [49].Liang L, Horvat M, Cernichiari E, Gelein B, Balogh S, Simple solvent extraction technique for elimination of matrix interferences in the determination of methylmercury in environmental and biological samples by ethylation-gas chromatography-cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectrometry, Talanta 43 (1996) 1883–1888. 10.1016/0039-9140(96)01964-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [50].Berzas Nevado JJ, Rodríguez Martín-Doimeadios RC, Guzmán Bernardo FJ, Jiménez Moreno M, Determination of monomethylmercury in low- and high-polluted sediments by microwave extraction and gas chromatography with atomic fluorescence detection, Anal. Chim. Acta 608 (2008) 30–37. 10.1016/j.aca.2007.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [51].Inoue Y, Munemori M, Coprecipitation of mercury(II) with iron(III) hydroxide, Environ. Sci. Technol 13 (1979) 443–445. 10.1021/es60152a001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [52].Ishino F, Munemori M, Coprecipitation of mercury(II) with bismuth(III) hydroxide, Nippon Kagaku Kaishi 1985 (1985) 1710–1714. 10.1246/nikkashi.1985.1710. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [53].Matlock MM, Howerton BS, Atwood DA, Irreversible precipitation of mercury and lead, J. Hazard. Mater 84 (2001) 73–82. 10.1016/S0304-3894(01)00190-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [54].Lewis AE, Review of metal sulphide precipitation, Hydrometallurgy 104 (2010) 222–234. 10.1016/j.hydromet.2010.06.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- [55].Issaro N, Abi-Ghanem C, Bermond A, Fractionation studies of mercury in soils and sediments: A review of the chemical reagents used for mercury extraction, Anal. Chim. Acta 631 (2009) 1–12. 10.1016/j.aca.2008.10.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


