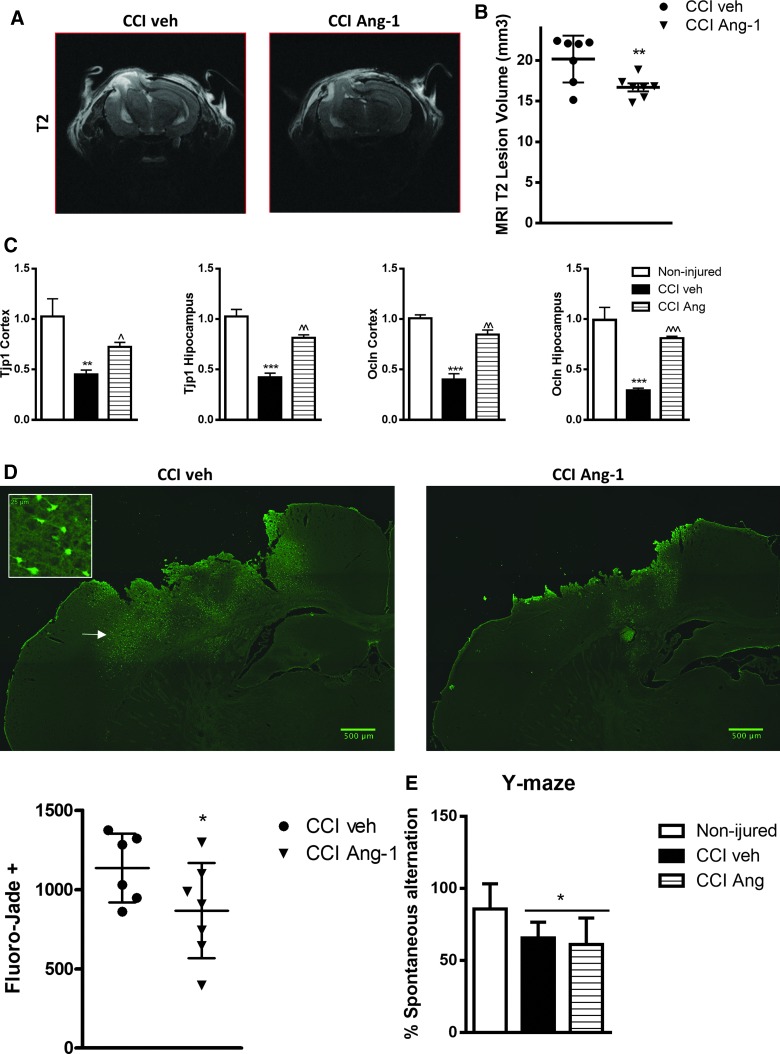
FIG. 9.
Treatment with Ang-1 significantly reduced neurodegeneration in 24 h after TBI. (A and B) Post-injury TBI-induced edema/lesion volume was quantified by T2-weighted MRI at 24 h after CCI. Treatment with Ang-1 significantly reduced the lesion volume compared to the CCI veh group (p < 0.01; CCI veh, N = 7; CCI Ang-1, N = 7). (C) qPCR quantification of Tjp1 and Ocln mRNA levels in injured cortex and hippocampus. Data represent the mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA, SNK post-hoc test; ***p < 0.001 versus noninjured; ^p < 0.05; ^^p < 0.01; ^^^p < 0.001 versus vehicle CCI group (noninjured, N = 4; vehicle CCI, N = 3; ANG-1 CCI, N = 5). (D) Fluoro-Jade B staining at 24 h post-injury of the injured hemispheres is displayed; magnified area whose localization is indicated by arrow illustrates the neuronal morphology/origin of the Fluoro-Jade–positive cells. Injury-induced neurodegeneration, indicated by higher number of Fluoro-Jade B–positive cells, was significantly attenuated by Ang-1 treatment (p < 0.05; CCI veh, N = 6; CCI Ang-1, N = 7). Analysis by one-tailed unpaired Student's t-test. Individual values for the experimental animals are displayed. (E) Treatment with Ang-1 did not improve TBI-induced long-term cognitive function deficits. Noninjured mice showed intact spatial working memory function and performed significantly better than the 50% chance level (N = 8). CCI veh and Ang-1 CCI groups showed significantly reduced percentages of spontaneous alternation (*p < 0.05; N = 10). No significant differences were observed between veh and Ang-1 groups. One-way ANOVA, SNK post-hoc test. Ang-1, angiopoietin-1; ANOVA, analysis of variance; CCI, controlled cortical impact; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; mRNA, messengter RNA; Ocln, occludin; qPCR, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; SEM, standard error of the mean; SNK, Student–Newman–Keuls; TBI, traumatic brain injury; Tjp1, tight junction protein 1. Color image is available online at www.liebertpub.com/neu