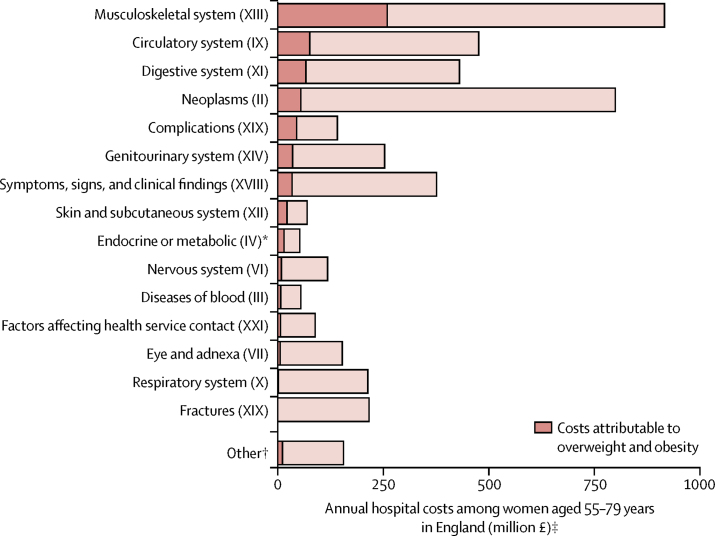
Figure 2.
Annual hospital costs attributed to overweight and obesity among women aged 55–79 years in England by diagnostic category
Overweight and obesity is defined as a BMI of 25 kg/m2 or more. ICD-10 chapters are ordered in the figure according to their contribution to overweight and obesity attributed costs. These estimates were derived by applying the estimates of excess costs by BMI category for each ICD-10 chapter (or combination) from the Million Women Study analysis (appendix p 11) to women aged 55–79 years in England using the Health Surveys for England 2012 and 2013 to estimate the population-level distribution of women by self-reported BMI category and UK Office for National Statistics mid-2013 population estimates (appendix p 2). We calculated excess costs relative to a BMI category of 20 kg/m2 to less than 25 kg/m2, estimated as a weighted average of the estimates of the two subcategories (20 kg/m2 to <22·5 kg/m2 and 22·5 kg/m2 to <25 kg/m2). BMI=body-mass index. *Hospital admissions were categorised by health conditions (ie, ICD-10 chapter of primary diagnosis). Although diabetes could be an underlying cause of many admissions, the categories in this figure represent the health condition for which the individual ultimately receives treatment in an inpatient setting. †All chapters with fewer than 10 000 admissions (certain infectious and parasitic diseases [I]; mental and behavioural disorders [V]; diseases of the ear and mastoid process [VIII]; pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium [XV]; certain conditions originating in the perinatal period [XVI]; and congenital malformations, deformations, and chromosomal abnormalities [XVII]) and the remainder of chapter XIX after the separation of fractures and medical and surgical complications. ‡In UK 2012 prices.