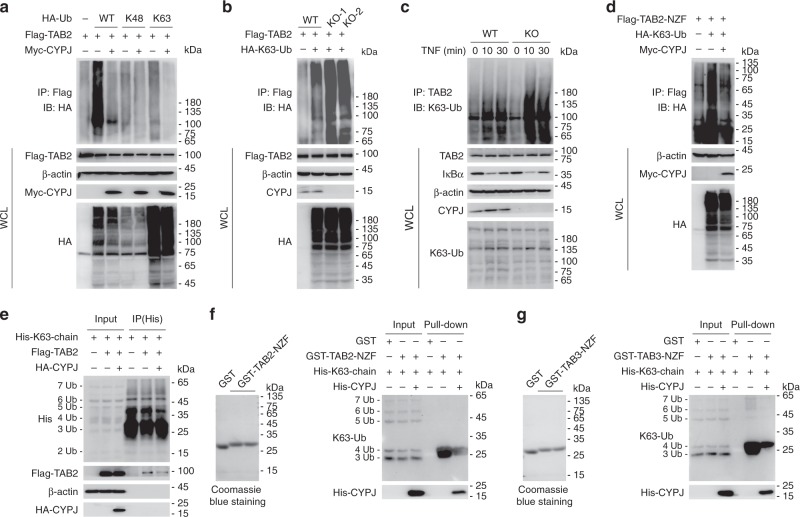
Fig. 5.
CYPJ disrupts the K63-linked ubiquitin-chain sensing of TAB2 and TAB3. a 293T cells were transfected with plasmids as indicated for 24 h. The enforced expressed Flag-TAB2 was immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody, and the polyubiquitin signals were detected with an anti-HA antibody. b WT or CYPJ-knockout (KO-1 and KO-2) 293T cells were transfected with or without HA-K63-Ub and Flag-TAB2 for 24 h, followed by IP and IB as indicated. c Lysates of WT or CYPJ-knockout 293T cells treated with TNF for different times were immunoprecipitated with an anti-TAB2 antibody, followed by IB with the indicated antibodies, including anti-K63 Ub. d 293T cells were co-transfected with Flag-TAB2-NZF, HA-K63-Ub, and Myc-CYPJ as indicated, and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an anti-Flag antibody followed by IB with an anti-HA antibody. e Lysates of Flag-TAB2 with or without HA-CYPJ-transfected 293T cells were incubated with in vitro synthesized His-K63-Ub chain (1 μg) as indicated. The His-K63-chain was immunoprecipitated with an anti-His antibody, and the bound Flag-TAB2 was detected with an anti-Flag antibody. f, g Binding of GST, GST-CYPJ, or GST-TAB2-NZF (f) or GST-TAB3-NZF (g) to the His-K63-chain was monitored by GST pull-down assays as indicated. Approximately 1 μg of the His-K63-chain was used in each reaction