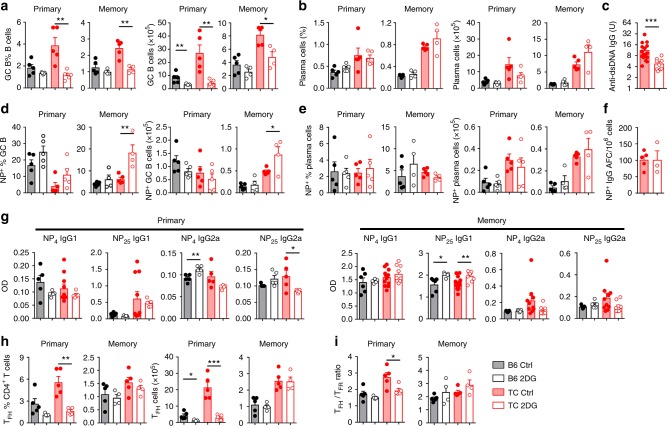
Fig. 3.
Glycolysis inhibition does not affect the TD-humoral response. After pre-treatment with 2DG for 2 weeks, 8–10-week-old B6 and TC mice were immunized with NP-KLH in alum and maintained under 2DG treatment until sacrifice. Mice were analyzed 10 d after immunization (primary), or 7 weeks after the first immunization following 2 boosts with same antigen 2 and 6 weeks after the primary immunization (memory). Frequency and number of total (a, b) or NP-specific (d, e) GC B cells and plasma cells (gating shown in supplementary Fig. 3). Serum anti-dsDNA IgG (c) and NP-specific IgG antibody-forming cells (f) in TC mice in the memory response. g Serum levels of high-affinity anti-NP4 and low-affinity anti-NP25 IgG1 and IgG2a in the primary (left) and memory (right) responses. Frequency and number of splenic TFH cells (h) and TFH/TFR cell ratio (i) in the primary and memory responses. All cell analyses were performed with splenocytes. Mean + s.e.m. of N = 5 mice per group compared with t tests. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. For simplification, statistical differences between strains are not shown