Figure 2.
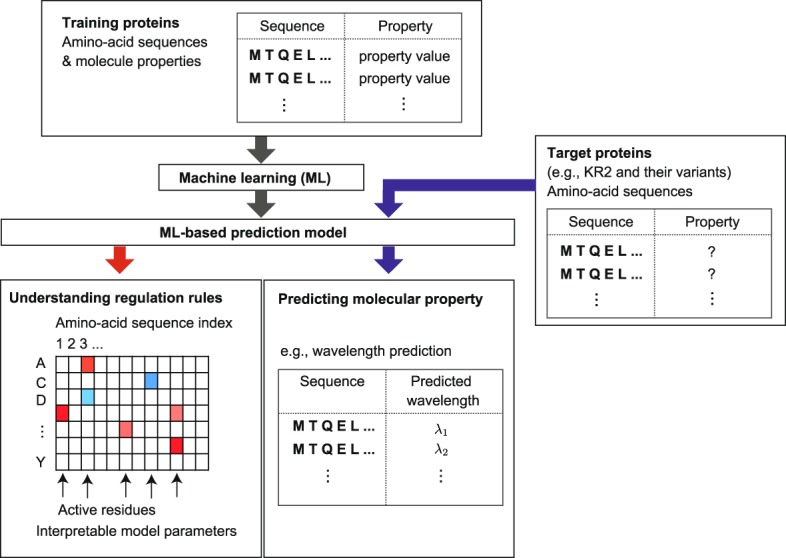
An overview of the machine-learning-based (ML-based) data-driven approach introduced in the present paper for functional protein studies. Using past experimental data, a training protein set containing pairs of amino-acid sequence and molecular properties is first constructed. Then, an ML method is applied to the training set, and an ML-based statistical model is constructed. The obtained ML model can be used in understanding the relationship between amino-acid sequences and molecular properties, such as the colour tuning rules in the case of microbial rhodopsins. The ML model can also be used to predict the molecular properties of new uninvestigated proteins. We refer to the set of new proteins as the target protein set. In the present paper, for the purpose of demonstration, we regard KR2 wildtype and its 118 variants as target proteins and other 677 rhodopsin proteins in the database as the training proteins.
