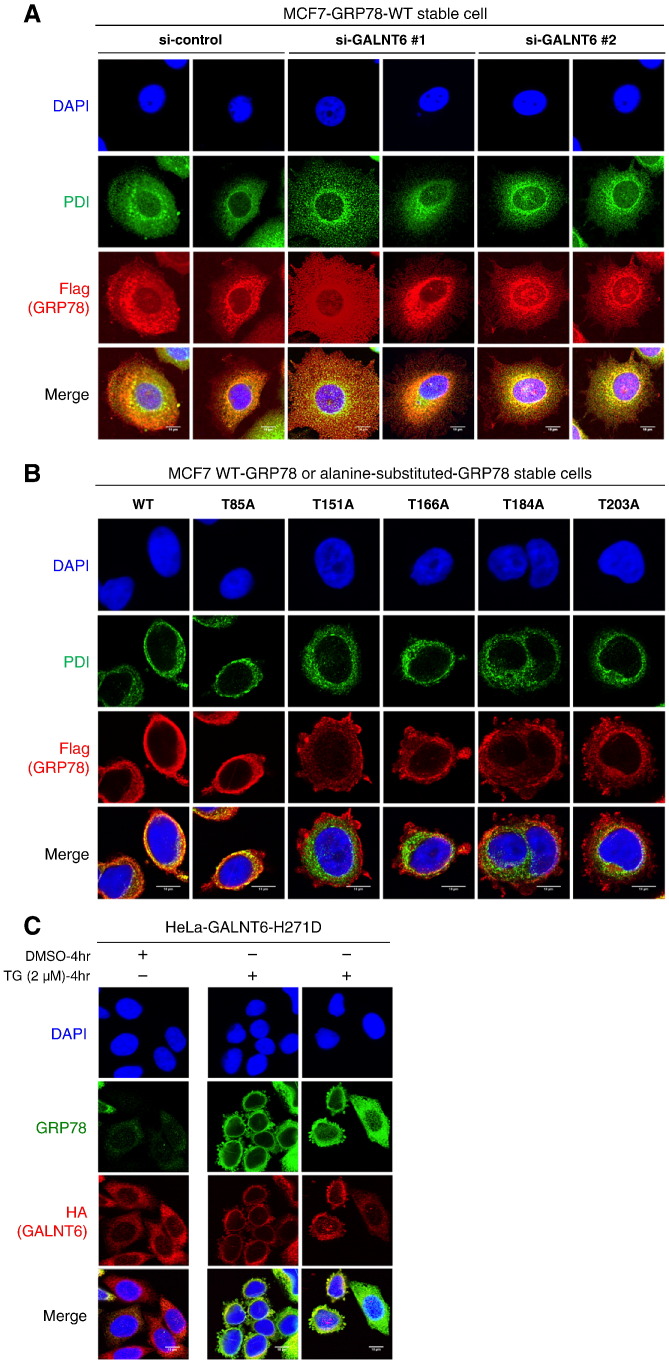
Figure 6.
O-glycosylation deficiency causes GRP78 ER-to-cytoplasm translocation. (A) GALNT6 was knocked down by siRNA for 72 h in MCF7-GRP78-WT stable cells, and then immunocytochemistry was performed. Flag-tagged GRP78 showed a diffuse and irregular distribution pattern in the cells in which GALNT6 was knocked down. Two fields were taken for each condition. (B) Immunocytochemistry was performed in MCF7-GRP78-WT and alanine-substituted GRP78 stable cells. We found that Flag-tagged GRP78 protein irregularly distributed out of ER in four cell lines harboring alanine-substitutions at O-glycosylation sites in the ATPase domain (T151A, T166A, T184A, or T203A). (C) HeLa-GALNT6-H271D stable cells were treated with DMSO or TG for 4 h, followed by immunocytochemistry. Irregular subcellular localization of endogenous GRP78 was also frequently observed in HeLa-GALNT6-H271D stable cells after induction of ER stress by TG treatment. Two fields were shown from TG-treated HeLa-GALNT6-H271D stable cells. More images from different fields for Figure 6, A and B, are provided in Supplementary Figure 3.