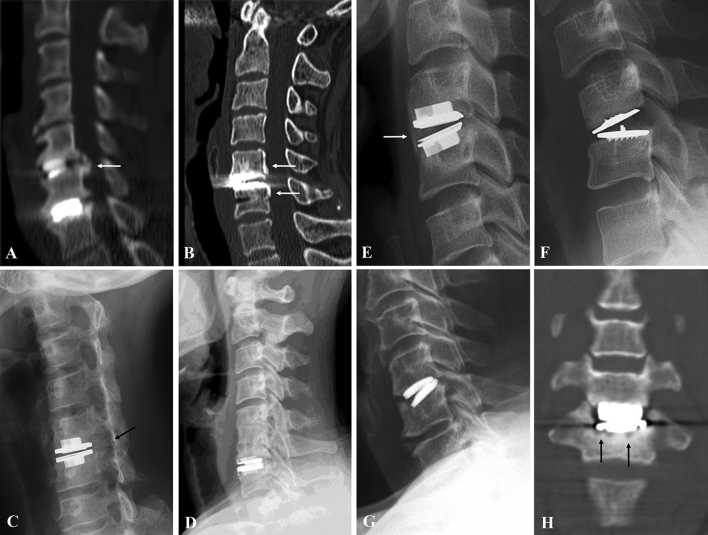
Fig. 1.
Causes of failure of artificial disc replacement of cervical spine: severe spondylosis (white arrow) (A), ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament (white arrows) (B), Foraminal stenosis (black arrow) (C), severe spondylosis adjacent to previous fusion (D), hyperlordotic positioning with heterotopic ossification (white arrow) (E), kyphotic positioning (F), subsidence (G), and osteolysis (black arrows) (H).