Figure 1.
Tumor Cell Killing Capacity of Rluc-RFP-TK-hAMSCs and Rluc-RFP-TK-FP-hAMSCs
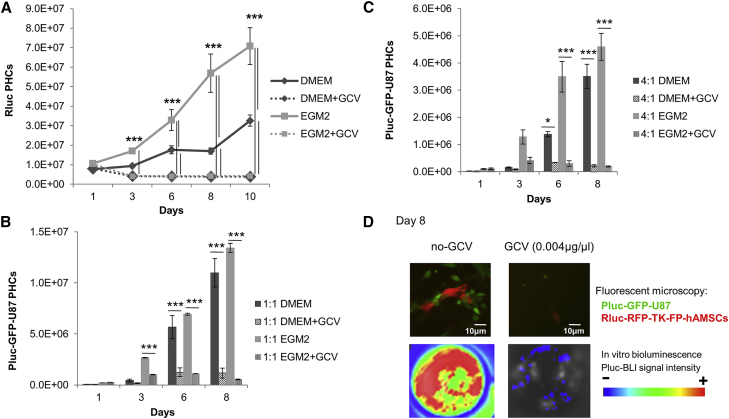
(A) Graph showing the effect of GCV (0.004 μg/μL) on growth rate of Rluc-RFP-TK-hAMSCs, cultured in DMEM, and Rluc-RFP-TK-FP-hAMSCs, cultured in EGM2 (n = 3 for each condition). Data are expressed as means ± SD. Significant differences were considered when ***p < 0.001 by two-way ANOVA test comparison and Bonferroni post-test. (B and C) Histograms comparing the in vitro bystander Pluc-GFP-U87 killing capacity of Rluc-RFP-TK-hAMSCs and Rluc-RFP-TK-FP-hAMSCs. Cells were co-cultured at a 1:1 (B) and 4:1 (C) proportion of cytotoxic hAMSCs:Pluc-GFP-U87 cells (n = 3 for each condition). Values represent means ± SD from three independent assays. Significant differences were considered when *p < 0.5 or ***p < 0.001, respectively, by two-way ANOVA test comparison and Bonferroni post-test. (D) Representative fluorescence microscope images of Rluc-RFP-TK-FP-hAMSCs (red) co-cultivated during 8 days with Pluc-GFP-U87 cells (green) with and without GCV (0.004 μg/μL), and Pluc-BLI images of the corresponding tissue culture wells. Arbitrary rainbow color scale depicts light intensity (red: highest; blue: lowest) in BLI images. Microscope images were taken with a Nikon eclipse ts100 microscope equipped with the 10× objective.