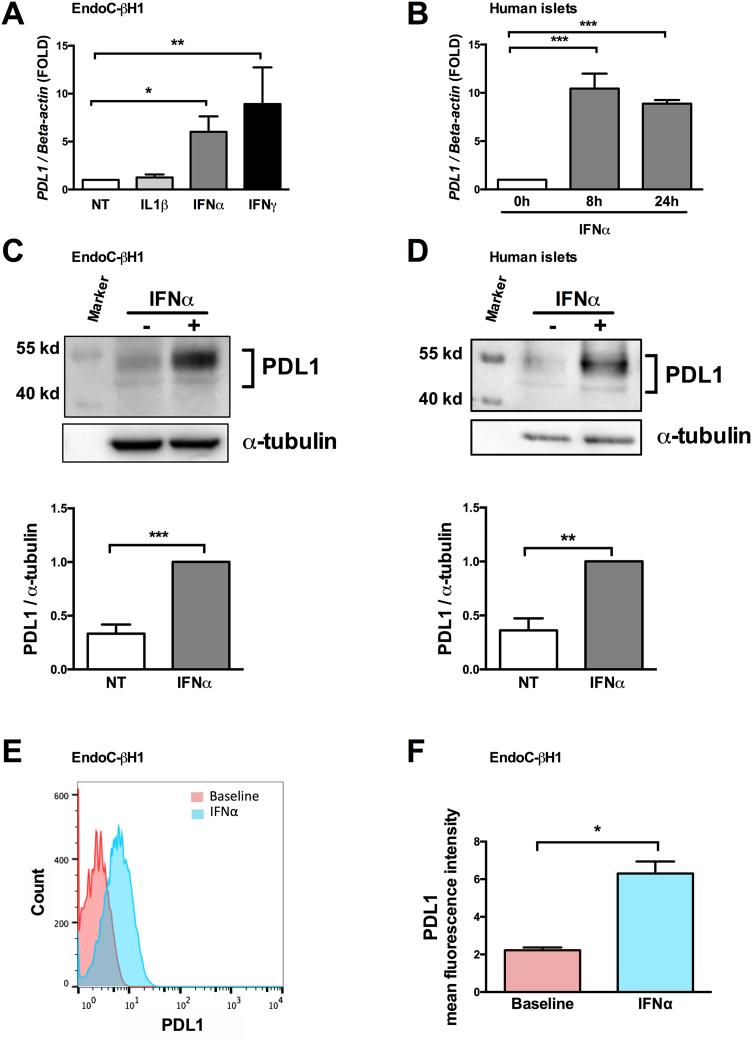
Fig. 2.
Interferons type I and II, but not interleukin-1β, up-regulate PDL1 mRNA and protein expression in human pancreatic beta cells.
EndoC-βH1 cells (A, C, E and F) and primary human islets (B and D) were exposed to interferon-α (IFNα, 2000 U/ml), interferon-γ (IFNγ, 1000 U/ml) or interleukin-1β (IL1β, 50 U/ml) for 24 h (A, C, D, E, F) for the indicated time points (B).
(A and B) PDL1 mRNA expression was evaluated by real time RT-PCR. The values were normalized by the housekeeping gene beta-actin and are represented as fold induction compared to non-treated control cells (NT) (n = 3–5, * p < .05, ** p < .01, *** p < .001, ANOVA with Bonferroni correction).
(C and D) PDL1 protein expression was determined by Western blot (upper part of the figure), quantified by densitometry and normalized by the housekeeping protein α-tubulin and then by the highest value of each experiment considered as 1 (n = 6–7, ** p < .01, *** p < .001, paired t-test).
(E and F) PDL1 cell surface expression was quantified by flow cytometry analysis at baseline or after exposure to IFNα.
(E) Histograms represent changes in mean fluorescence intensity.
(F) The geometric mean of the mean fluorescence intensity was quantified at baseline and after exposure to IFNα (n = 3, * p < .05, paired t-test).
The mean values ± SEM are shown.