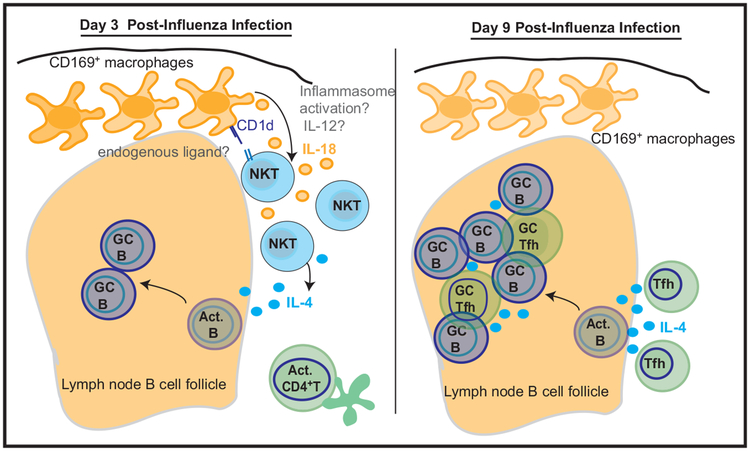
Figure 1. Early Production of IL-4 by NKT Cells Promotes Germinal Center Formation.
Soon after lung infection with influenza virus, CD169+ macrophages in the draining lymph nodes activate nearby NKT cells through both CD1d engagement and secretion of IL-18. These signals induce NKT cells to produce IL-4, which acts on B cells to promote germinal center (GC) formation and production of virus-specific antibodies (left). Later in infection, T follicular helper (Tfh) cells overtake NKT cells as the dominant IL-4 producers and, presumably, as principle orchestrators of B cell maturation (right). Outstanding questions include the nature of the CD1d ligand that contributes to activation of NKT cells; whether and how the inflammasome is activated to produce secreted IL-18; and whether other cytokines, such as IL-12, may be important in driving NKT cell activation. Abbreviation: Act., activated.