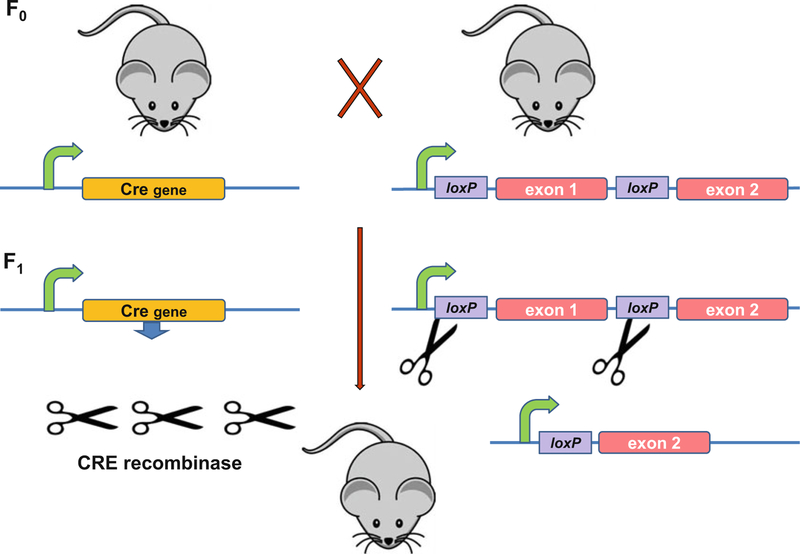
Fig. 3.
Conditional gene knockouts in mice using the Cre recombinase-loxP recombination system. A conditional knockout allele is produced by gene targeting as shown in Fig. 2. In this instance, the targeting construct contains two 34 bp loxP sites inserted in intergenic DNA sequence, usually in introns flanking an exon, multiple exons, or an exon plus the promoter of the targeted gene (right side of figure). The loxP sites do not interfere with gene expression. The resultant mice are bred with Cre expression mice (left side of figure), in which Cre recombinase gene expression is driven by a tissue-specific, developmental stage-specific, or inducible promoter, or a combination of these. Cre recombinase catalyzes excision of the loxP-flanked (floxed) DNA sequences, resulting in a targeted deletion and leaving behind a single loxP site. Intergenic sequences are shown in blue; promoters are indicated as curved green lines