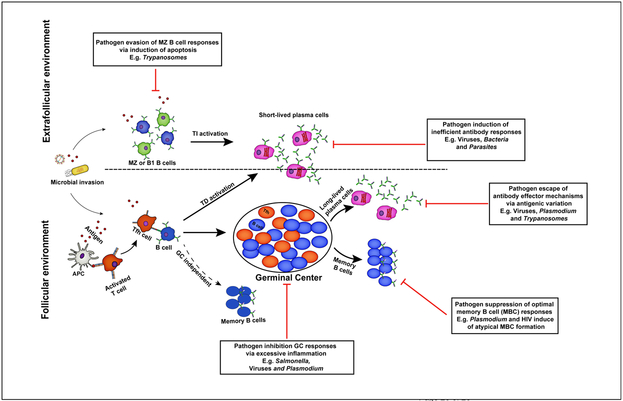
Figure 1. A schematic view of humoral immune responses to infection.
Extrafollicular and follicular antibody responses contribute to protection against invading microbial pathogens. B cells activated within the extrafollicular environment in the presence or absence of T cell help differentiate into short-lived antibody secreting cells that mediate early protection against infection. However, the formation of germinal center dependent or independent memory B cells and long-lived plasma cells in the B cell follicles facilitates complete resolution of primary infections and long-term protection against reinfection. For their survival, pathogens have evolved strategies that enable them to evade specific antibody-dependent killing mechanisms.