Fig. 1.
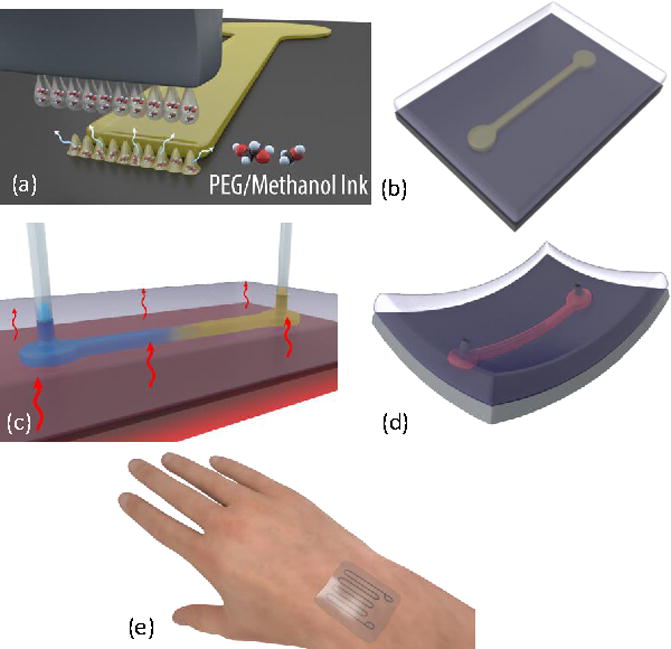
Illustration of the fabrication process. (a) Array of liquid PEG droplets are ejected from the inkjet printer and land on the target substrate to solidify and form the sacrificial layer of the microfluidic channel. (b) The structural layer is cast and cured to encapsulate the sacrificial layer. (c) Inlet and outlet ports are punched through the structural layer, PEG is heated above its phase change temperature, and IPA is injected from inlet to outlet to remove the PEG. (d) The flexible microfluidic channel is then filled with the target fluid. (e) Flexible and wearable liquid metal-based microfluidic strain sensor is an example application.
