Figure 3.
Neural Migration and Polarization
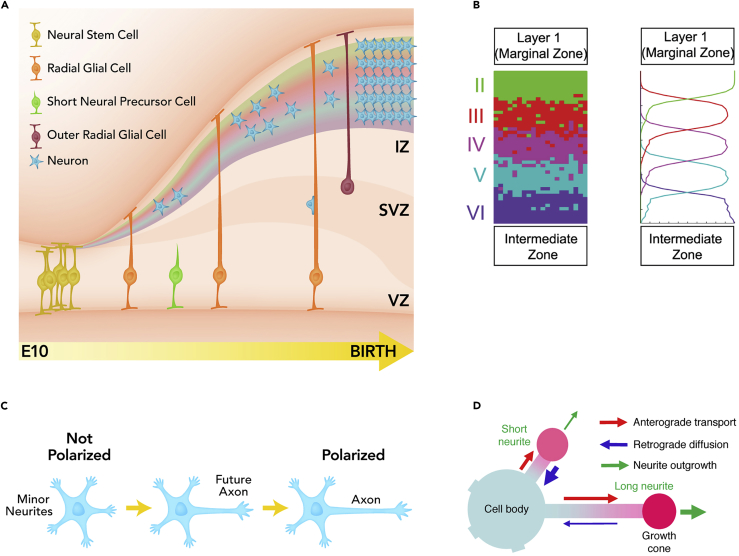
(A) In the developing cortex neurons migrate from their place of birth along radial glia, forming the layers of the cortex in an inside-out fashion. IZ, intermediate zone; VZ, ventricular zone; SVZ, subventricular zone. Time axis is for mouse (E10; embryonic day 10).
(B) Left: the results of a single simulation of cortical layer formation in the model of Caffrey et al. (2014). Right: average of 50 simulations, where the vertical axis is distance and horizontal axis is agent density. Reproduced from Caffrey et al. (2014).
(C) In general, several neurites sprout from a neuron, and then the longest becomes the axon, whereas the others become dendrites.
(D) The mechanism of polarization modeled in Toriyama et al. (2010): accumulation of shootin1 in the growth cone provides a positive feedback loop.