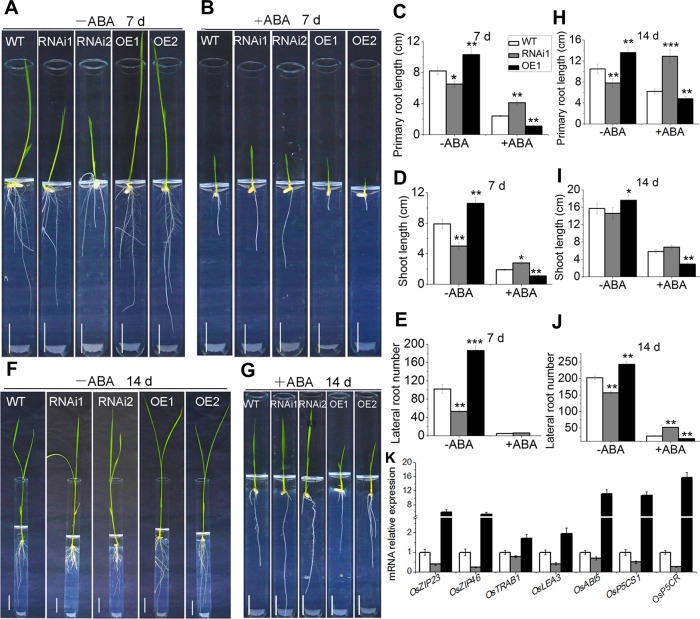
Fig 7. OsMADS25 increases the ABA sensitivity of rice.
A and B. Phenotype of wild type and OsMADS25 transgenic seedlings grown in standard 1/2 MS medium with or without 5 μM ABA for 7 days. Scale bars, 2 cm. C–E. Statistical analysis of primary root length, shoot length and lateral root number of wild type and OsMADS25 transgenic seedlings, respectively, in images A and B. F and G. Phenotype of wild type and OsMADS25 transgenic seedlings grown in standard 1/2 MS medium with or without 5 μM ABA for 14 days. Scale bars, 2 cm. H–J. Statistical analysis of primary root length, shoot length and lateral root number of wild type and OsMADS25 transgenic seedlings, respectively, in images F and G. K. Relative transcription levels of key genes involved in ABA–dependent stress response pathway in 2–week–old wild type and OsMADS25 transgenic seedlings. To investigate the effect of ABA on rice growth, germinated seeds were grown in standard 1/2 MS medium with or without 5 μM ABA. WT, wild type. RNAi1 and RNAi2, OsMADS25–RNAi transgenic lines. OE1 and OE2, OsMADS25 overexpression transgenic lines. Three independent experiments were performed, and data are means ± SE (n = 15). The statistical significance of the measurements using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was determined using Student’s t–test. Asterisks indicate the significant difference between OsMADS25 transgenic lines and WT plants (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 or ***P < 0.001).