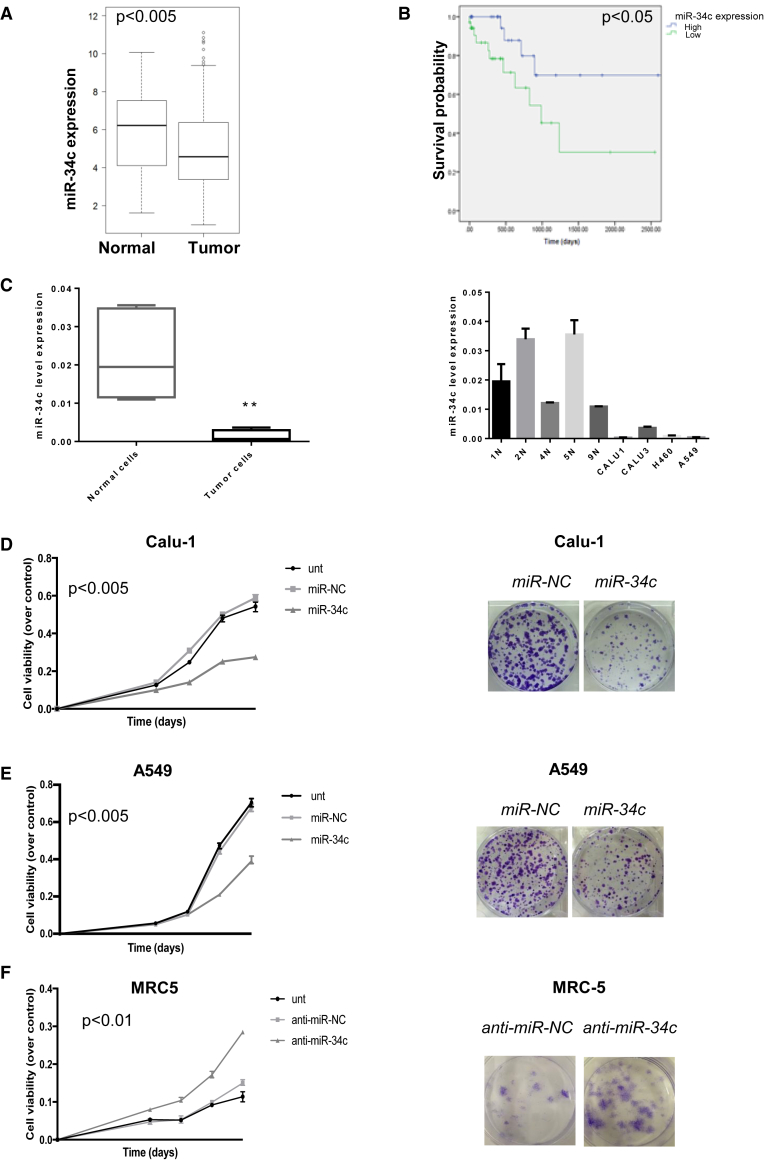
Figure 1.
miR-34c in Human NSCLC Tissues
(A) Significant increase of miR-34c expression was identified in normal lung versus adenocarcinoma tissues collected from the TCGA database (t test, p < 0,005). (B) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for TCGA NSCLC patients with high and low miR-34c expression. The survival data were compared using the log rank test (p < 0.05). (C) Expression of miR-34c-3p in several tumor cell lines (Calu-1, A549, Calu-3, and H460) was lower compared to normal primary lung cell lines (1N, 2N, 4N, 5N, and 9N). MiR-34c-3p expression was assessed by real-time PCR. The transcript level was normalized over RNU6B expression, used as an internal reference. Bar graphs indicate mean value ± SD and the p value is calculated by using Student’s t test, **p < 0.01. (D) Calu-1 and (E) A549 cells were transfected with control miR (miR-NC) or miR-34c-3p, and cell proliferation was analyzed by MTS assay 3, 4, 5, and 6 days after transfection (left). Bar graphs indicate mean value ± SD and the p value is calculated by using Student’s t test, p < 0.005 compared to the non-transfected cells (Unt); Calu-1 and A549 cells were transfected with miR-NC or miR-34c-3p. Overexpression of miR-34c-3p significantly inhibited colony formation (right). (F) MTS assay determined cell proliferation in MRC-5 cells following downregulation of miR-34c-3p (left). Bar graphs indicate mean value ± SD and the p value is calculated by using Student’s t test, p < 0.01, compared to non-transfected cells (Unt); colony-formation assay determined the effect of downregulated miR-34c-3p on colony-forming ability in MRC-5 cell lines (right). Downregulation of miR-34c-3p in normal lung cells promotes cell proliferation and allows colony formation.