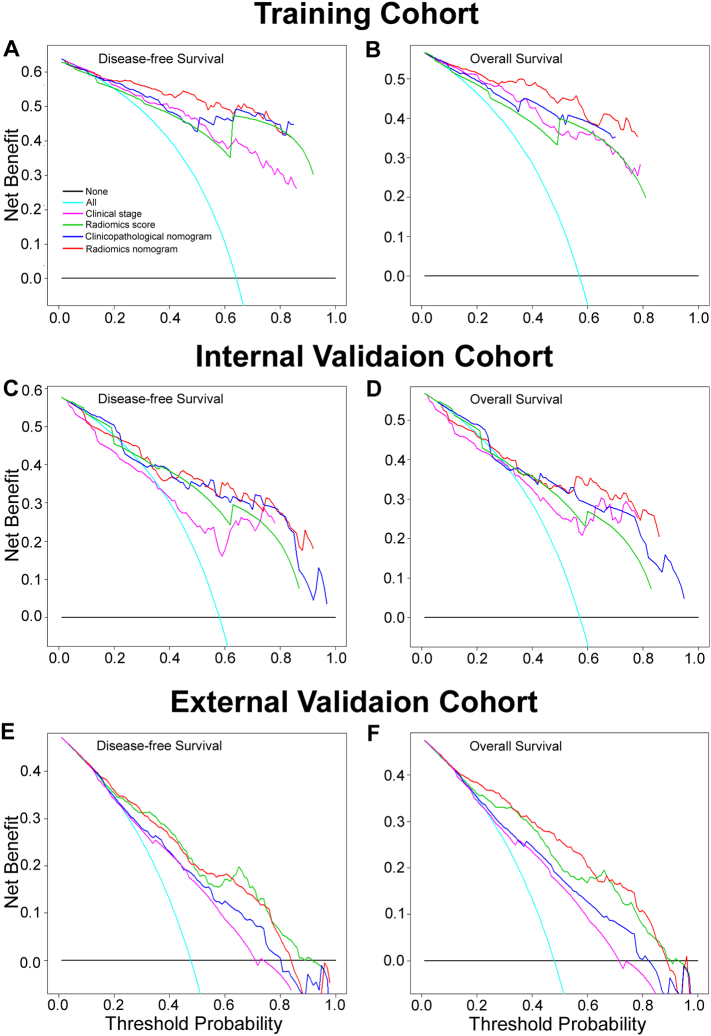
Fig. 4.
Decision curve analysis for each model in the training and validation cohorts. The y-axis measures the net benefit. The net benefit was calculated by summing the benefits (true positive results) and subtracting the harms (false positive results), weighting the latter by a factor related to the relative harm of an undetected cancer compared with the harm of unnecessary treatment. The radiomics model had the highest net benefit compared to both the other models and simple strategies such as follow-up of all patients (green line) or no patients (horizontal black line) across the full range of threshold probabilities at which a patient would choose to undergo imaging follow-up.