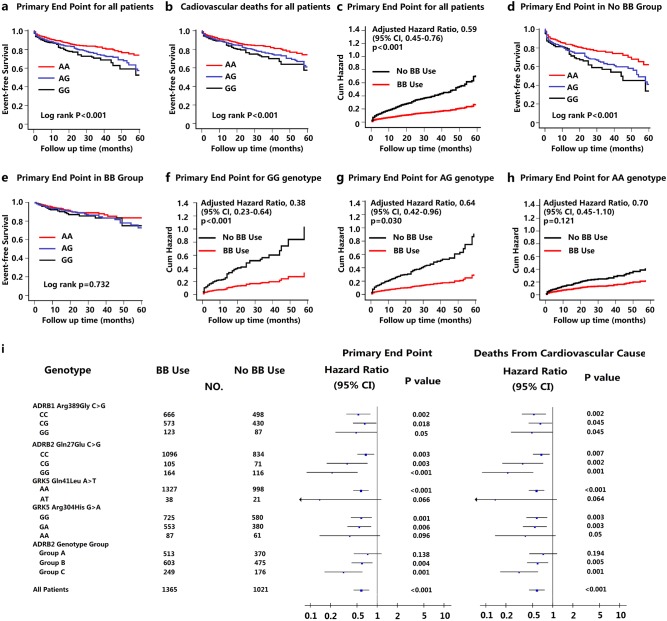
Fig. 2. Clinical outcomes of heart failure patients and responses to β-blockers.
a Kaplan−Meier curves of the primary composite end point showing that the clinical outcomes significantly varied among the groups of patients with the different genotypes at ADRB2 amino acid site 16 (P < 0.001 by stratified log-rank test). G allele carriers had worse outcomes compared with those who were homozygous for AA (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.21−1.83; P < 0.001 for AG/GG versus AA). b Kaplan−Meier curves of cardiac death demonstrating a similar association with the genotype of this SNP to the primary end point. The G allele was associated with increased risk of this individual end point (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.16−1.79; P = 0.001 for AG/GG versus AA). c Among the entire cohort, β-blocker treatment was significantly associated with a reduced risk of the composite end point of cardiovascular death or heart transplantation (adjusted HR, 0.59; 95% CI, 0.45−0.76; P < 0.001). d For the patients who were not using BB therapy, Kaplan−Meier curves for the primary end point showed that the ADRB2 Arg16Gly genotype was significantly associated with reduced transplantation-free survival (P < 0.001 by log-rank test). e For the patients who received BB therapy for ≥6 months during the study, the genotype-based heterogeneity was not significantly different (log-rank P = 0.732). The probability of the composite primary end point (cardiovascular death or heart transplantation) was significantly decreased with β-blocker use among patients with f the GG genotype (adjusted HR, 0.38; 95% CI, 0.23−0.64; P < 0.001) and g the AG genotype (adjusted HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.42−0.96; P = 0.03), but not with h the AA genotype (adjusted HR, 0.70; 95% CI, 0.45−1.10, P = 0.121). The extent of benefit of β-blocker treatment seemed to be G allele-dose-dependent. i Adjusted HRs are shown for the composite primary end point and for the individual end point of death from a cardiovascular cause for patients in the five specified missense variant subgroups. To assess the impact of both of the ADRB2 missense polymorphisms together, we also examined outcomes for patients stratified according to three genotype combinations: homozygous for both Arg16 and Gln27 (that is, patients with only the major alleles; designated as group A), homozygous for both Gly16 and Glu27 (that is, patients with only the minor alleles; designated as group C), and other genotypes (designated as group B). The blue squares and black lines represent the HRs and 95% CIs. The size of the blue square corresponds to the number of patients in the subgroup. The P values were calculated by Cox proportional hazard models, with a two-sided P value of 0.05 indicating statistical significance after adjustment for the clinical covariants, with an unbalanced distribution between groups. BB β-blocker, CI confidence interval, HR hazard ratio