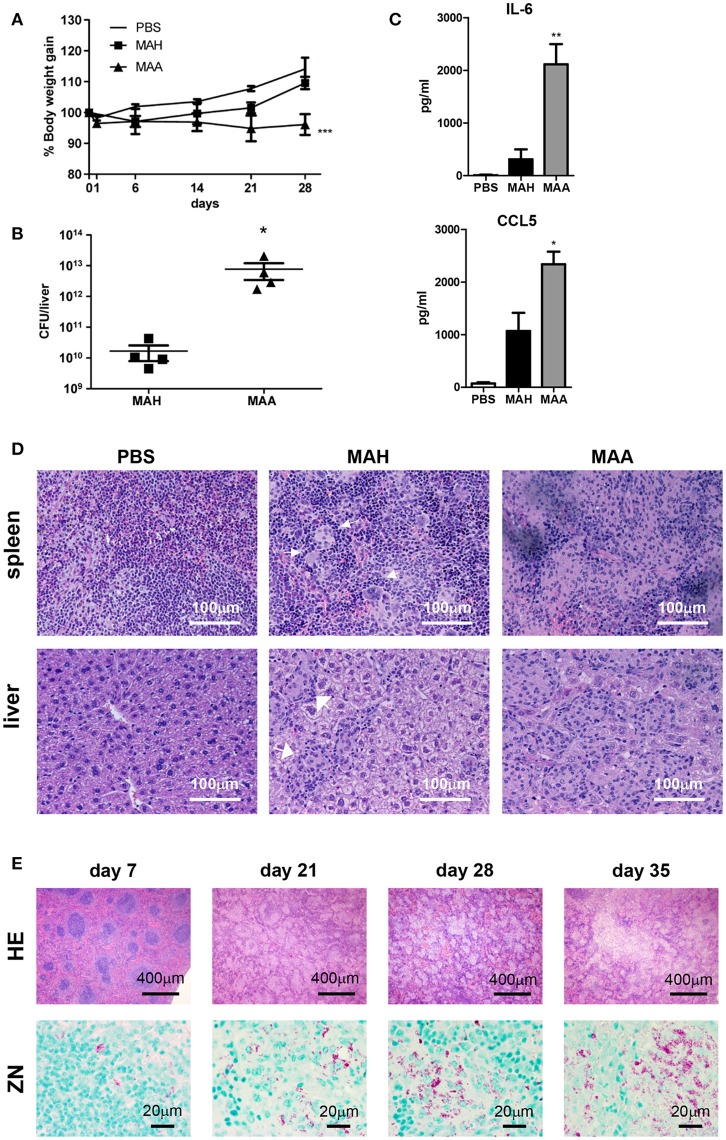
Figure 1.
Chronic MAA infection induces accumulation of mycobacteria harboring histiocytic cells in murine spleen. (A) Body weight of female C57BL/6J mice infected with MAA or MAH (Mean+SEM, ***p < 0.001: two way ANOVA). (B) Bacterial load in livers of mice infected with MAA or MAH 5 weeks post infection (p.i.). Colony forming units (CFU) were determined by plating of liver lysates. (C) Serum cytokine levels 5 weeks p.i. as determined by ELISA. Statistics shown is difference between two strains. (D) Hematoxylin/Eosin (HE) staining of spleen and liver of mice infected with MAA or MAH for five weeks. Arrows indicate well defined granuloma surrounded by rim of lymphocytes. (E) HE and Ziehl Neelsen (ZN) staining of MAA infected mice spleen at day 7 until day 35. (A,B,D,E: 3-5 mice per group. A,D: representative of least two independent experiments. C: 6 mice for MAA and MAH groups and 3 mice for PBS control) (Mean+SEM, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005: One way ANOVA).