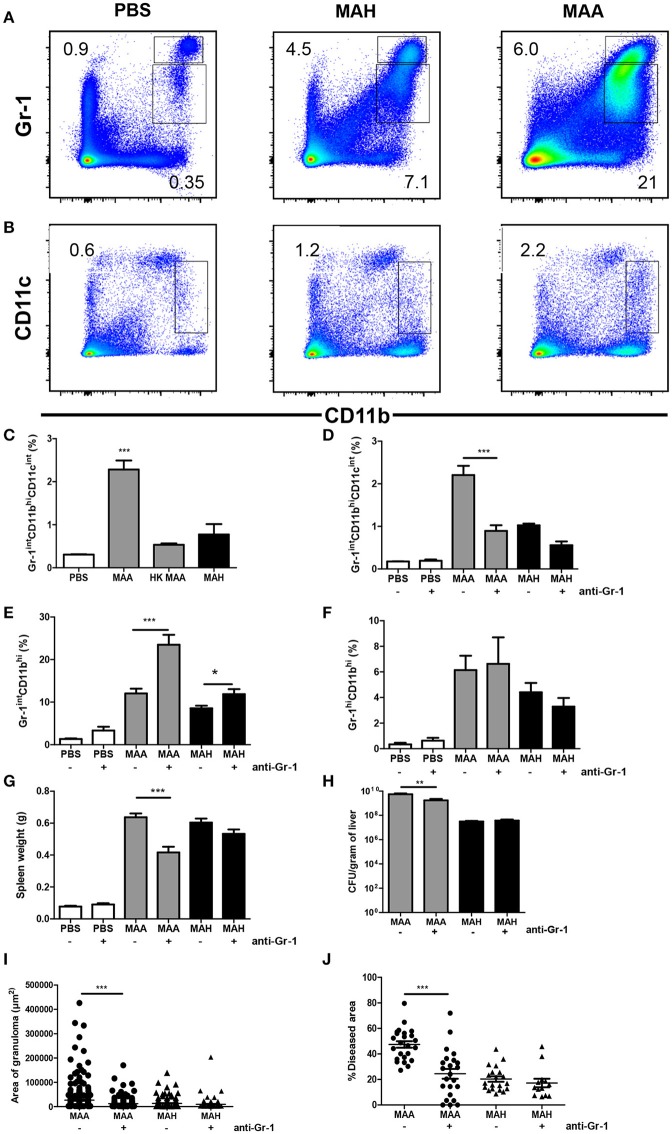
Figure 2.
Chronic MAA infection induces accumulation of disease aggravating Gr-1intCD11bhiCD11cint cells in murine spleen. (A,B) Flow cytometry of spleen cell suspensions from MAA or MAH-infected mice showing the percentage of Gr-1hi/int and CD11bhi splenic myeloid cells. (C) Percentage of spleen CD11bhiCD11cint cells of MAA, HK (heat killed) MAA or MAH-infected mice as determined by flow cytometry (***p < 0.001: one way ANOVA). (D–J) Mice infected with MAA or MAH were treated with PBS or an anti-Gr-1 antibody according to the schedule described in Material and Methods. Percentage of splenic Gr-1intCD11bhiCD11cint cells (D), Gr-1intCD11bhi (E), and Gr-1hi CD11bhi (F). (G) Spleen weights. (H) Bacterial load from liver homogenate. (I,J) Morphometry of liver pathology shown by the area of granuloma and the percentage of diseased area per 100x magnification of liver section (at least five fields were analyzed per section). Analysis 3.1 software package (Soft Imaging System) was used for quantification. Figure (A–C) shows representative of at least two experiments (3-5 mice per group). (D–J) represents two independent experiments of 3-5 mice per group. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001: t-test).