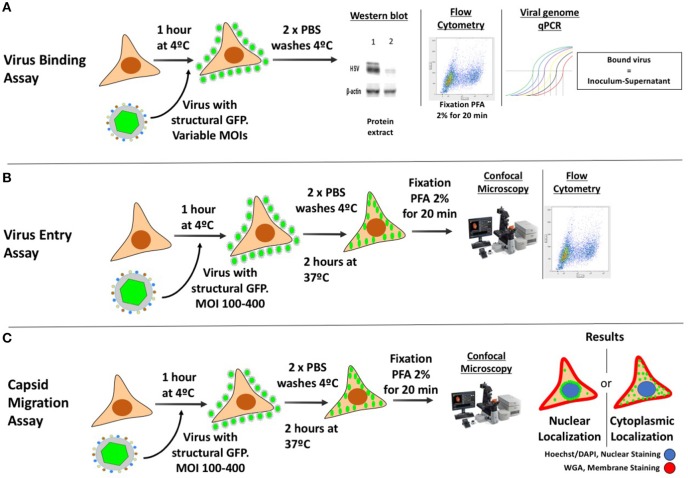
Figure 4.
Methodologies for assessing binding, entry and viral capsid transport to the nucleus in HSV-infected cells. (A) Protocol for assessing the binding of HSV to the cell surface. The culture must be brought to 4°C and then inoculated with virus (with or without a structural reporter such as GFP) at different MOIs. The plate is incubated at 4°C for 4 h to allow the virus to adsorb to the cells without entering. Afterwards, 2 cold PBS washes are performed in order to wash the unbound virus and samples are then analyzed either by Western blot, blotting against viral structural proteins, by flow cytometry analyzing GFP (requires PFA fixation), or by qPCR quantifying viral genome (bound virus is equal to the difference between the inoculum titter and virus detected in the supernatant with unbound virus). (B) Protocol for assessing the entry of viral capsids into the cytoplasm. The culture is brought to 4°C and then inoculated with virus (with a structural reporter such as GFP). Afterwards, PBS washes will remove the unbound virus and the plate is then incubated at 37°C for 2 h to allow the coordinated entry of the viral capsids into the cell. Then, the cells are trypsinized, fixed with PFA and analyzed either by confocal microscopy or flow cytometry to determine the amount of GFP associated to the cells. (C) Protocol to assess viral capsid migration to the nucleus. The procedure is similar to that for assessing the entry of viral capsids into the cytoplasm, except that the sample are analyzed by confocal microscopy after staining the nucleus and cell membrane with dyes, such as DAPI and WGA, respectively.