Abstract
AIM
To determine factors correlated with postoperative radial shortening in patients with distal radius fractures treated with volar locking distal radius plates.
METHODS
A total of 250 patients with a distal radius fracture stabilised with volar locking plates between January 2010 and December 2014 were included in a multicentre retrospective cohort study. We measured the distance of the distal locking screws to the joint line immediately postoperatively and then measured radial shortening after six to eight weeks using the change in ulnar variance.
RESULTS
Multivariate linear regression analysis showed that there was a significant linear association between the distance of the screws from the joint line and radial shortening. No other patient, injury, or treatment-related characteristic significantly influenced radial shortening in multivariate analysis.
CONCLUSION
Distal locking screws should be placed as close as possible to the subchondral joint line to prevent postoperative loss of reduction.
Keywords: Loss of reduction, Volar locking distal radius plate, Distal radius fracture, Screw placement, Cohort study
Core tip: The aim of this study was to determine risk factors for postoperative radial shortening in patients with distal radius fractures treated with volar locking distal radius plates. Retrospective analysis of 250 X-rays and clinical data determined immediate post-operative distance of the distal locking screws from the joint line and degree of radial shortening 6-8 wk post-operatively. Radial shortening was significantly and linearly correlated with increased distance of locking screws from the joint line. No other factor analysed in the study was significant. We recommend subchondral placement of distal locking screws in order to maintain reduction postoperatively.
INTRODUCTION
Distal radius fractures are the most common type of fracture of the human skeleton[1-3]. The treatment of distal radius fractures has undergone a paradigm shift in the last fifteen years, and fixation with volar locking distal radius plates (VLDRP) has become the operative standard[1,4-6], despite lack of clear evidence of benefit over any other treatment modality[7-10]. VLDRP dohave a distinct advantage over any other treatment method as they allow immediate postoperative mobilisation[11], provided optimal placement of the plate/screw construct is achievedintraoperatively. Biomechanical studies[12-15] and clinical observations[16-20] indicate the best placement of the distal locking screws is as close as possible to the subchondral area of the joint to prevent loss of postoperative reduction. The aim of our study was to evaluate the relationship between distal screw placement and postoperative radial shortening in a large consecutive cohort of dorsally displaced distal radius fractures plated with VLDRP. Our hypothesis was that loss of reduction after plating is related to the distance the distal locking screws are placed from the subchondral joint line.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
We performed a longitudinal multicentre retrospective cohort study including patients who underwent VLDRP fixation of a dorsally displaced distal radius fracture. X-rays and charts of patients undergoing surgery at two Australian regional hospitals between January 2010 and December 2014 were assessed (Ethics approval HREC/15/QTHS/10).
Participants
Consecutive patients with dorsally displaced distal radius fractures managed with VLDRP were included. Ten patients had bilateral wrists fractures - one wrist was randomly chosen for inclusion for each. Patients with Kirschner wires in addition to VLDRP were excluded. Patients without documented follow-up were excluded.
Data collection
Data were collected from pre-, intra- and post-operative standard anterior-posterior and lateral X-rays. Images were measured using digital radiology software (AGFAR HealthCare Impax 6, Belgium). Fracture classification, angle and distance measurements were assessed by the second author. The first author validated all measurements. If there was more than ten percent difference between measurements, a board-certified radiologist repeated the measurement.
We recorded anterior-posterior radial inclination (degrees), ulnar variance (radial length; millimetre) and lateral volar tilt (degrees). The distance of distal locking screws from the deepest point of the subchondral joint line was measured on intra-operative lateral tilted images. The subchondral line was defined as the dense area, which denotes the articular surface. The optimal most distal screw placement was defined as the area just proximal to the subchondral line without breaching it. Radial shortening as a parameter of reduction loss was determined as the change in ulnar variance between six and eight weeks post-operatively (Figure 1). Pre-operative images were used for AO fracture classification[21]. Patient age, gender, mechanism of injury (high or low energy), likelihood of osteoporosis and comorbidities [American Society of Anaesthesiologists (ASA)] classification[22] and postoperative immobilisation were sourced from patient charts.
Figure 1.
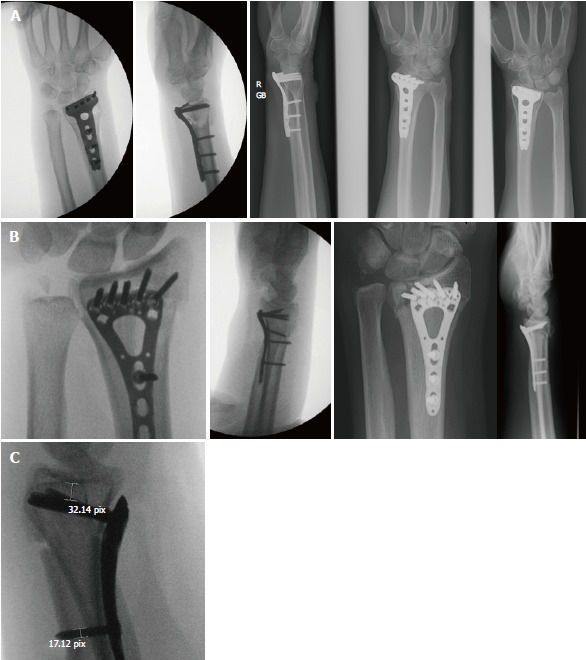
Examples of distal screw placement. A: Intraoperative image shows that screws are placed immediate to the subchondral joint line. Postoperative image does not show any loss of reduction; B: Placing the screws at a distance from the subchondral joint line causes postoperative loss of radial length; C: Intraoperative measurement. As the diameter of the screws was known, the distance of the screws was able to be calculated.
Statistical methods
A pilot study including 31 cases was used to calculate the sample size, as variability was unknown. Accounting for eight potential independent characteristics, the R2 was 0.28 and Cohen’s f2 effect size was 0.39, indicating that 50 fractures would be required to have power in excess of 80% and a level of significance of 0.05.
Bivariate statistical comparisons used unpaired t-tests, one-way Analysis of Variance, Pearson’s correlation coefficient and Spearman rank correlation coefficient (r) to identify factors influencing postoperative radial shortening. Factors included in the analysis were age, sex, mechanism of injury, affected wrist (left or right), AO classification, time between injury and surgery, VLDRP characteristics including number of distal screw rows, total number of distal screws, distance of the distal locking screws from the subchondral joint line, and whether the wrist was immobilised postoperatively.
Multiple linear regression analysis identified independent factors associated with postoperative radial shortening. A Kolmogorov-Smirnov test verified that the outcome measure was normally distributed (P = 0.240). After identifying independent significant factors, the remaining variables were investigated for potential confounding effects. Statistical analysis was conducted using Stata release 12 (StataCorp LP, Texas, United States) and SPSS for Windows, Version 22 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, United States). Statistical analysis was performed by one of the authors, PB, a biostatistician (www.tropicalhealthsolutions.com/petrabuttner).
RESULTS
For detailed results, see Table 1. A total of 250 patients were included from Hospital 1 (n = 141; 56.4%) and Hospital 2 (n = 109; 43.6%). In all, 186 plates (74.4%) had two distal screw rows. Plates used were MedartisR Aptus TriMedR volar fixed angle plates or SynthesR VA. Sixty-four plates (25.6%) had one distal screw row (SynthesR volar locking buttress plate 2.4 mm). There was disagreement regarding two fractures. The board-certified radiologist agreed with the first author’s measurements.
Table 1.
Description of characteristics of 2501 patients with 250 dorsally displaced distal radius fractures managed with volar locking distal radius plates documented between 2010 and 2014 at two regional hospitals in north Queensland, Australia
| Characteristic | Descriptive statistics | |
| Patient | ||
| Mean age (SD)2; range (yr) | 49.1 (16.7); range 16 to 88 | |
| Female | 63.2% (n = 158) | |
| Comorbidities (ASA classification)4 (n = 67) | ||
| ASA 1 | 34.3% (n = 23) | |
| ASA 2 | 59.7% (n = 40) | |
| ASA 3 | 6.0% (n = 4) | |
| With Osteoporosis5 (n = 164) | 51.2% (n = 84) | |
| Injury | ||
| High energy mechanism (n = 160) | 46.9% (n = 75) | |
| Right wrist fractured (n = 248) | 42.3% (n = 105) | |
| AO fracture classification6 | ||
| A2 | 14.8% (n = 37) | |
| A3 | 14.8% (n = 37) | |
| B1 | 2.8% (n = 7) | |
| B2 | 4.0% (n = 10) | |
| C1 | 12% (n = 30) | |
| C2 | 34.4% (n = 86) | |
| C3 | 17.2% (n = 43) | |
| Median number of days from injury to surgery (IQR)3; range (n = 164) | 6 (1, 16); range 0 to 71 | |
| Treatment | ||
| With 1 distal screw row | 25.6% (n = 64) | |
| Median number of distal screws (IQR); range | 4 (4, 5); range 3 to 8 | |
| Median number of distal screws in first row (IQR); range | 4 (4, 4.25); range 2 to 5 | |
| Median number of distal screws in second row (IQR); range | 2 (1, 3); range 1 to 4 | |
| With 4 or less distal screws in most distal row | 75.2% (n = 188) | |
| Median distance from joint line (IQR); range (mm) | 3.1 (2.1, 4.1) range 0 to 11 | |
| Postoperative immobilisation7 (n = 224) | 87.9% (n = 197) | |
| Outcome measure | ||
| Mean radial shortening (SD); range (mm) | 1.9 (1.3); range 0 to 5.6 |
1n = 250 unless otherwise stated;
SD = standard deviation;
IQR = inter-quartile range;
ASA classification;
osteoporosis was classified as “yes” when chart information was available and in females > 60 years of age with low energy trauma;
AO fracture classification. B3 fractures were excluded from the analysis as they are volar shear fractures and follow different biomechanical principles;
postoperative immobilisation was either by cast (n = 128) or by thermoplastic splint (n = 77). Duration of immobilisation varied between two and four weeks. ASA: American Society of Anaesthesiologists.
Factors influencing postoperative loss of radial length
Bivariate analysis showed that the mean postoperative loss of radial length was higher for AO type A and C fractures (mean: 2.0, SD: 1.3) and less for AO type B fractures (mean: 1.2, SD: 0.8) (P = 0.033). There was a weak negative correlation between number of distal screws in the most distal screw row and radial shortening (r = -0.13; P = 0.042). There was a strong positive correlation between the distance of the distal locking screws from the subchondral joint line and postoperative loss of radial length (r = 0.61; P < 0.001). None of the other factors (see Table 1 for complete list of factors investigated) was statistically significantly related to radial shortening.
Multiple linear regression analysis showed that the distance of distal locking screws from the subchondral joint line was the only independent factor statistically significantly associated with radial shortening (coefficient 0.379, 95%CI: 0.304-0.454; P < 0.001). No confounding variables were identified. The linear regression line was estimated as radial shortening = 0.7 mm + 0.4 × the distance from joint line (mm) (P < 0.001) (Figure 2). Volar tilt and the change of radial inclination did not change in the postoperative period and were not analysed.
Figure 2.
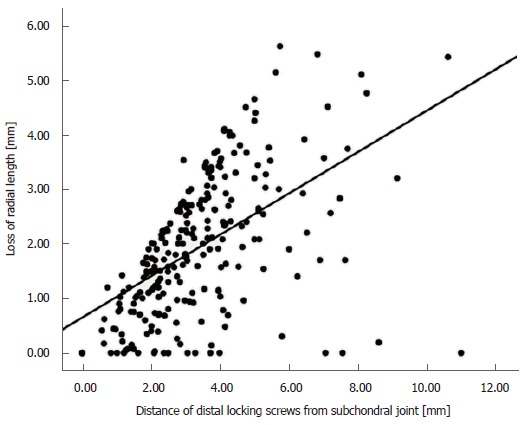
Correlation of loss of radial length (mm) and distance of distal locking screws from the subchondral joint line (mm) of 250 patients with dorsally displaced distal radius fractures managed with volar locking distal radius plates. The linear regression line was: radial shortening = 0.7 mm + 0.38 × distance from joint line (mm) (P < 0.001).
DISCUSSION
The results of our study show that placement of distal locking screws is the only independent factor significantly associated with postoperative loss of radial length. Postoperative shortening is proportional to the distance of the distal locking screws from the subchondral joint line. The soft metaphyseal bone of the distal radius fragment cannot support the distal locking screws. The distal fragment will settle and “sink through” until the screws are in the hard subchondral area just proximal of the joint. Placing the distal screws as close as possible to the joint line prevents loss of postoperative displacement, independent of age, gender, osteoporosis and immobilisation.
Our study expands on a previous biomechanical study and clinical observations[13,16,18-20,23]. Drobetz et al[13] found a statistically significant linear association between loss of radial length and distance of the distal locking screws from the subchondral joint line. They also noted that the distal fragment “sank straight” without loss of volar tilt and radial inclination, an observation which was confirmed in our study population. The current study translates these findings into a clinical setting. The clinical relevance of our results is that “distance from the joint line” is a modifiable risk factor. Postoperative loss of reduction therefore seems to be mainly surgeon-dependent.
Our findings also indicate that loss of reduction is independent of the number of distal screws, provided there are at least four distal screws with a minimum diameter of 2.3 mm each (the type of plates we assessed). A second distal screw row does not have any positive influence on postoperative radial shortening. This is in accordance with biomechanical studies[12,14,24-26].
The clinical and biomechanical advantage of a second distal screw row eludes the authors. According to operation manuals of various implant companies, two screw rows either provide a “three-dimensional scaffold for optimal subchondral support” or “intra- operative solutions for different fracture requirements”, “intra- operative fine contouring of the radial and intermediate columns”, “optional three point support for more stability” or “creation of a scaffold to allow two plane fixation of distal metaphyseal fragments”. Katsunori[27] and Kawasaki[28] have reported on a double tiered subchondral support (DSS) procedure in which the screws of the second distal screw row are placed long, so that their tips support the dorsal part of the distal radius. Their findings showed less loss of radial length and volar tilt when using the DSS construct compared to placing screws only in the distal row. Other studies[29-31], found that a screw length of 75% of the sagittal distal radius diameter is sufficient to withstand postoperative displacement loads, which somewhat contradicts Katsunori’s and Kawasaki’s findings.
Our findings further demonstrated that immediate postoperative mobilisation did not lead to increased loss of radial length and consequently that postoperative immobilisation did not prevent loss of radial length when the distal screws were placed into the soft metaphyseal bone. Only 12.4% of fractures underwent early mobilisation, the remainder being immobilised by splint or a cast (Table 1). We speculate that this is an ingrained surgeon practice rather than behaviour based on evidence.
Previous studies have identified osteoporosis as a risk factor for radial shortening after plating with VLDRP[32], and it has been postulated that this is due to poor bone quality. This finding was not supported in our study. Age could be considered to be a surrogate marker for osteoporosis, but this was also not shown to be associated with radial shortening. Our findings highlight that volar locking plates are suitable and effective in this subset of patients. However, it was difficult to diagnose osteoporosis, as chart information was limited and it was not feasible to retrospectively perform bone mineral density measurements on all patients. This is a weakness of our study. Osteoporosis was classified as “yes” when chart information was available and in females > 60 years of age with low energy trauma[5].
There were other limitations in our study. We did not evaluate clinical outcomes in our patient population, but this was not within the scope of our study. However, a recent prospective cohort study[3] showed that radial shortening of more than 2 mm was associated with worse patient-reported outcome scores. These findings indirectly indicate the possible clinical relevance of our paper. There are also several other studies which show that “function follows form”, i.e., that good clinical outcomes are associated with healing in near anatomical position[33-35].
The study strengths are adequate sample size and the large number of variables analysed. In addition to measurements performed by two authors independently, the same X-ray departments, machines and viewing program counteracted possible bias. In summary, the distance of the distal screws in relation of the subchondral joint line is the only independent variable associated with postoperative loss of reduction. The loss of reduction is independent of age, gender, osteoporosis, ASA status, fracture severity, immobilisation, number of distal screws and the presence or absence of a second distal screw row. Surgeons using VLDRPs for fixation of distal radius fractures should attempt to place the distal screws as close as possible to the subchondral joint line.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Treatment of distal radius fractures with volar locking distal radius plates (VLDRP) has become the most popular treatment method in the last ten years. Biomechanical and clinical studies indicate that distal screw placement as close as possible to the articular surface is crucial to prevent loss of postoperative reduction. To our knowledge, no study has been undertaken that proves or disproves this observation.
Research motivation
Our hypothesis was that postoperative loss of reduction will occur when the distal VLDRP screws are placed more proximal, in the distal radius fragment metaphysis, rather than in the subchondral hard area close to the articular surface. We also hypothesized that the loss of postoperative reduction is directly related to the distance of the distal screws from the articular surface. We undertook a retrospective study analyzing pre- and postoperative X-rays of 250 consecutive distal radius fractures treated with VLDRP.
Research objectives
Objectives of the study were to determine factors correlated with postoperative radial shortening in patients with distal radius fractures treated with VLDRPs.
Research methods
This is a longitudinal multicentre retrospective cohort study including patients who underwent VLDRP fixation of a dorsally displaced distal radius fracture in which 250 wrist fractures were included. Collected parameters were fracture classification, radial length, radial inclination, volar inclination of the joint surface, patient age, gender, mechanism of injury, likelihood of osteoporosis, comorbidities and postoperative immobilisation. The distance of the distal locking screws to the articular surface was measured on intraoperative lateral tilted X-rays. Radial shortening as a parameter of loss of reduction was measured on X-rays obtained at a minimum of six weeks postoperatively. Bivariate statistical comparisons were used to identify factors influencing postoperative radial shortening. Multiple linear regression analysis then identified independent factors associated with postoperative radial shortening.
Research results
Multiple linear regression analysis showed that the distance of the distal locking screws from the articular surface was the only independent factor associated with radial shortening. The relationship between shortening and distance of the distal screws to the articular surface was linear and statistically highly significant.
Research conclusions
Our study showed that in order to prevent postoperative loss of reduction in fractures plated with VLDRP, it is crucial that the distal screws are placed as close as possible to the articular surface. The study further indicated that loss of postoperative reduction is not associated with any other parameters measured - age, gender, osteoporosis, ASA status, fracture severity, immobilisation, number of distal screws and the presence or absence of a second distal screw row.
Research perspectives
A major advantage of treating distal radius fractures with VLDRP is that patients can be treated without postoperative immobilisation. VLDRP are in fact the only treatment modality that allows for immediate postoperative use of the wrist. Based on the findings of our study and provided that the distal screws are placed as close as possible to the articular surface, immediate postoperative mobilization should be possible without loss of reduction. Future studies should attempt to verify our findings in a clinical setting.
Footnotes
Institutional review board statement: This study was reviewed and approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of Queensland Health, Australia.
Informed consent statement: Patients were not required to give informed consent to the study because the analysis used anonymous clinical data that were obtained after each patient agreed to treatment by written consent.
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declare no conflicts-of-interest related to this article.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Peer-review started: April 30, 2018
First decision: May 16, 2018
Article in press: August 21, 2018
Specialty type: Orthopedics
Country of origin: Australia
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P- Reviewer: Liu JY, Emara KM S- Editor: Dou Y L- Editor: Filipodia E- Editor: Song H
Contributor Information
Herwig Drobetz, James Cook University School of Medicine and Dentistry, Mackay 4740, Queensland, Australia; Mackay Institute of Research and Innovation, Mackay Hospital, Mackay 4740, Queensland, Australia; Mackay Base Hospital Orthopaedic Department, Mackay Hospital, Mackay 4740, Queensland, Australia. herwig.dro@gmail.com.
Alyce Black, James Cook University School of Medicine and Dentistry, Mackay 4740, Queensland, Australia.
Jonathan Davies, Mackay Institute of Research and Innovation, Mackay Hospital, Mackay 4740, Queensland, Australia; Mackay Base Hospital Orthopaedic Department, Mackay Hospital, Mackay 4740, Queensland, Australia.
Petra Buttner, Tropical Health Solutions PTY Ltd, Townsville 4810, Queensland, Australia; Centre for Chronic Disease Prevention, James Cook University, Cairns 4878, Queensland, Australia.
Clare Heal, James Cook University School of Medicine and Dentistry, Mackay 4740, Queensland, Australia; Mackay Institute of Research and Innovation, Mackay Hospital, Mackay 4740, Queensland, Australia; Anton Breinl Research Centre for Health Systems Strengthening, Townsville 4810, Queensland, Australia.
References
- 1.Chen NC, Jupiter JB. Management of distal radial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89:2051–2062. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.G.00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gehrmann SV, Windolf J, Kaufmann RA. Distal radius fracture management in elderly patients: a literature review. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33:421–429. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2007.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Larouche J, Pike J, Slobogean GP, Guy P, Broekhuyse H, O’Brien P, Lefaivre KA. Determinants of Functional Outcome in Distal Radius Fractures in High-Functioning Patients Older Than 55 Years. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30:445–449. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mattila VM, Huttunen TT, Sillanpää P, Niemi S, Pihlajamäki H, Kannus P. Significant change in the surgical treatment of distal radius fractures: a nationwide study between 1998 and 2008 in Finland. J Trauma. 2011;71:939–942; discussion 942-943. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3182231af9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bartl C, Stengel D, Gülke J, Gebhard F. Clinical results following conservative and surgical treatment of osteoporotic distal radius fractures in the elderly: Overview of best available evidence. Unfallchirurg. 2016;119:723–731. doi: 10.1007/s00113-016-0216-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mellstrand-Navarro C, Pettersson HJ, Tornqvist H, Ponzer S. The operative treatment of fractures of the distal radius is increasing: results from a nationwide Swedish study. Bone Joint J. 2014;96-B:963–969. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.96B7.33149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Costa ML, Achten J, Parsons NR, Rangan A, Griffin D, Tubeuf S, Lamb SE; DRAFFT Study Group. Percutaneous fixation with Kirschner wires versus volar locking plate fixation in adults with dorsally displaced fracture of distal radius: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2014;349:g4807. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g4807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Arora R, Lutz M, Deml C, Krappinger D, Haug L, Gabl M. A prospective randomized trial comparing nonoperative treatment with volar locking plate fixation for displaced and unstable distal radial fractures in patients sixty-five years of age and older. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93:2146–2153. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.J.01597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zong SL, Kan SL, Su LX, Wang B. Meta-analysis for dorsally displaced distal radius fracture fixation: volar locking plate versus percutaneous Kirschner wires. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:108. doi: 10.1186/s13018-015-0252-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mellstrand Navarro C, Ahrengart L, Törnqvist H, Ponzer S. Volar Locking Plate or External Fixation With Optional Addition of K-Wires for Dorsally Displaced Distal Radius Fractures: A Randomized Controlled Study. J Orthop Trauma. 2016;30:217–224. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Drobetz H, Koval L, Weninger P, Luscombe R, Jeffries P, Ehrendorfer S, Heal C. Volar locking distal radius plates show better short-term results than other treatment options: A prospective randomised controlled trial. World J Orthop. 2016;7:687–694. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i10.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Drobetz H, Weninger P, Grant C, Heal C, Muller R, Schuetz M, Pham M, Steck R. More is not necessarily better. A biomechanical study on distal screw numbers in volar locking distal radius plates. Injury. 2013;44:535–539. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2012.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Drobetz H, Bryant AL, Pokorny T, Spitaler R, Leixnering M, Jupiter JB. Volar fixed-angle plating of distal radius extension fractures: influence of plate position on secondary loss of reduction--a biomechanic study in a cadaveric model. J Hand Surg Am. 2006;31:615–622. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2006.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Weninger P, Dall’Ara E, Drobetz H, Nemec W, Figl M, Redl H, Hertz H, Zysset P. Multidirectional volar fixed-angle plating using cancellous locking screws for distal radius fractures--evaluation of three screw configurations in an extra-articular fracture model. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2011;123:4–10. doi: 10.1007/s00508-010-1488-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hart A, Collins M, Chhatwal D, Steffen T, Harvey EJ, Martineau PA. Can the use of variable-angle volar locking plates compensate for suboptimal plate positioning in unstable distal radius fractures? A biomechanical study. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29:e1–e6. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Osada D, Kamei S, Masuzaki K, Takai M, Kameda M, Tamai K. Prospective study of distal radius fractures treated with a volar locking plate system. J Hand Surg Am. 2008;33:691–700. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2008.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wich M, Sixto R, Spranger N. Design of distal radius volar locking plates: Anatomical, surgical and biomechanical aspects. Unfallchirurg. 2016;119:742–746. doi: 10.1007/s00113-016-0218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Orbay JL, Fernandez DL. Volar fixation for dorsally displaced fractures of the distal radius: a preliminary report. J Hand Surg Am. 2002;27:205–215. doi: 10.1053/jhsu.2002.32081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Drobetz H, Kutscha-Lissberg E. Osteosynthesis of distal radial fractures with a volar locking screw plate system. Int Orthop. 2003;27:1–6. doi: 10.1007/s00264-002-0393-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Orbay JL, Fernandez DL. Volar fixed-angle plate fixation for unstable distal radius fractures in the elderly patient. J Hand Surg Am. 2004;29:96–102. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2003.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Müller E, Koch P, Nazarian S, Schatzker J. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 1990. The Comprehensive classification of fractures of long bones. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Owens WD, Felts JA, Spitznagel EL Jr. ASA physical status classifications: a study of consistency of ratings. Anesthesiology. 1978;49:239–243. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197810000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Berglund LM, Messer TM. Complications of volar plate fixation for managing distal radius fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2009;17:369–377. doi: 10.5435/00124635-200906000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Drobetz H, Schueller M, Tschegg EK, Heal C, Redl H, Muller R. Influence of screw diameter and number on reduction loss after plating of distal radius fractures. ANZ J Surg. 2011;81:46–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.2010.05479.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Moss DP, Means KR Jr, Parks BG, Forthman CL. A biomechanical comparison of volar locked plating of intra-articular distal radius fractures: use of 4 versus 7 screws for distal fixation. J Hand Surg Am. 2011;36:1907–1911. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2011.08.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Neuhaus V, Badri O, Ferree S, Bot AG, Ring DC, Mudgal CS. Radiographic alignment of unstable distal radius fractures fixed with 1 or 2 rows of screws in volar locking plates. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38:297–301. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2012.10.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Inagaki K, Kawasaki K. Distal radius fractures-Design of locking mechanism in plate system and recent surgical procedures. J Orthop Sci. 2016;21:258–262. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2015.12.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kawasaki K, Nemoto T, Inagaki K, Tomita K, Ueno Y. Variable-angle locking plate with or without double-tiered subchondral support procedure in the treatment of intra-articular distal radius fracture. J Orthop Traumatol. 2014;15:271–274. doi: 10.1007/s10195-014-0292-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gabl M, Arora R, Schmidle G. Biomechanics of distal radius fractures: Basics principles and GPS treatment strategy for locking plate osteosynthesis. Unfallchirurg. 2016;119:715–722. doi: 10.1007/s00113-016-0219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Baumbach SF, Synek A, Traxler H, Mutschler W, Pahr D, Chevalier Y. The influence of distal screw length on the primary stability of volar plate osteosynthesis--a biomechanical study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:139. doi: 10.1186/s13018-015-0283-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wall LB, Brodt MD, Silva MJ, Boyer MI, Calfee RP. The effects of screw length on stability of simulated osteoporotic distal radius fractures fixed with volar locking plates. J Hand Surg Am. 2012;37:446–453. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2011.12.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Rhee SH, Kim J, Lee YH, Gong HS, Lee HJ, Baek GH. Factors affecting late displacement following volar locking plate fixation for distal radial fractures in elderly female patients. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B:396–400. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.95B3.30514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Trumble TE, Culp RW, Hanel DP, Geissler WB, Berger RA. Intra-articular fractures of the distal aspect of the radius. Instr Course Lect. 1999;48:465–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.McQueen M, Caspers J. Colles fracture: does the anatomical result affect the final function? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988;70:649–651. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.70B4.3403617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kazuki K, Kusunoki M, Yamada J, Yasuda M, Shimazu A. Cineradiographic study of wrist motion after fracture of the distal radius. J Hand Surg Am. 1993;18:41–46. doi: 10.1016/0363-5023(93)90242-U. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


