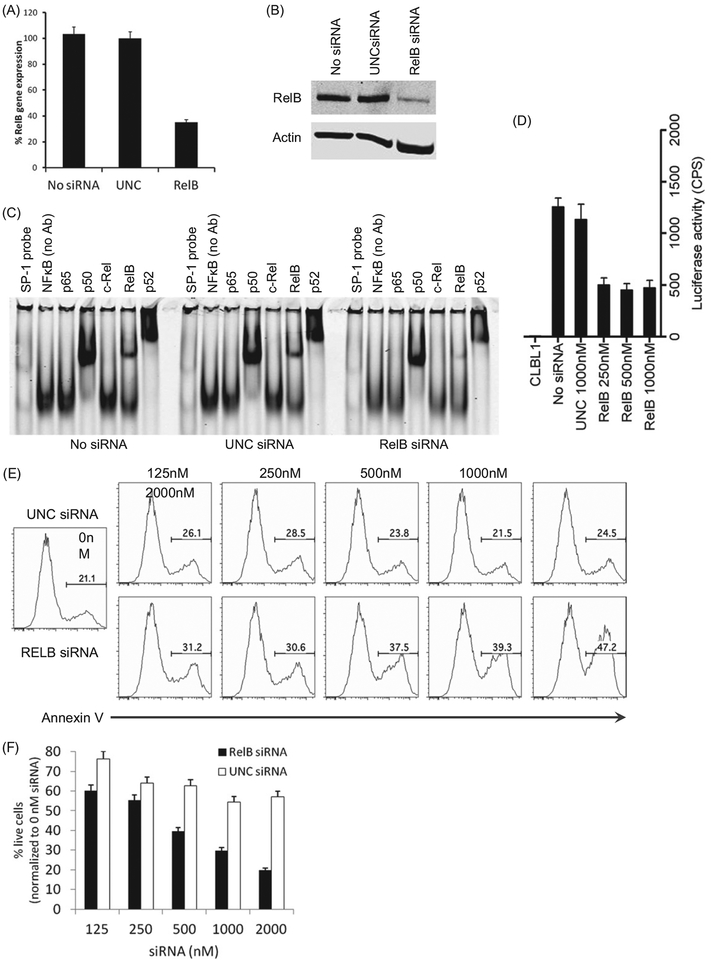
Figure 3.
Inhibition of the alternative NFκB pathway induces apoptosis in CLBL1 cells. (A) CLBL1 cells were transfected with 1000 nM (=10 pmol siRNA per 1 × 105 cells) RelB or UNC siRNA using a nucleofection method. After 24 h, the expression level of RelB gene was analyzed using quantitative RT-PCR. RelB gene expression levels were normalized by beta-actin gene expression among samples. (B) Expression of RelB protein in CLBL1 treated by no siRNA, UNC siRNA, or RelB siRNA was analyzed by immuno-blotting. (C) NFκB pathway in CLBL1-NFκB-luc cells was effectively inhibited by RelB siRNA treatment. (D) Inhibition effect of RelB siRNA was analyzed using nuclear lysates prepared from CLBL1 treated by no siRNA, UNC siRNA, and RelB siRNA using the super-shift EMSA. (E) Induction of apoptosis in CLBL1 cells treated by RelB siRNA was analyzed by Annexin V binding on flow cytometry. (F) CLBL1 cells were treated with UNC or RelB siRNA for 72 h and the cell viability was analyzed using the CellTiter 96® AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay. Where applicable, error bars represent the 95% confidence interval as determined by either Excel or GraphPad Prism.