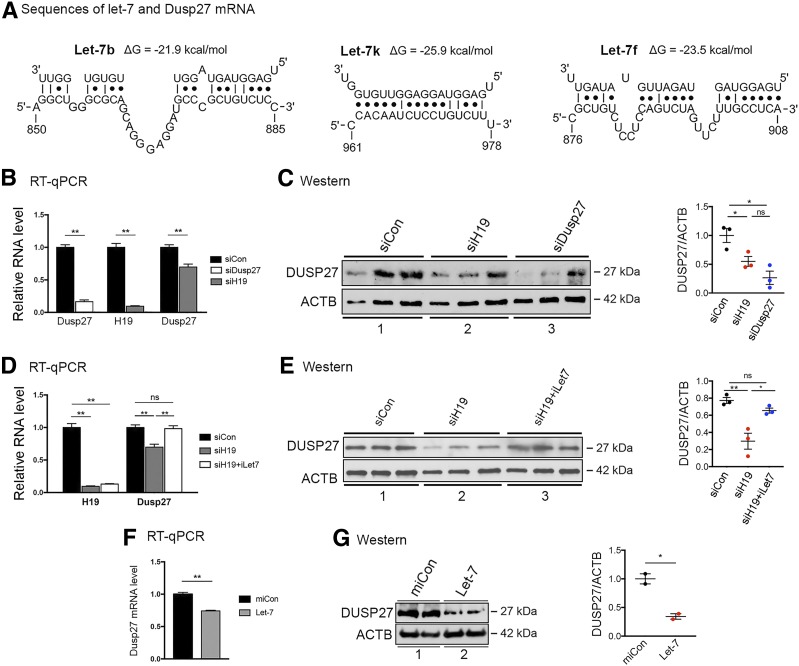
Figure 3.
H19 regulates DUSP27 expression via the H19/let-7 axis. A: Bioinformatics predicted three let-7 binding sites at the 3′-UTR of mouse DUSP27 mRNA. Sequences of three let-7 subtypes (top strands) and partial sequences of DUSP27 mRNA (bottom strands) are shown. Numbers are in nucleotides relative to the transcriptional start site of DUSP27. B: RT-qPCR results of DUSP27 and H19 expression in myotubes 48 h after transfection of siCon, siH19, or DUSP27-specific siRNA (siDusp27). C: Western blots (left) and densitometry results (right) of DUSP27 and ACTB proteins from experiments shown in B. Lanes were loaded in increasing amounts of cell lysates. D: RT-qPCR results of H19 and DUSP27 expression in myotubes 48 h after transfection of siCon, siH19, and siH19 plus iLet-7. E: Western blots (left) and densitometry (right) results of DUSP27 and ACTB protein levels from experiments shown in D. F: RT-qPCR results of DUSP27 mRNA levels in myotubes 24 h after transfection of miCon (negative control miRNA) or let-7. Lanes were loaded in duplicate. G: Western blots (left) and densitometry (right) results of DUSP27 and ACTB protein levels from experiments shown in F. All data are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. ns, no statistical difference.