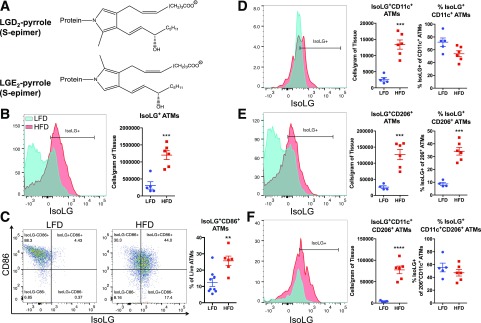
Figure 7.
HFD induces formation of immunogenic isoLGs and expression of B7 ligand CD86 in ATMs. Total leukocytes were isolated from AT of mice fed an LFD or HFD, and isoLG content was quantified using previously described gating schema. A: Structure of the major isoLG protein adducts. The major intermediates are a pair of pyrrolic epimers whose covalently bonded nitrogen originates from lysine residues on proteins. Phospholipids attached to isoLGs derive from polyunsaturated acids, arachidonic acids, and phospholipids thereof. B: Representative flow cytometry plot and average data showing intracellular staining for isoLG protein adducts in ATMs using the single-chain antibody D-11 single-chain variable fragment. C: Representative FACS plots and average data showing surface expression of CD86 and isoLGs in ATMs (proportion of ATMs staining CD86+isoLG+). D–F: Representative flow cytometry plots and average data showing the number of isoLG+ cells per gram of tissue and percentage of isoLG+ cells per ATM subsets CD11c+ (D), CD206+ (E), and CD11c+CD206+ (F) of HFD-fed mice. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 5−10 mice/group). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001.