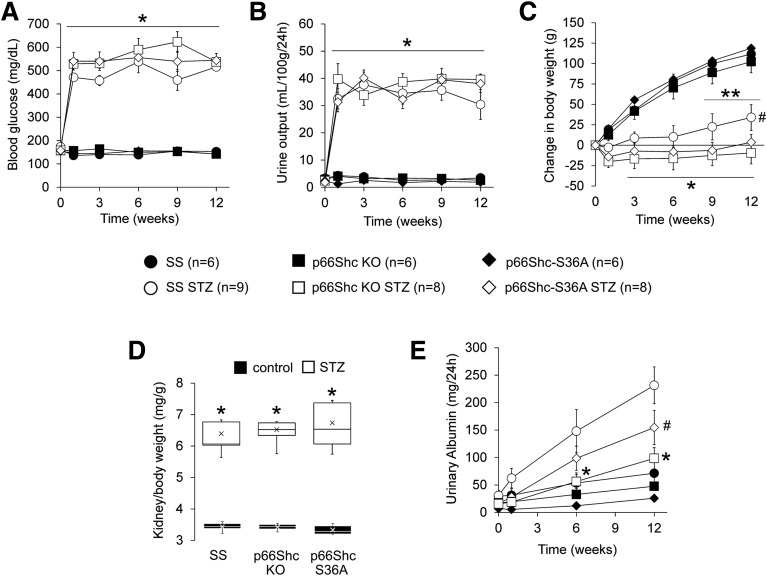
Figure 2.
Knockout of p66Shc inhibits progression of DN. Type 1 diabetes was induced in control and genetically modified male rats through STZ injection and evaluated for 12 weeks after treatment. A and B: Hyperglycemia (A) and polyuria (B) indicate that diabetes was induced after 1 week and was maintained throughout the protocol. *P < 0.001 vs. controls. C: Induction of diabetes significantly reduced weight gain in all rats. STZ-treated SS rats (SS STZ) gained weight by week 9. *P < 0.001 vs. controls at week 1; **P < 0.01 vs. SS STZ at week 1; #P < 0.05 vs. STZ-treated p66ShcKO rats (p66Shc KO STZ) at week 12. D: Kidney weight–to–body weight ratio increased in STZ-treated rats but did not differ between genotypes. Within the boxes, the × symbols represent the mean values and the horizontal lines represent the medians. *P < 0.001. E: Albuminuria significantly increased by week 6 in SS STZ (P < 0.001), whereas p66ShcKO and p66Shc-S36A rats had significantly reduced albuminuria at 6 and 12 weeks, respectively, when compared with SS STZ. *P < 0.01; #P < 0.05. p66Shc-S36A STZ, STZ-treated p66Shc-S36A rats.