Figure 3. Key cellular and molecular pathways regulating blood-brain barrier integrity.
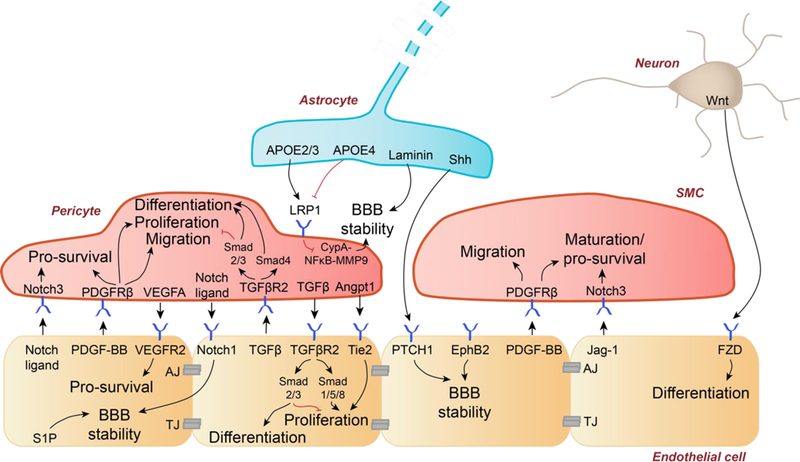
BBB integrity is maintained by tight junction (TJ) and adherens junction (AJ) proteins between endothelial cells and low-level bulk flow transcytosis. Pericyte-endothelial cells crosstalk: Notch ligands-Notch3 receptor signaling promotes pericyte survival. Platelet-derived growth factor-BB (PDGF-BB) binds to PDGFRβ on pericytes causing pericyte survival, proliferation, and migration. Vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGFA) binds to endothelial VEGF receptor-2 (VEGFR2) mediating endothelial survival. Pericyte-derived notch ligands bind to endothelial Notch1 receptor which mediates BBB stability, as does endothelial sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P). Transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ) and TGFβ receptor-2 (TGFβR2) signaling occurs bi-directionally between pericytes and endothelial cells. Pericyte-secreted angiopoietin-1 (Angpt1) binds Tie2 receptor on endothelial cells to promote proliferation. Astrocyte-endothelial cells crosstalk: Astrocyte-secreted APOE2 and APOE3, in contrast to APOE4, suppresses the pro-inflammatory signaling cyclophilin A-NFkB-matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9) pathway in pericytes to maintain BBB stability. Similarly, astrocyte-produced laminin maintains BBB stability. Astrocyte-secreted sonic hedgehog (Shh) interacts with patched-1 (PTCH1) at the endothelium to further promote BBB stability. Smooth muscle cell (SMC)-endothelial cells crosstalk: Ephrin B2 (EphB2) on the endothelium promotes BBB stability. PDGF-BB binds PDGFRβ on SMCs to promote survival and migration. Endothelial-secreted jagged-1 (Jag-1) binds Notch3 to promote SMC maturation and survival. Neuron-endothelial cells crosstalk. Neuron secreted Wnt is a ligand of frizzled (FZD) at the endothelium that promotes endothelial cell differentiation.
