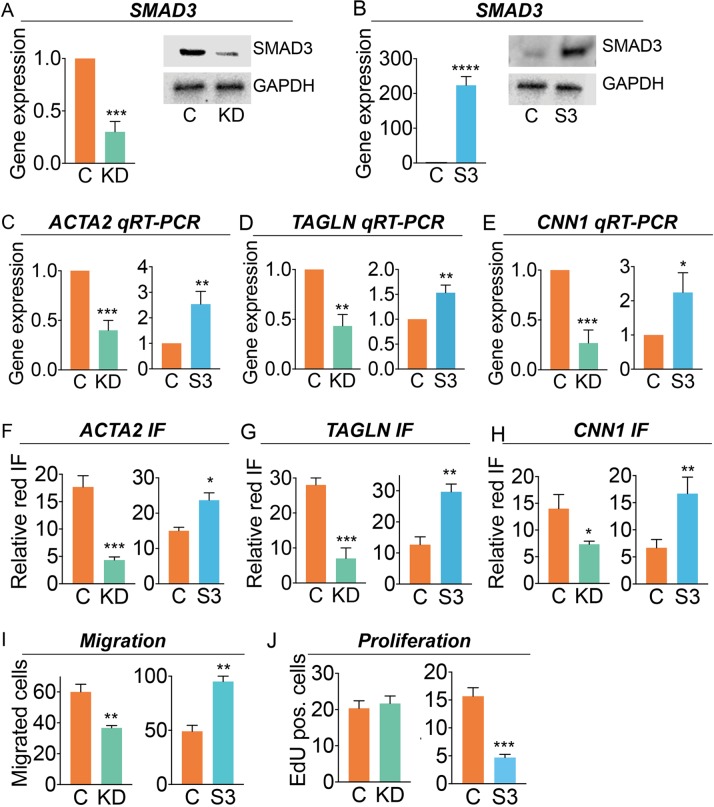
Fig 1. SMAD3 promotes expression of HCASMC differentiation markers.
A, B) HCASMC were treated with SMAD3 specific (KD, green bars) or scrambled sequence (C) siRNA molecules, or transfected with a SMAD3 encoding expression plasmid (S3, blue bars) or control plasmid (C). SMAD3 expression was evaluated by qRT-PCR and western blot analysis with GAPDH protein levels evaluated as a control. C, D, E) Gene expression was quantified for HCASMC lineage markers ACTA2, TAGLN and CNN1 by qRT-PCR in cells with SMAD3 knockdown and over-expression, shown here, and western blot (S1A Fig). F, G, H) Differentiation marker expression was also evaluated by quantitative immunofluorescence (IF) for cell-specific genes ACTA2, TAGLN and CNN1 by SMAD3 knockdown or increased expression. I) HCASMC with SMAD3 knockdown or over-expression were evaluated for HCASMC migratory activity with a gap closure assay. J) To evaluate the effect of SMAD3 expression on cell division, we labeled cells with EdU (5-ethynyl-2’ -deoxyuridine), imaged for nuclear fluorescence, and quantified the relative number of EdU positive DAPI stained cells for HCASMC undergoing SMAD3 knockdown or increased expression. p-values: ****, p<0.0001; ***, p<0.001; **, p<0.01; *, p<0.05.