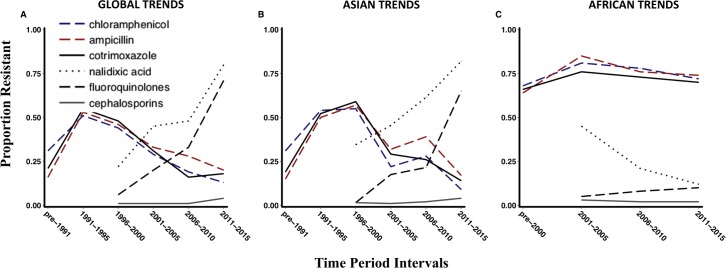
Fig 2.
Antimicrobial non-susceptible trends of S. Typhi over time A) Global trends, B) Trends in Asia C) Trends in Africa. Fig 2A is Graphical representation of the proportion of S. Typhi isolates obtained from reports that were resistant to antimicrobials (indicated by coloured lines). Isolates represented in this graph were consolidated from published reports between 1973 and 2017 from endemic and epidemic sources, assembled systematically. In comparison to Fig 2A, Fig 2B represents the AMR trends obtained from Asian reports. Note the similarity in the trend between 2a and 2b; it is evident that non-susceptibility to first-line antimicrobials (chloramphenicol, co-trimoxazole and ampicillin) has decreased over time. Fig 2C represents the AMR trends from African reports. MDR Typhoid is widely prevalent while fluoroquinolone resistance is low.