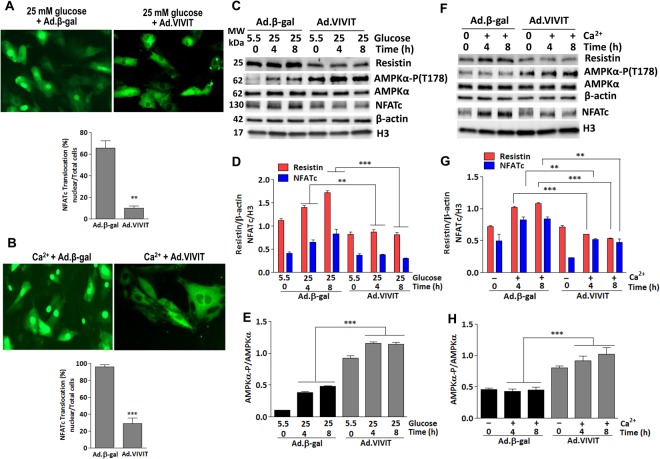
Figure 4.
Glucose and Ca2+ fail to induce resistin expression in NFATc-inhibited cells-Representative fluorescence microscopic images of H9c2 cells co-infected with Ad.NFATc-GFP and Ad.VIVIT for 48 hours then treated with either high glucose (A) or Ca2+ (B) for 4 hours and NFATc-GFP nuclear translocation was visualized and quantified in more than 5 images in each condition (A and B, respectively). **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 vs Ad.βGal. (C–H) VIVIT-expressing H9c2 cells were stimulated with 25 mM glucose (C) or 4 mM Ca2+ (F) for the indicated times. The protein expression of resistin and NFATc (nuclear), and phosphorylation of AMPKα were analyzed by western blotting (C,F) and densitometry quantifications were determined (D,G, and E,H, respectively). The phosphorylation of AMPK status is reported as phospho-AMPK/AMPK ratio. H3 was used as an internal control for NFATc nuclear expression, β-actin was used as an internal control for the other proteins. The data are mean ± SEM of three experiments in triplicates. **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 Ad.βGal vs Ad.VIVIT.