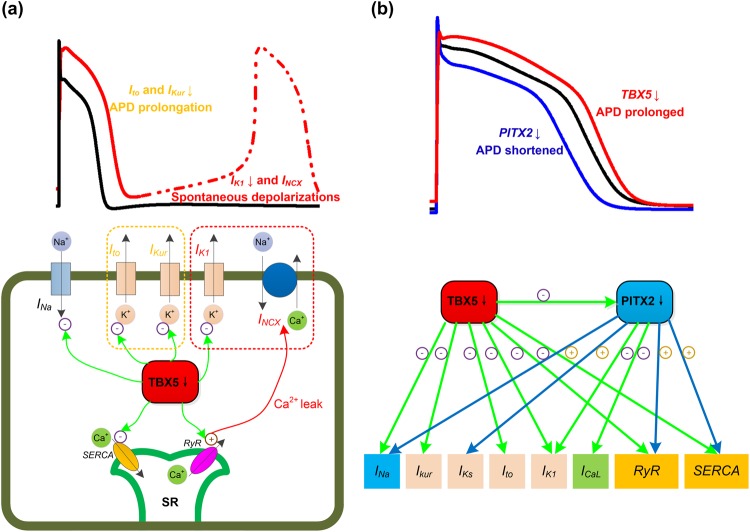
Figure 6.
The role of electrical remodeling of TBX5 insufficiency in atrial fibrillation. (a) The schematic illustration of the impact of TBX5 loss-of-function mutation on ionic currents/action potential duration (APD). TBX5-deletion leads to reductions in INa, Ito, IKur, IK1, SERCA and RyR. Reduced repolarizing potassium currents (e.g., Ito and IKur) lead to prolonged APD. Suppression of IK1 and increased INCX due to cytosolic calcium overload lead to phase 4 depolarization and predispose to spontaneous depolarizations. (b) TBX5 regulates PITX2 expression, and TBX5 and PITX2 antagonistically regulate downstream targets. Reduced PITX2 leads to upregulation of INa, IKs, SERCA and RyR, and downregulation of ICaL and IK1. Loss of TBX5 leads to prolonged APD, whereas loss of PITX2 leads to shortened APD. Therefore, reduced PITX2 in TBX5-mutant atria contributes to a protective mechanism.