Fig. 2.
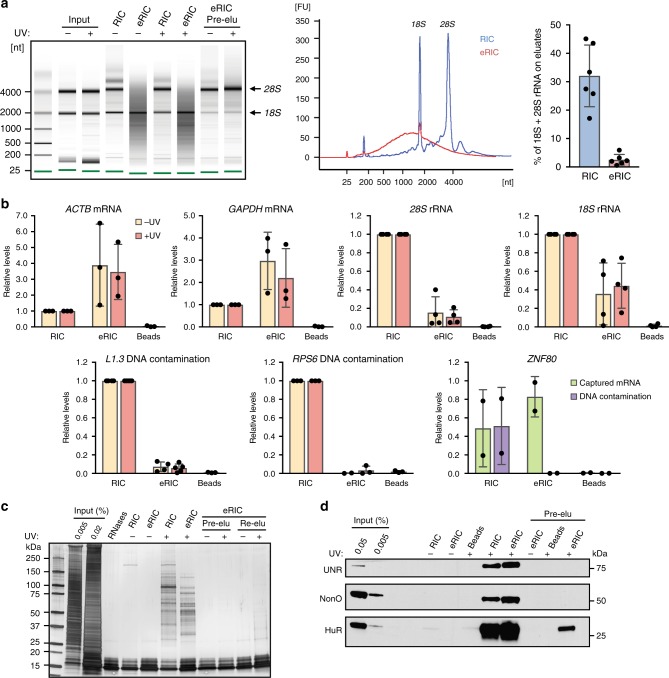
eRIC captures polyadenylated RNA and covalently crosslinked proteins with high specificity. a, b Nucleic acids isolated by eRIC, RIC, or using uncoupled beads along the eRIC protocol on irradiated material (“Beads”) were analyzed using a 6000 Pico bioanalyzer (a) or by RT-qPCR (b). Note that the pre-elution step (“Pre-elu”) incorporated in eRIC leads to an effective removal of rRNAs, specially the 28S rRNA, without compromising the capture of poly(A) RNAs. a Representative result are shown in the left and middle panels; data on the right panel correspond to mean and standard deviation (s.d.) from six biologically independent experiments. −UV non-irradiated controls, +UV irradiated samples, [nt] length of RNA in number of nucleotides, [FU] fluorescence units. b Data correspond to mean and s.d. from at least three biologically independent experiments except for ZNF80 (two experiments). c, d Isolated proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and silver-stained (c) or analyzed by western blot with antibodies to the positive control RBPs UNR, NonO, and HuR (d). The lane “RNases” contains a dilution of RNases A and T1. Note that lower bands in silver staining correspond to these enzymes. Re-elu heat elution performed after RNAse treatment. Note that a minor fraction of HuR appears to be associated with non-polyadenylated RNAs39