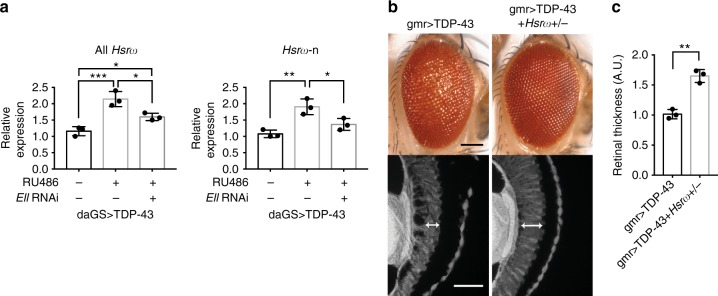
Fig. 4.
Hsrω is elevated and contributes to TDP-43 toxicity. a RT-qPCR analysis of fly heads shows that expression of TDP-43 driven by a drug-inducible promoter daGS leads to an increase of total Hsrω and Hsrω-n. Knockdown of Ell reduces the elevated levels of total Hsrω and Hsrω-n. RU486 (4 mg/ml) was used to induce expression for 4 days. Relative RNA levels were normalized to Pgk, RpL32, and RpS20 mRNAs (geometric mean). n = 3 biological replicates. Bars represent mean (SD). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test). Genotype: daGS > TDP-43 is daGS-GAL4/+; UAS-TDP-43/+. daGS > TDP-43 + Ell RNAi is daGS-GAL4/+; UAS-TDP-43/UAS-Ell.RNAiHMS00277. b Images of external eyes (top) and internal retina (bottom) show that loss of one copy of Hsrω ameliorates TDP-43-caused eye degeneration. Scale bars: external eye, 100 μm; internal retina section, 5 μm. Genotypes: gmr > TDP-43 is UAS-TDP-43/+; gmr-GAL4(YH3)/+. gmr > TDP-43 + Hsrω+/- is UAS-TDP-43/+; gmr-GAL4(YH3)/Hsrω66. c Quantification of retina thickness related to Fig. 4b. Three flies of each genotypes were measured (n = 3). Bars represent mean (SD). **P < 0.01 (two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test). Genotypes are the same as indicated in b. A.U., arbitrary units