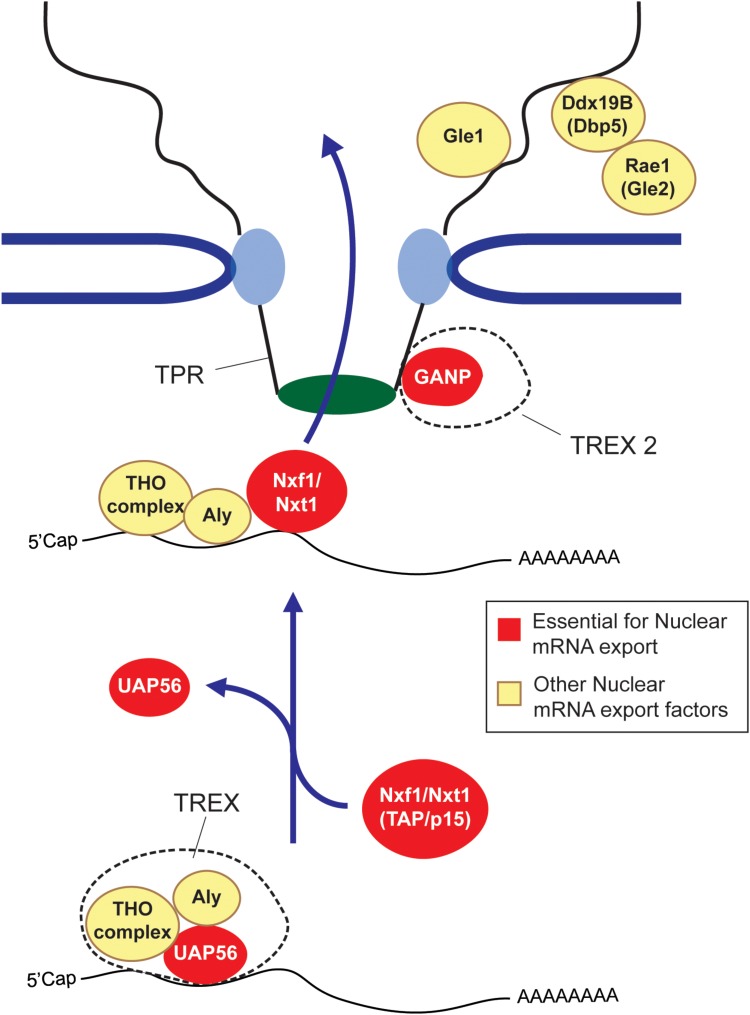
FIGURE 1.
The mRNA nuclear export pathway. The TREX complex, which is composed of the Tho complex, the RNA helicase UAP56 (or its paralog URH49) and Aly are loaded onto the mRNA co-transcriptionally or by processing events. At some point, the UAP56 hydrolyses ATP and then is replaced by the nuclear export receptor composed of Nxf1 and Nxt1 (also known as TAP and p15) to form an export competent mRNP. The Nxf1-Nxt1 heterodimer physically interacts with the FG repeats of Nups to ferry its cargo across the nuclear pore. GANP, which forms part o the TREX2 complex is also required for export, although its exact role is not understood. After passing through the nuclear pore complex, the mRNP is furthered remodeled by cytoplasmic pore-associated proteins such as Gle1, Dbp5 and Rae1/Gle2. It is though that these remodeling events remove certain nuclear associated exported factors, which are then recycled back into the nuclear pore. In some cases these mRNP remodeling events render the mRNP more ‘translationally’ competent (Palazzo and Truong, 2016). Factors that are essential for mRNA export are depicted in red, other export factors are depicted in yellow.