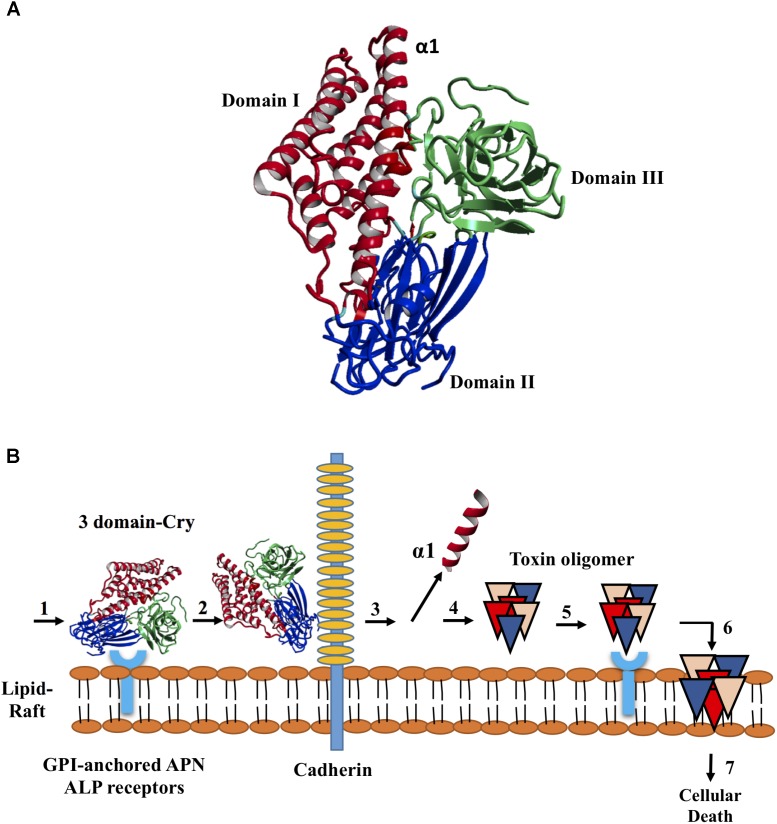
FIGURE 1.
Structure of the Cry toxins, domains, and their mode of action. (A) Ribbon diagram of Cry deduced 3D structure. Three domains are colored in red blue and green, respectively. (B) Sequential binding mechanism. 1. The toxin binds to GPI-anchored APN and ALP receptors in the lipid rafts; 2. Binding to cadherin receptor 3. Proteolytic cleavage of the helix α1 at N-terminal end; 4. N-terminal cleavage induces the formation of pre-pore oligomer 5. Increasing of the oligomer binding affinity to GPI-anchored APN and ALP receptors; 6. Oligomer inserts into the membrane, leading to pore-formation and cell lysis; and 7. Cellular death.