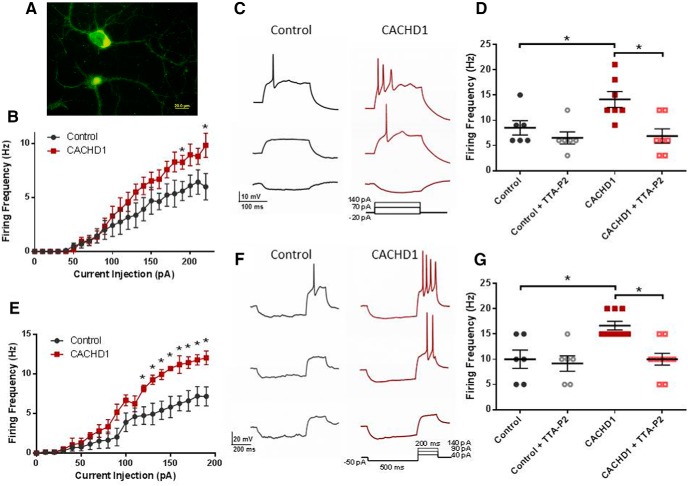
Figure 9.
Effects of CACHD1 in hippocampal neurons. A, Colabeling of hippocampal neurons with CACHD1 and mVenus. B, CACHD1 increased the firing frequency of hippocampal neurons. C, Example traces representing depolarizing current injections steps of −20, 70, and 140 pA. D, Summary data from separate experiments confirming CACHD1-mediated increased firing frequency and also showing that TTA-P2 (1 μm) reduced firing rates in CACHD1-expressing neurons, but not in controls. E, Rebound APs were evoked using a −50 pA hyperpolarizing prepulse followed by a depolarizing step from 0 to 200 pA in steps of 10 pA for 200 ms, CACHD1-expressing neurons displayed a significantly greater number of rebound APs compared with controls. F, Example traces representing depolarizing current injection steps of 40, 90 and 140 pA. G, Summary data from separate experiments confirming CACHD1-mediated increased in rebound APs and also showing that TTA-P2 (1 μm) reduced firing rates in CACHD1-expressing neurons, but not in controls. *p < 0.05 throughout, two-tailed paired Student's t test or one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. Figure 9 is supported by analysis of the effects of CACHD1 and TTA-P2 on biophysical properties of hippocampal neurons (Figure 9-1).