Figure 7.
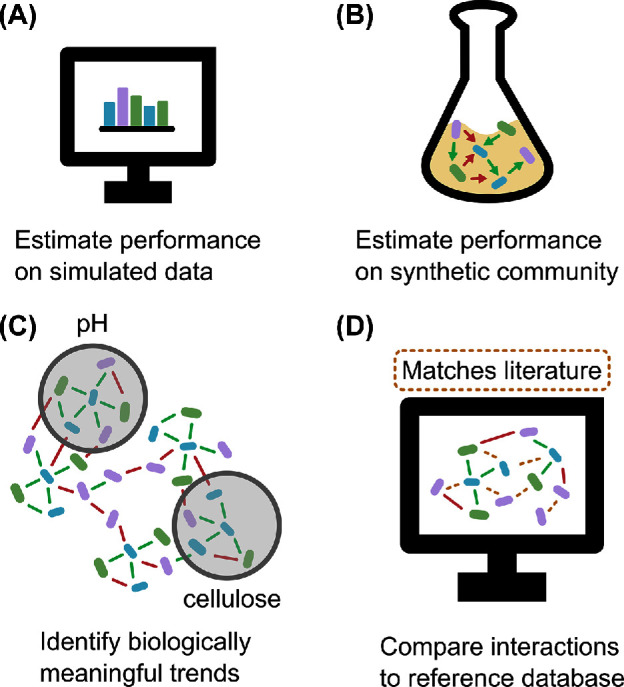
Types of benchmark suites for evaluation of network inference tools. (A) Simulated datasets using different models can help evaluate whether tools are able to identify ecological interactions and network properties. (B) Synthetic communities can provide a ground-truth network with known interactions, which can then be used to evaluate tool precision on real-world data. (C) Network modules can be associated with specific environmental factors or metabolic properties. Inferred networks could be evaluated for their visualization of such modules, if prior biological knowledge is available. (D) A reference database could be used to match inferred edges to known interactions. In this way, the sensitivity of network inference can be assessed for real-world communities. While it is straightforward to assess precision in simulated and synthetic communities, it is difficult to measure it for real-world communities, since the absence of a predicted interaction is hard to prove.
