Figure 1.
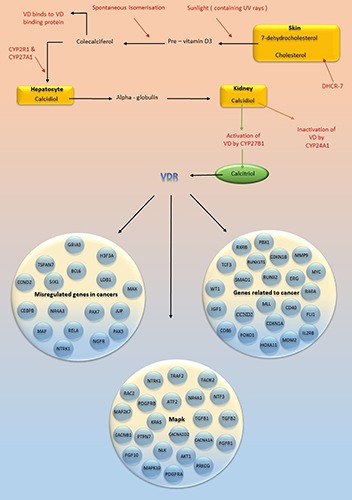
Vitamin D metabolism and targets of vitamin D receptor are shown in this figure. Vitamin D receptor targets different genes and thus affects biological functions. VD: vitamin D; CYP: cytochrome P; DHCR-7: 7-Dehydrocholesterol reductase; VDR: vitamin D receptor; TSPAN7: Tetraspanin-7; BCL6: B-cell lymphoma 6 protein; LDB1: LIM domain-binding protein 1; MAX: myc-associated factor X; CEBPB: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta; NR4A3: nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 3; RXRB: Retinoid X receptor beta; TCF3: Transcription factor 3; CDKN1B: Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B; MMP9: Matrix metallopeptidase 9; ERG: ETS-related gene; WT1: Wilm's tumor; IGF1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; MLL: myeloid/lymphoid or mixed-lineage leukemia; RARA; Retinoic acid receptor alpha;FLI1: Friend leukemia integration 1; MDM2: Mouse double minute 2 homolog; IL2RB: Interleukin-2 receptor subunit beta; TRAF2: TNF receptor-associated factor 2; RAC2: Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 2; PDGFR: platelet-derived growth factor receptor; ATF2: Activating transcription factor 2; TGFB: Transforming growth factor beta; PTPN7: Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 7; AKT1: RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase; FGFR1: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 ; FGF10; Fibroblast growth factor 10; MAPK10: Mitogen-activated protein kinase 10; PRKCG: Protein kinase C gamma type.
