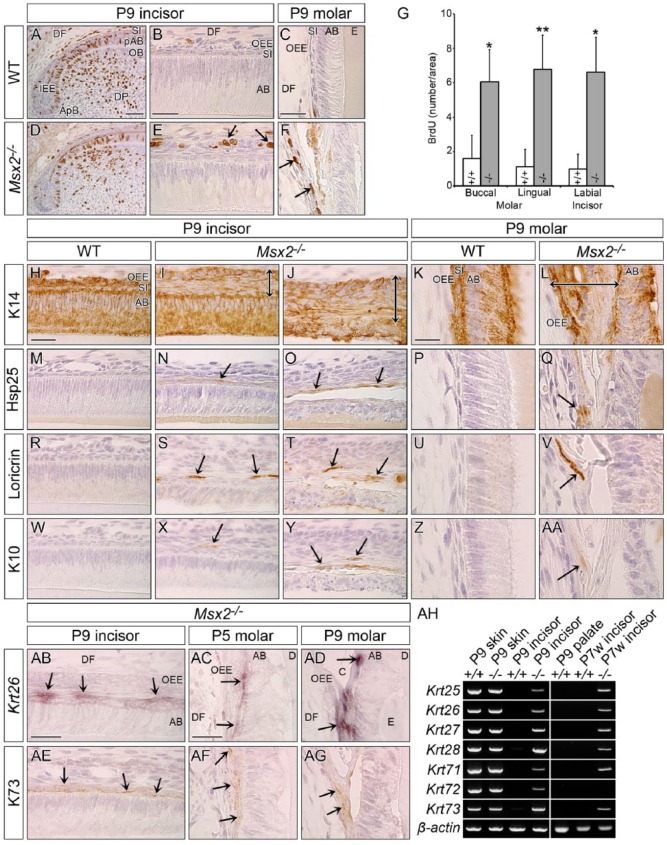
Figure 3.
The mutant outer enamel epithelium is transformed to a highly proliferative keratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Genotypes and stages are indicated. (A, B, D, E, H–J, M–O, R–T, W–Y, AB, AE) Sagittally sectioned upper incisors (incisal edge side to right). (C, F, K, L, P, Q, U, V, Z, AA, AC, AD, AF, AG) Frontally sectioned lower first molars. (A–F) Immunohistochemical cell proliferation assay using BrdU 1 h labeling. Proliferating cells in the inner enamel epithelium (IEE) are strongly labeled with BrdU in both genotypes (A, D; see also Appendix Fig. 8). Compared with wild-type (WT), proliferative cells are ectopically observed in the outermost area of the mutant enamel organ (arrows in E, F). (G) Statistical analysis (Student’s t test, 2-tailed) of cell proliferation in the outer enamel epithelium (OEE) of the buccal and lingual sides of molars and of the labial side of incisors reveals that the BrdU index is significantly higher in Msx2−/− than in WT (mean ± SD, n = 3). *P < 0.05. **P < 0.01. (H–AA) Immunohistochemistry for Keratin 14 (K14), Heat shock protein 25 (Hsp25), Loricrin, and Keratin 10 (K10). (I, N, S, X) are at the early secretory stage and (J, O, T, Y) show ameloblasts already depolarized. K14-immunoreactivity confirms that the abnormally expanded mutant enamel organ is an epithelial-derived tissue (double-headed arrow in I, J, L). Keratinized stratified squamous epithelium markers Hsp25, Loricrin, and K10 are ectopically expressed in the mutant enamel organ (arrows). (AB–AG) Keratin 26 (Krt26) and Keratin 73 (K73) are upregulated in the mutant enamel organ (arrows), whereas no such expression is observed in WT (Appendix Fig. 13). (AH) Conventional reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis using complementary DNA obtained from facial skin and palatal mucosa as a control tissue and the apical end of the labial epithelium in lower incisors at P9 and P7w. Hair follicle specific keratins are upregulated in the mutant tooth germ at both stages, except for Krt72 at P7w. β-actin was used as an internal control. AB, ameloblast; ApB, apical bud; C, cyst; D, dentin; DF, dental follicle; DP, dental pulp; E, enamel; OB, odontoblast; pAB, preameloblast; SI, stratum intermedium. Bars: 50 µm in A for A and D, 25 µm in B for B and E, 25 µm in C for C and F, 25 µm in H for incisors, 15 µm in K for molars, 25 µm in AB for AB and AE, and 25 µm in AC for AC, AD, AF, and AG.