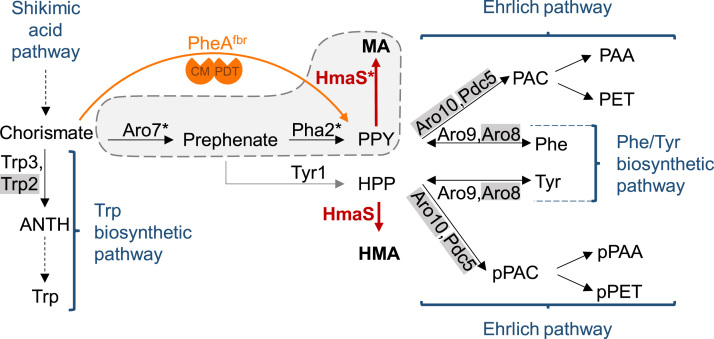
Fig. 1.
Applied modifications of the aromatic amino acid pathway of S. cerevisiae for mandelic acid production. The heterologous hydroxymandelate synthase (HmaS, red) converts the intermediates of the aromatic amino acid pathway phenylpyruvate (PPY) and hydroxyphenylpyruvate (HPP) to mandelic acid (MA) and hydroxymandelic acid (HMA), respectively. Enzymes that were targeted to mitochondria/peroxisomes in our compartmentalization approach are marked with a star. The compartment (mitochondrion or peroxisome) containing the three consecutive enzymes Aro7fbr, Pha2 and HmaS is depicted as a grey area surrounded by a dashed line. The bifunctional E. coli enzyme PheAfbr is indicated in orange (CM, chorismate mutase; PDT, prephenate dehydratase). Dashed arrows indicate multiple enzymatic steps. Enzymes whose genes were deleted in a part of the strains used in this work are labeled in grey. ANTH, anthranilate; Trp, tryptophan; PAC, phenylacetaldehyde; pPAC, p-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde; Phe, phenylalanine; Tyr, tyrosine; PAA, phenylacetic acid; pPAA, p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid; PET, phenylethanol; pPET, p-hydroxyphenylethanol.