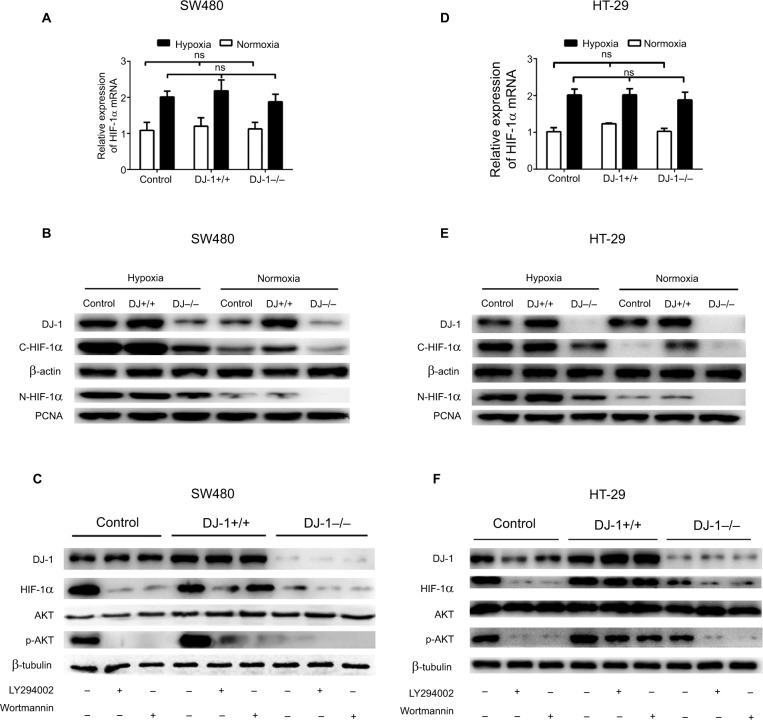
Figure 3.
Effects of DJ-1 knockdown and overexpression on HIF-1α expression and AKT phosphorylation.
Notes: Parental SW480/HT-29, SW480/HT-29-DJ-1–/–, and SW480/HT-29-DJ-1+/+ cells in six-well plates were cultured under either normoxic (21% O2) or hypoxic (2% O2, 12 hours) conditions. mRNA levels of HIF-1α were determined by RT-PCR. Protein levels of DJ-1, HIF-1α, AKT, and p-AKT were determined by Western blot. (A, D) The mRNA expression levels of HIF-1α in parental SW480/HT-29, SW480/HT-29-DJ-1–/–, and SW480/HT-29-DJ-1+/+ cells. Data shown are the mean fold induction ± SD of mRNA compared to base expression as determined using control SW480/HT-29 cells. (B, E) The protein levels of C-HIF-1α (cytoplasm) and N-HIF-1α (nucleus) in parental SW480, SW480/HT-29-DJ-1–/–, and SW480/HT-29-DJ-1+/+ cells. (C, F) Parental SW480/HT-29, SW480/HT-29-DJ-1–/–, and SW480/HT-29-DJ-1+/+cells were treated separately with the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 (10 µM) or wortmannin (100 nM) in hypoxic condition, and cells were collected and analyzed by immunoblotting after 12 hours. The experiments were repeated three times.
Abbreviations: HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; p-AKT, phospho-AKT; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; ns, no significant statistical difference; RT-PCR, reverse transcription-PCR; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen.