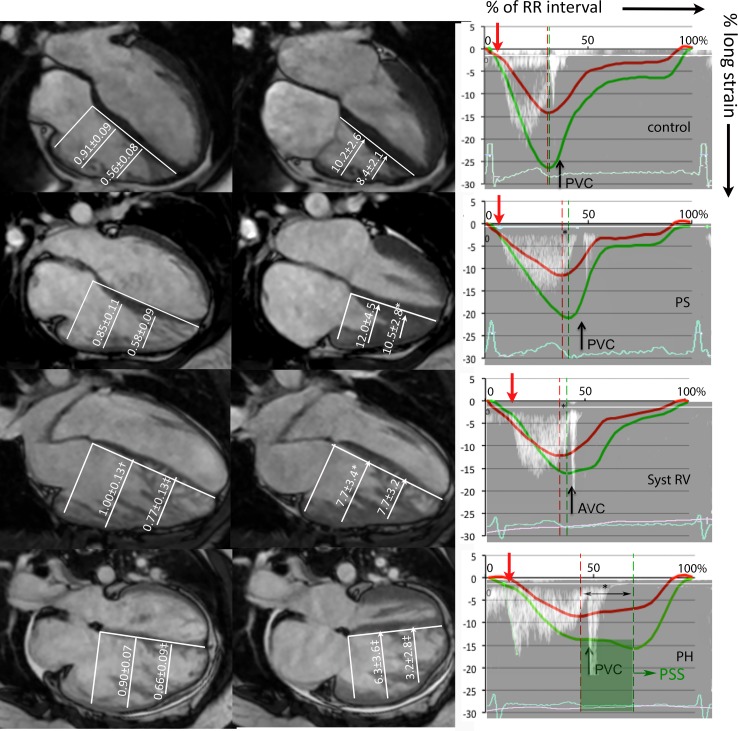
Fig 3. RV geometry, transverse motion, and timing of contraction.
Left column: RV mid-basal and apical-basal ratio. Mid column: RV transverse motion at mid and apical level. The right column: timing of RV free wall (green) strain, septal (red) longitudinal strain, and RVOT Doppler tracing from a representative patient presented as percentage (0–100%) of the RR interval. Pulmonary valve opening (red arrow), pulmonary valve closure (PVC) and the difference between septal and free wall peak (*) are also shown. Patients were compared to controls using ANOVA with posthoc Dunnet’s; *p<0.05; †p<0.01; ‡p<0.001. PS = pulmonary stenosis; Syst RV = systemic righ ventricle; PH = pulmonary hypertension.