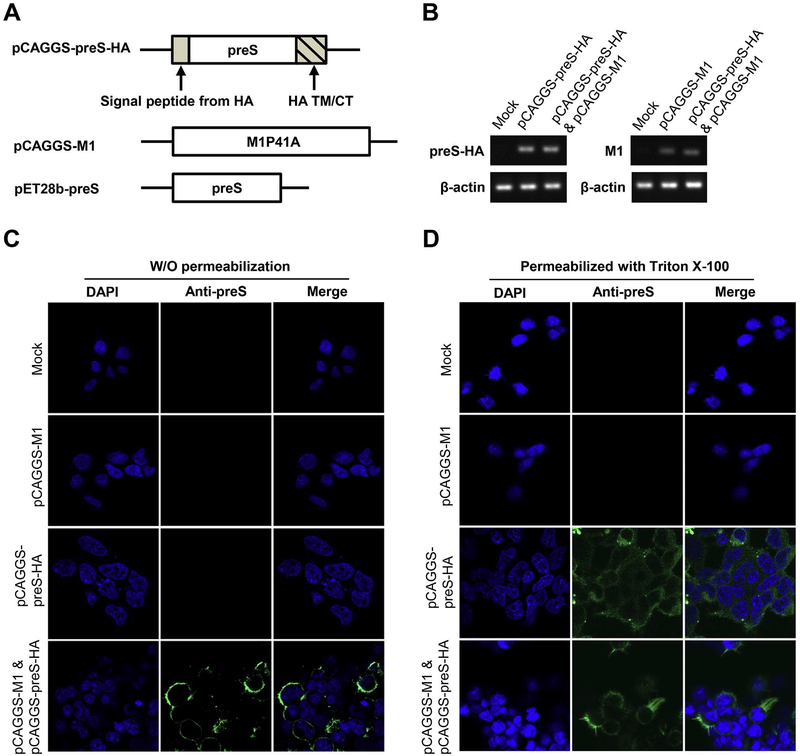
Fig. 1. Construction and production of preS VLP.
(A) Schematic representation of pCAGGS-preS-HA and pCAGGS-Ml used for preS VLP production, and pET28b-preS used for the expression of recombinant preS antigen. (B) qRT-PCR analysis was used to confirm the transcription of preS-HA and M1. (C, D) Immunofluorescent imaging of preS-HA expressing cells. (C) 293T cells were transfected with mock control, pCAGGS-M1, pCAGGS-preS-HA, or both plasmids. Cells were not permeabilized with Triton X-100 before staining. The nuclei were stained w ith DAPI (blue), and the preS antigen was stained with purified polyclonal rabbit anti-preS antibody, detected with Alexa Fluor® 488-Conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody. (D) The cells were the same as those in panel C, except that the cells were permeabilized with Triton X-100 before staining. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)