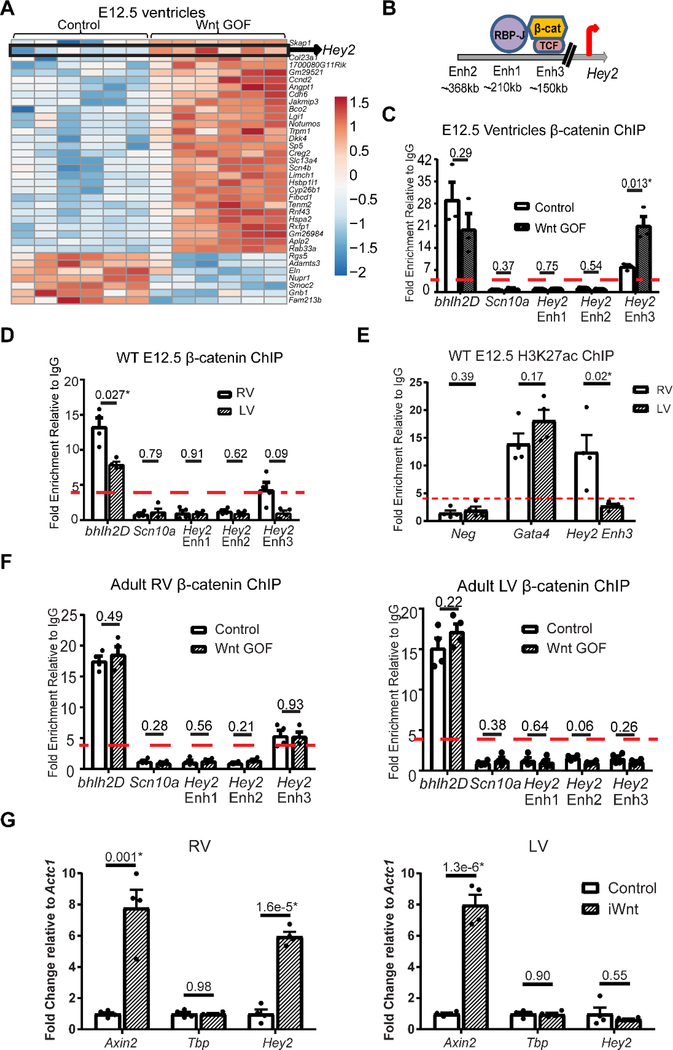
Figure 3 – Hey2 is a direct target of Wnt signaling in the right ventricle with differential enhancer binding of β-catenin.
(A) Heat map representation of RNA sequencing of Wnt GOF (αMHC-Cre; Ctnnb1fl(ex3)/+) versus littermate control (Ctnnb1fl(ex3)/+) embryonic ventricles (n=6 each) reveals 36 differentially-regulated transcripts including Hey2. (B) Genomic regions of murine Hey2 delineating known upstream cardiac enhancers with location relative to the transcription start site, and putative Notch and Wnt transcriptional effector binding sites. (C) ChIP for β-catenin in embryonic day 12.5 (E12.5) Wnt GOF (αMHC-Cre; Ctnnb1fl(ex3)/+) and littermate control (Ctnnb1fl(ex3)/+) ventricles (RV and LV combined, n=3 each) shows basal binding to the positive control bhlh2D locus, without binding at the negative control Scn10a locus, Hey2 Enhancer (Enh) 1, nor Enh 2. 7-fold enrichment of β–catenin was detected in controls at the consensus Wnt-responsive element within Hey2 Enh 3, with further 19-fold enrichment in Wnt GOF ventricles (a threshold of 4-fold enrichment over IgG was considered binding). (D) ChIP for β-catenin in wild type (WT) E12.5 RV versus LV reveals 4-fold enrichment of β-catenin binding at Hey2 Enh3 in RV, without enrichment in the LV, at this early developmental stage (n=4). (E) ChIP for H3K27ac in WT E12.5 RV versus LV shows enrichment at the positive control Gata4 locus, but not at the negative control gene desert (neg) in both RV and LV. There is more than 12-fold enrichment of H3K27ac in the RV at Hey2 Enh3, however, in contrast there is less than 4-fold enrichment in the LV (n=4). (F) ChIP in adult RV shows β-catenin binding at the positive control bhlh2D locus, as well as Hey2 Enh3 in controls (Mlc2vCre/+), without further enrichment in littermate Wnt GOF mice (Mlc2vCre/+; Ctnnb1fl(ex3)/+). Binding is not detected at the negative control Scn10a promoter, nor at Hey2 Enh1,2 (n=4 each). In adult control and Wnt GOF LV, β-catenin binds at the positive control bhlh2D locus, without enrichment at the negative control Scn10a promoter, nor Hey2 Enh1–3. β-catenin binding at Hey2 Enh3 is not detected in Wnt GOF LV despite increased β-catenin levels, suggesting that levels alone may not account for the lack of Enh3 binding in the LV (n= 4 each). (G) qRT-PCR from inducible Wnt GOF mice (iWnt, αMHCrtTA; TetO-Cre; Ctnnb1fl(ex3)/+), where Wnt signaling was induced in adulthood, versus control (TetO-Cre; Ctnnb1fl(ex3)/+) mice, shows increased expression of the direct Wnt target Axin2 in both ventricles, no change in expression of Tbp (negative control), while Hey2 expression increases in the RV only (n=4 each). An equal variance Student’s t-test was used for comparisons, with all two-tailed P-values indicated. *P<0.05 considered statistically significant.