Figure 6. EFA-6 (EFA6) and CNT-1 (ACAP2) regulate ARF-6.
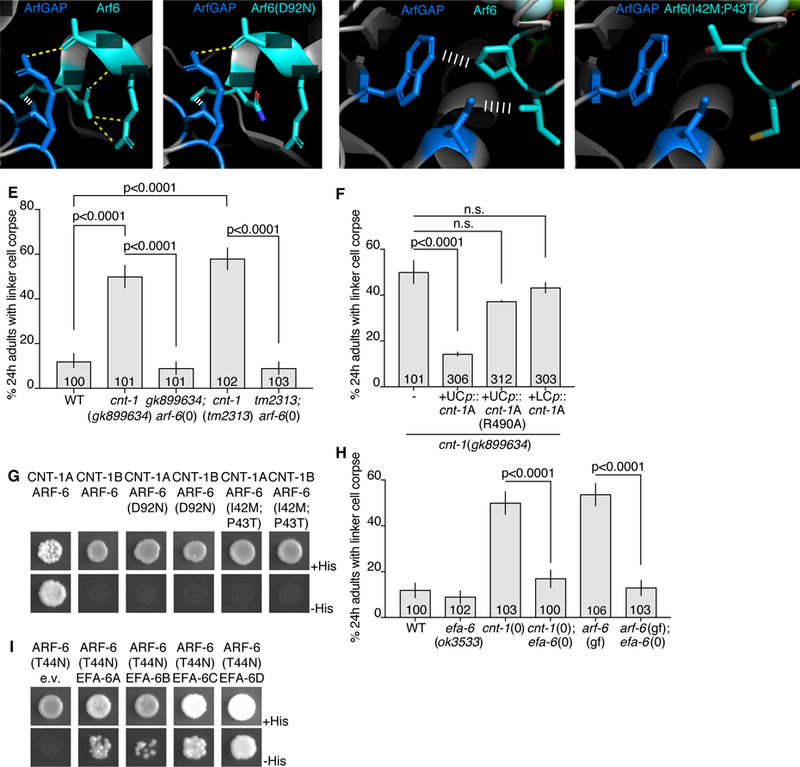
(A) Protein structures of human Arf6 (teal) and ArfGAP (blue) from (Ismail et al., 2010). PDB: 3LVQ. Relevant amino acids indicated in white. Yellow dotted line, hydrogen bonds. White ladder, hydrophobic interactions. Amino acids shown are conserved in C. elegans ARF-6 and CNT-1. (B) D92N mutation mapped onto Arf6. Protein structure information as in (A). (C) Different region of Arf6 and ArfGAP. Protein structure information as in (A). (D) I42M, P43T mutations mapped onto Arf6. (E,F) Histogram details as in Figure 2B. (G) Yeast two-hybrid assay with LexA-CNT-1A or LexA-CNT-1B as bait, GAD-ARF-6, GAD-ARF-6(D92N) or GAD-ARF-6(I42M,P43T) as prey. Top: histidine present. Bottom: histidine absence. Growth on -His plates indicates physical interaction. (H) Histogram details as in (E). (I) As in (G), with LexA-ARF-6[T44N] (GDP) as bait, GAD-EFA-6A-D as prey. See also Figure S5 and Table S3.
